串口通信基础与应用
一、串口的基本认识
串口(Serial Port),也称为串行端口,是一种数据通信的物理接口,它允许数据以连续的比特流形式在计算机和外部设备之间进行传输。串口通信在多种应用中非常普遍,如传感器连接、嵌入式系统、通信设备、GPS接收器和打印机等。
串口的特点:
-
点对点通信:通常用于连接一台计算机和一个外部设备。
-
逐位传输:数据按照特定的时间间隔一位一位地传输。
-
波特率:串口通信可以采用不同的波特率,如9600、115200等。
串口通信标准:
串口通信遵循一些标准,如RS-232、RS-485、UART等,这些标准规定了信号电平、数据位数、校验位等通信参数。
-
RS-232:定义了串行通信的电气和机械特性。
-
RS-485:多点半双工串口标准,适用于工业控制和数据通信。
串口通信参数:
为了确保通信双方的一致性,需要配置以下参数:
-
波特率:每秒传输的比特数。
-
数据位:每个字节的位数。
-
停止位:字节之间的停止间隔。
-
校验位:用于检测数据的完整性。
数据传输:
串口通信将数据分成字节,然后逐位传输,通常包括起始位、数据位、可选的校验位和停止位。
流控制:
串口通信可以使用硬件流控制(RTS/CTS)或软件流控制(XON/XOFF)来管理数据流,防止数据溢出。
串口设备:
串口设备通过串口端口(如COM端口)连接到计算机,在Linux系统中,串口设备通常位于 /dev 目录下。
应用领域:
串口通信广泛应用于数据采集、嵌入式系统通信、传感器连接、外部设备控制、GPS数据接收等。
编程:
在编程中,可以使用合适的编程语言(如C/C++)和串口库进行串口通信。通常的步骤包括打开串口设备、配置通信参数、读取和写入数据。
二、串口关于电气标准和协议标准
串口通信涉及电气标准和协议标准两个方面:
电气标准:
-
RS-232:使用正负电平表示逻辑值。
-
RS-485:多点半双工串口标准。
-
TTL:数字电平标准。
-
CMOS:数字电路和微控制器中常用的电平标准。
-
LVDS:差分信号标准,用于高速数据传输。
协议标准:
-
UART:异步串行通信协议。
-
SPI:同步串行通信协议,用于连接微控制器、传感器等。
-
I2C:串行通信协议,用于多设备通信。
-
Modbus:工业自动化串行通信协议。
-
CAN:汽车和工业控制领域的串行通信协议。
-
USB:通用的串行通信标准。
三、串口通信协议
串口通信协议中的参数如波特率、奇偶检验位和停止位等非常重要,决定了数据的传输方式和完整性检查。
-
波特率:传输速率,如9600、115200。
-
数据位:每个数据字节中的位数,通常为8位。
-
奇偶检验位:用于检测数据传输中的错误。
-
停止位:表示数据字节的结束,常见为1位。
正确配置这些参数对于串口通信至关重要,因为通信双方必须使用相同的参数以避免数据传输错误。
四、Linux系统中使用串口通信
在Linux系统中,串口通信的一般步骤包括:
-
打开串口设备:使用
open函数打开/dev目录下的串口设备文件。 -
配置串口参数:使用
termios结构和tcsetattr函数配置通信参数。 -
读取和写入数据:使用
read和write函数进行数据交换。 -
关闭串口:使用
close函数关闭串口设备。
了解串口通信的基本概念和参数设置对于成功进行串口通信非常重要。不同的应用和硬件要求可能需要不同的电气标准和协议标准,因此在进行串口通信时,需要了解所使用的设备的规格和要求。
以下是一个示例C程序,演示如何在Linux系统中打开串口、配置串口参数、读取和写入数据:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
int fd;
struct termios serial;
// 打开串口设备
fd = open("/dev/ttyS0", O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 配置串口参数
tcgetattr(fd, &serial);
serial.c_cflag = B9600; // 波特率 9600
serial.c_cflag |= CS8; // 8位数据位
serial.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; // 无奇偶校验
tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &serial);
char data_to_send[] = "Hello, Serial!";
write(fd, data_to_send, strlen(data_to_send));
char buffer[100];
ssize_t n = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if (n > 0) {
buffer[n] = '\0';
printf("Received data: %s\n", buffer);
}
close(fd); // 关闭串口
return 0;
}
这个示例演示了如何与串口设备进行基本的数据交换。请注意,串口设备的配置参数需要与你连接的设备匹配,因此根据设备的要求来调整波特率和其他参数。此示例中使用的是 /dev/ttyS0,你可能需要根据你的系统和硬件配置来指定正确的串口设备。
五、外设应用程序开发之串口
1. 接线
orangepi zero2有两组串口,本次连接26引脚处的串口。
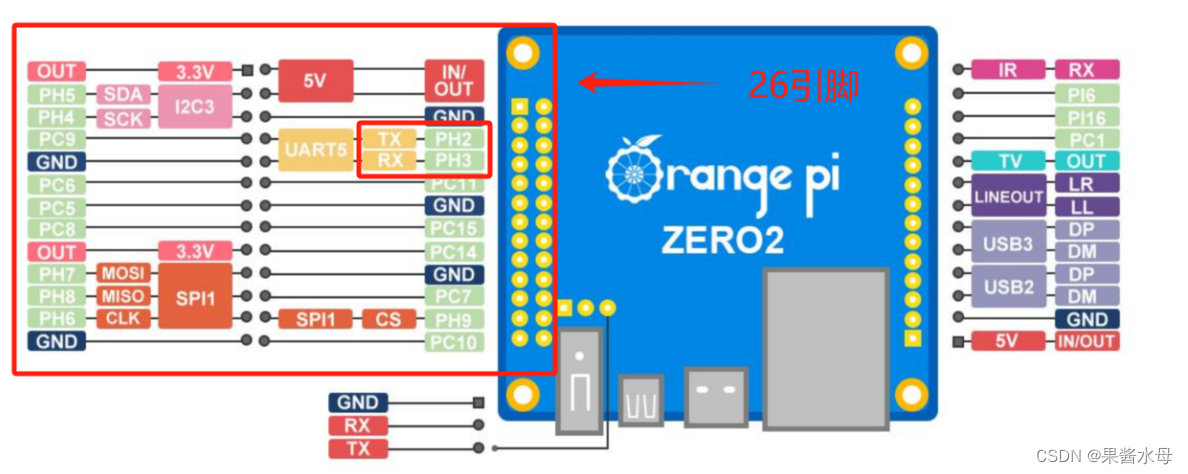
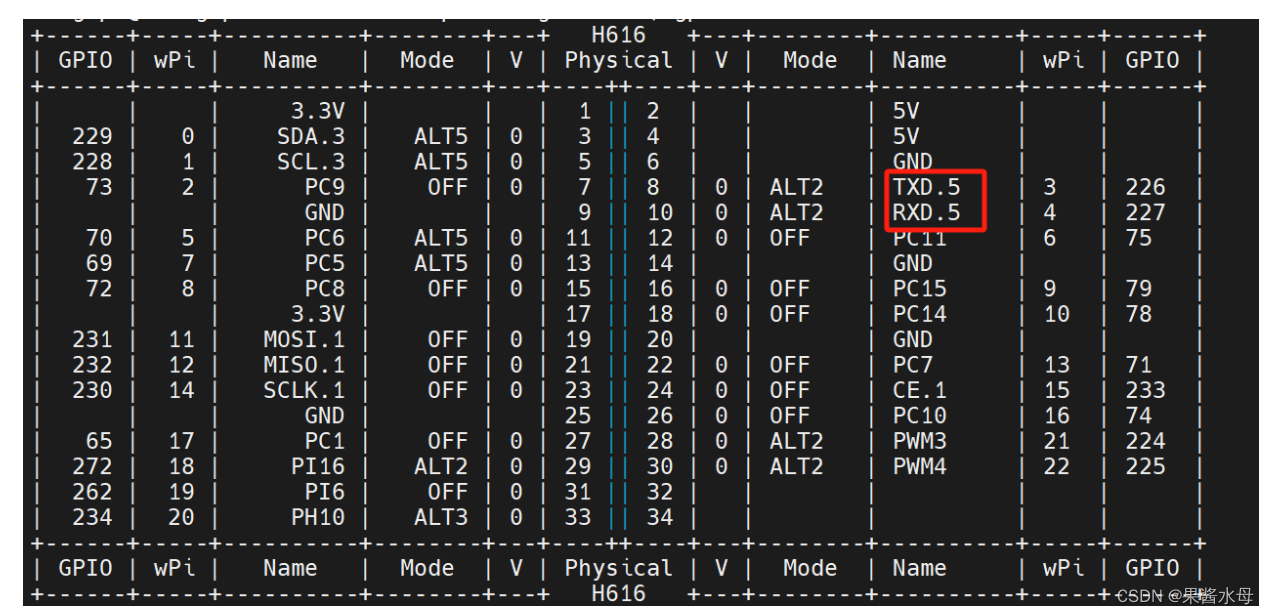
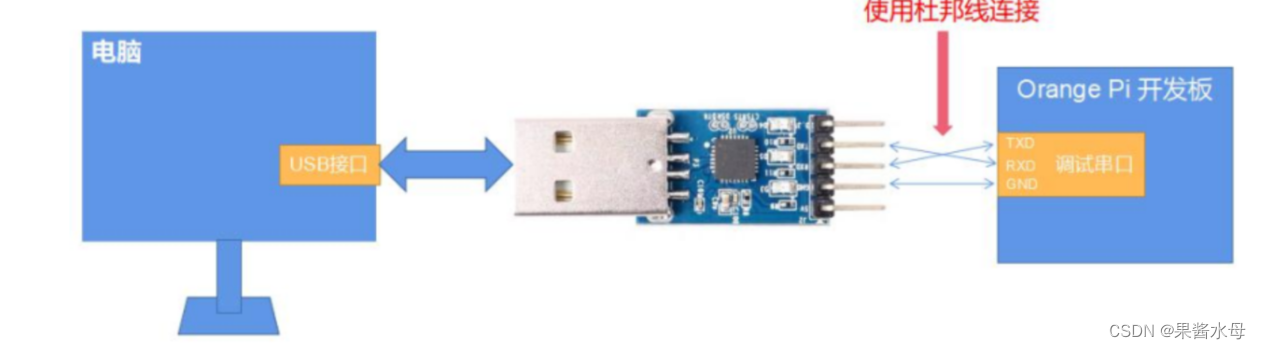
2. 串行测试 serialtest
找到wiringOP库下的serialtest源文件,复制一份出来,我们操作一下。
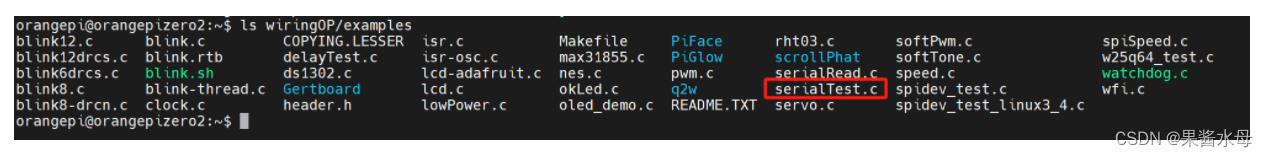
源代码:
/*
* serialTest.c:
* Very simple program to test the serial port. Expects
* the port to be looped back to itself
*
* Copyright (c) 2012-2013 Gordon Henderson. <projects@drogon.net>
***********************************************************************
* This file is part of wiringPi:
* https://projects.drogon.net/raspberry-pi/wiringpi/
*
* wiringPi is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* wiringPi is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
* along with wiringPi. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
***********************************************************************
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <wiringSerial.h>
int main ()
{
int fd ;
int count ;
unsigned int nextTime ;
if ((fd = serialOpen ("/dev/ttyS2", 115200)) < 0)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Unable to open serial device: %s\n", strerror (errno)) ;
return 1 ;
}
if (wiringPiSetup () == -1)
{
fprintf (stdout, "Unable to start wiringPi: %s\n", strerror (errno)) ;
return 1 ;
}
nextTime = millis () + 300 ;
for (count = 0 ; count < 256 ; )
{
if (millis () > nextTime)
{
printf ("\nOut: %3d: ", count) ;
fflush (stdout) ;
serialPutchar (fd, count) ;
nextTime += 300 ;
++count ;
}
delay (3) ;
while (serialDataAvail (fd))
{
printf (" -> %3d", serialGetchar (fd)) ;
fflush (stdout) ;
}
}
printf ("\n") ;
return 0 ;
}
编译后:
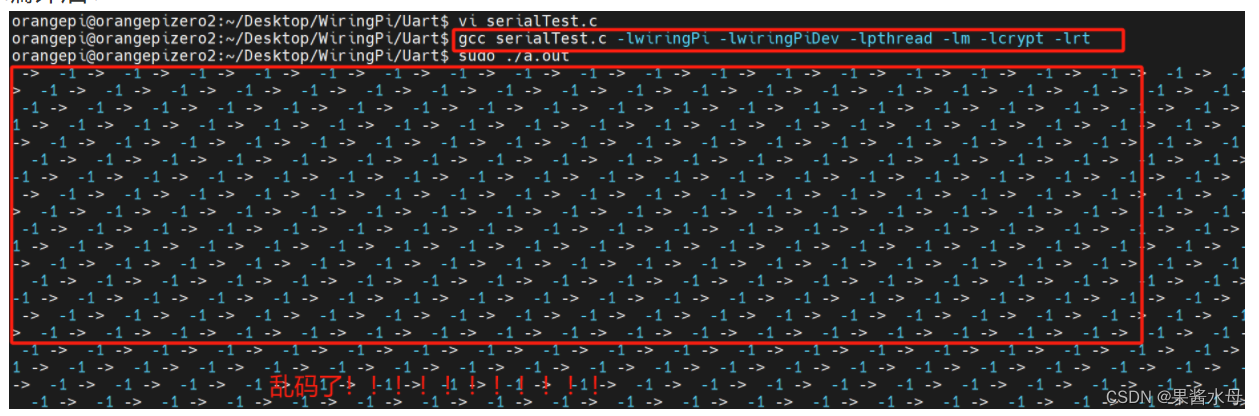
出现乱码,说明串口没有配置或没有配置好,那么查看手册,修改配置文件打开外设的串口配置模式。
2.1 根据手册修改配置文件
1.首先确保代码配置好串口
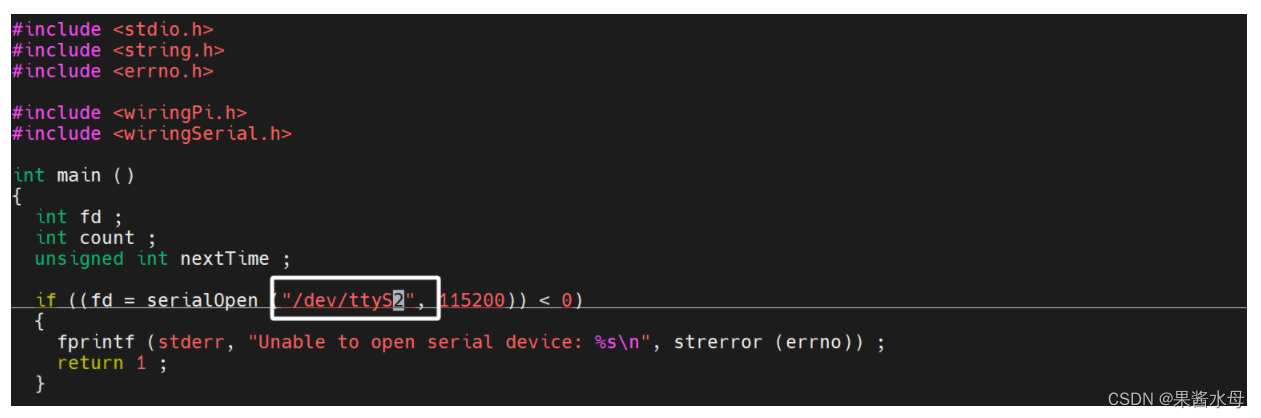
改为5
2.确保香橙派打开了外设串口模式
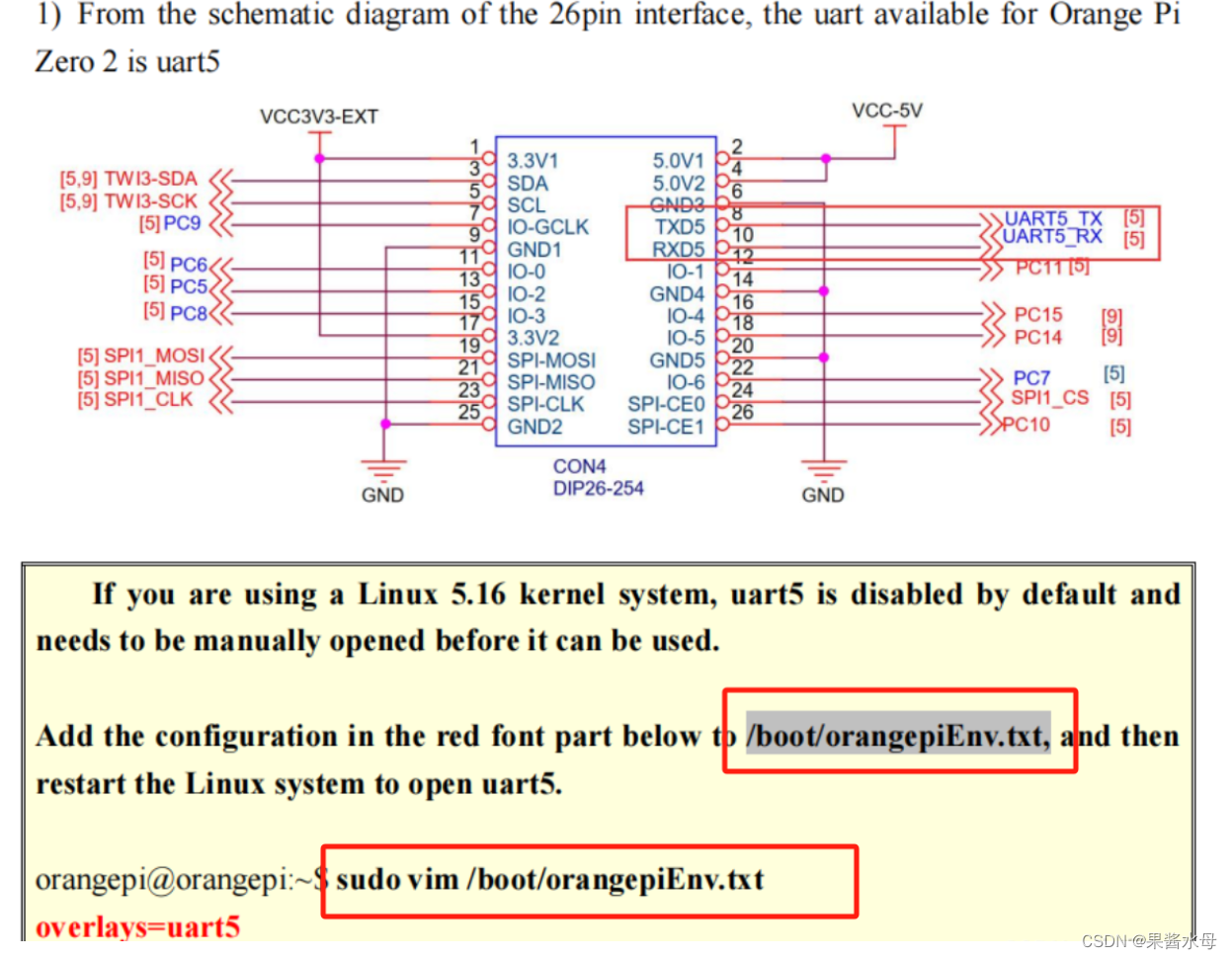
在“/boot/orangepiEnv.txt”中加入 uart5的配置,然后重启香橙派就可以打开 uart5了,具体操作如下:
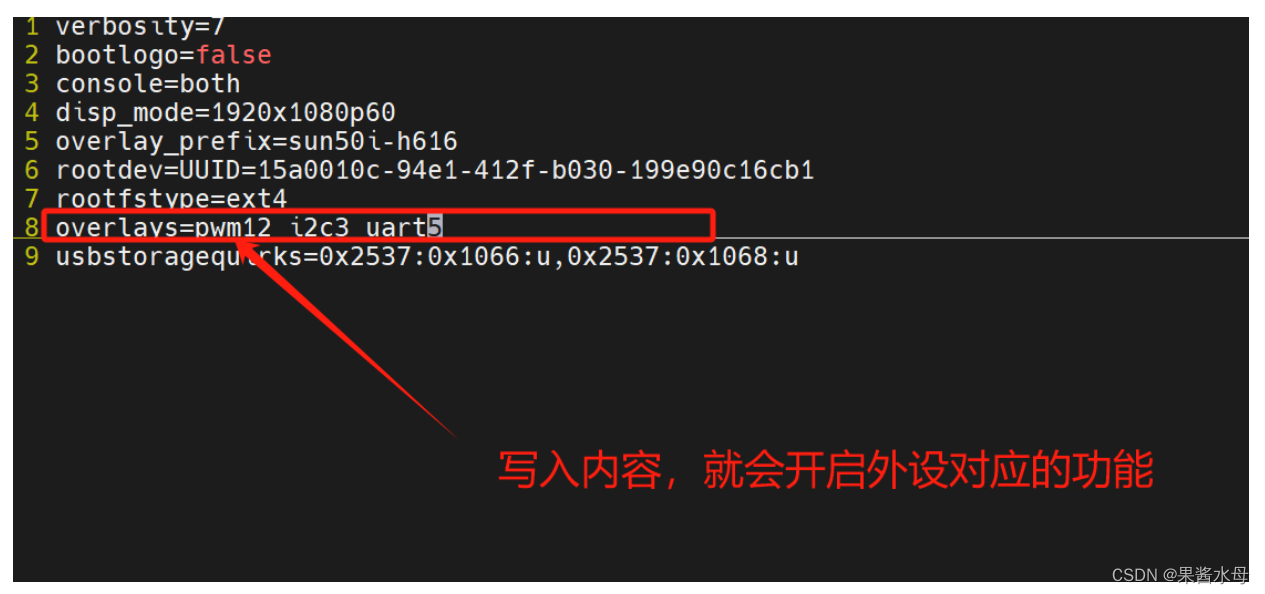
重启香橙派后,终端输入ls /dev/ttyS*,只要有出现/dev/ttyS5,就说明已经打开了ttyS5相应 的通道了。
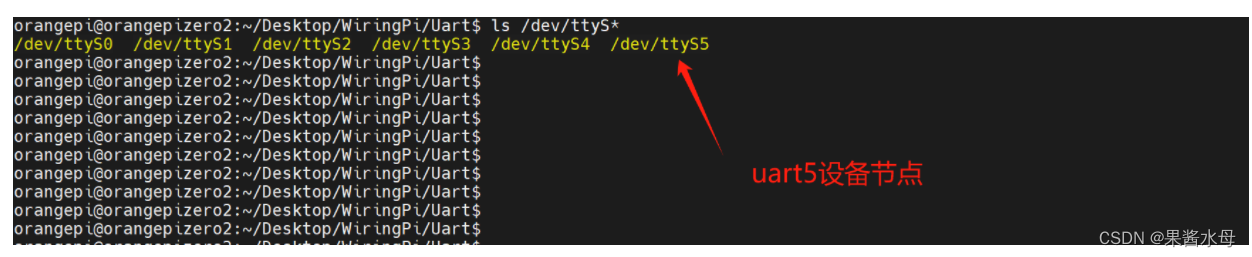
/dev下存在uart5设备节点,Orangepi Zero2 全志H616可用串口协议为ttyS5,用作信息交互串口,(注意:/dev/ttysS0为调试串口,本人踩过坑,接错会出现把Linux系统映射到串口的类似现象,可自行配置使用)
2.2 数据交互
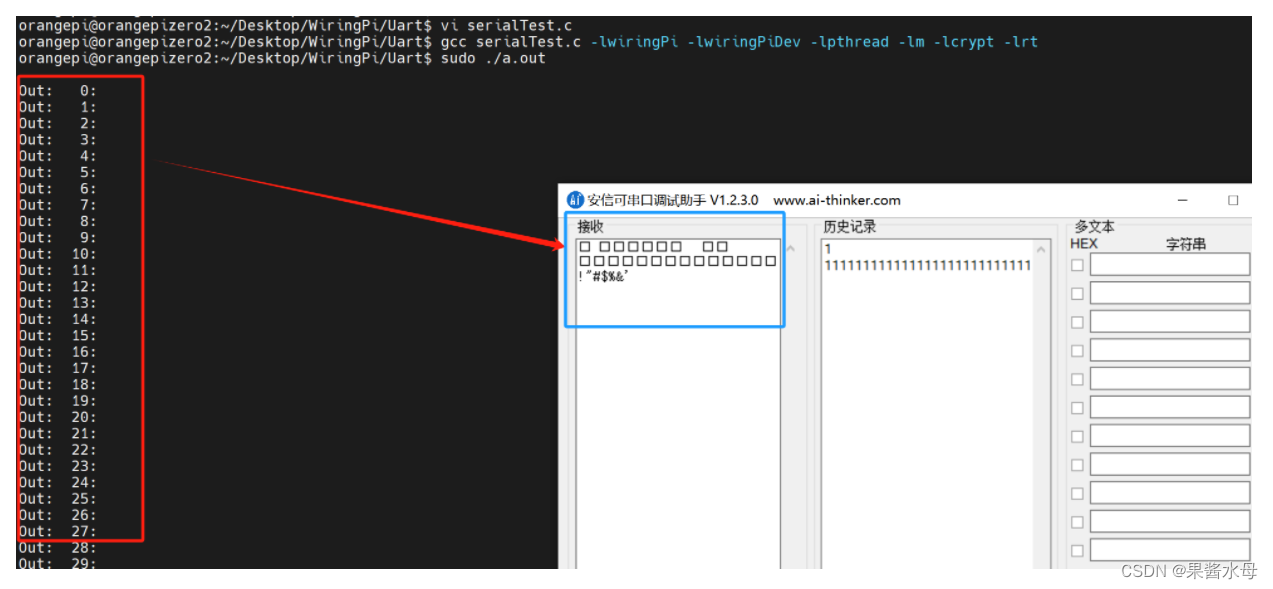
3. 基于 wiringPi 的串口开发
3.1 改为双线程交互
-
实现串口通信的双线程交互,以提高数据传输的效率和稳定性。
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <wiringPi.h> #include <wiringSerial.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> int fd; void* Sendhandler() { char *sendBuf; sendBuf = (char *)malloc(32*sizeof(32)); while (1){ memset(sendBuf, '\0', 32); scanf("%s", sendBuf); while (*sendBuf){ serialPutchar(fd, *sendBuf++); } } } void* Revhandler() { while (1){ while (serialDataAvail(fd)){ printf("%c", serialGetchar(fd)); fflush(stdout); } } } int main() { int count; unsigned int nextTime; pthread_t idSend; pthread_t idRev; if ((fd = serialOpen("/dev/ttyS5", 115200)) < 0){ fprintf(stderr, "Unable to open serial device: %s\n", strerror(errno)); return 1; } pthread_create(&idSend, NULL, Sendhandler, NULL); pthread_create(&idRev, NULL, Revhandler, NULL); if (wiringPiSetup() == -1){ fprintf(stdout, "Unable to start wiringPi: %s\n", strerror(errno)); return 1 ; } while (1){sleep(10);} printf("\n"); return 0; } 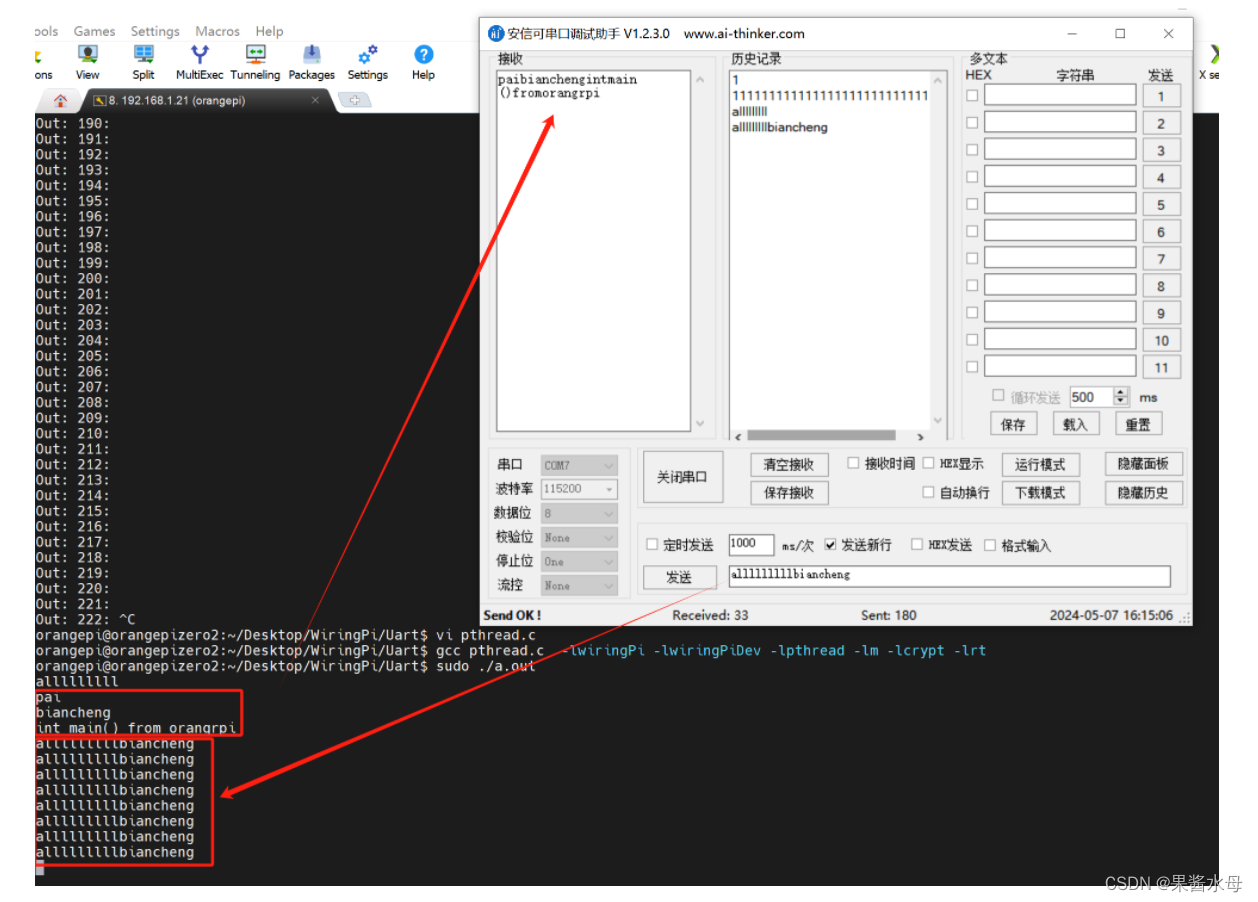
4. 分析源码来实现的串口通信
-
分析串口通信实现的源码,理解其工作原理和实现细节。
/*
* wiringSerial.c:
* Handle a serial port
***********************************************************************
* This file is part of wiringPi:
* https://projects.drogon.net/raspberry-pi/wiringpi/
*
* wiringPi is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* wiringPi is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
* along with wiringPi. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
***********************************************************************
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include "wiringSerial.h"
/*
* serialOpen:
* Open and initialise the serial port, setting all the right
* port parameters - or as many as are required - hopefully!
*********************************************************************************
*/
int serialOpen (const char *device, const int baud)
{
struct termios options ;
speed_t myBaud ;
int status, fd ;
switch (baud)
{
case 50: myBaud = B50 ; break ;
case 75: myBaud = B75 ; break ;
case 110: myBaud = B110 ; break ;
case 134: myBaud = B134 ; break ;
case 150: myBaud = B150 ; break ;
case 200: myBaud = B200 ; break ;
case 300: myBaud = B300 ; break ;
case 600: myBaud = B600 ; break ;
case 1200: myBaud = B1200 ; break ;
case 1800: myBaud = B1800 ; break ;
case 2400: myBaud = B2400 ; break ;
case 4800: myBaud = B4800 ; break ;
case 9600: myBaud = B9600 ; break ;
case 19200: myBaud = B19200 ; break ;
case 38400: myBaud = B38400 ; break ;
case 57600: myBaud = B57600 ; break ;
case 115200: myBaud = B115200 ; break ;
case 230400: myBaud = B230400 ; break ;
case 460800: myBaud = B460800 ; break ;
case 500000: myBaud = B500000 ; break ;
case 576000: myBaud = B576000 ; break ;
case 921600: myBaud = B921600 ; break ;
case 1000000: myBaud = B1000000 ; break ;
case 1152000: myBaud = B1152000 ; break ;
case 1500000: myBaud = B1500000 ; break ;
case 2000000: myBaud = B2000000 ; break ;
case 2500000: myBaud = B2500000 ; break ;
case 3000000: myBaud = B3000000 ; break ;
case 3500000: myBaud = B3500000 ; break ;
case 4000000: myBaud = B4000000 ; break ;
default:
return -2 ;
}
if ((fd = open (device, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY | O_NONBLOCK)) == -1)
return -1 ;
fcntl (fd, F_SETFL, O_RDWR) ;
// Get and modify current options:
tcgetattr (fd, &options) ;
cfmakeraw (&options) ;
cfsetispeed (&options, myBaud) ;
cfsetospeed (&options, myBaud) ;
options.c_cflag |= (CLOCAL | CREAD) ;
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB ;
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB ;
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE ;
options.c_cflag |= CS8 ;
options.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG) ;
options.c_oflag &= ~OPOST ;
options.c_cc [VMIN] = 0 ;
options.c_cc [VTIME] = 100 ; // Ten seconds (100 deciseconds)
tcsetattr (fd, TCSANOW, &options) ;
ioctl (fd, TIOCMGET, &status);
status |= TIOCM_DTR ;
status |= TIOCM_RTS ;
ioctl (fd, TIOCMSET, &status);
usleep (10000) ; // 10mS
return fd ;
}
/*
* serialFlush:
* Flush the serial buffers (both tx & rx)
*********************************************************************************
*/
void serialFlush (const int fd)
{
tcflush (fd, TCIOFLUSH) ;
}
/*
* serialClose:
* Release the serial port
*********************************************************************************
*/
void serialClose (const int fd)
{
close (fd) ;
}
/*
* serialPutchar:
* Send a single character to the serial port
*********************************************************************************
*/
void serialPutchar (const int fd, const unsigned char c)
{
int ret;
ret = write (fd, &c, 1) ;
if (ret < 0)
printf("Serial Putchar Error\n");
}
/*
* serialPuts:
* Send a string to the serial port
*********************************************************************************
*/
void serialPuts (const int fd, const char *s)
{
int ret;
ret = write (fd, s, strlen (s));
if (ret < 0)
printf("Serial Puts Error\n");
}
/*
* serialPrintf:
* Printf over Serial
*********************************************************************************
*/
void serialPrintf (const int fd, const char *message, ...)
{
va_list argp ;
char buffer [1024] ;
va_start (argp, message) ;
vsnprintf (buffer, 1023, message, argp) ;
va_end (argp) ;
serialPuts (fd, buffer) ;
}
/*
* serialDataAvail:
* Return the number of bytes of data avalable to be read in the serial port
*********************************************************************************
*/
int serialDataAvail (const int fd)
{
int result ;
if (ioctl (fd, FIONREAD, &result) == -1)
return -1 ;
return result ;
}
/*
* serialGetchar:
* Get a single character from the serial device.
* Note: Zero is a valid character and this function will time-out after
* 10 seconds.
*********************************************************************************
*/
int serialGetchar (const int fd)
{
uint8_t x ;
if (read (fd, &x, 1) != 1)
return -1 ;
return ((int)x) & 0xFF ;
}
自己编写头文件
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <stdarg.h> #include <string.h> #include <termios.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include "wiringSerial.h" int my_serialOpen (const char *device, const int baud) ; void my_serialSendstring (const int fd, const char *s) ; int my_serialGetstring (const int fd, char *buffer) ;
对应的c文件
#include "wiringSerial.h"
#include "uartTool.h"
int my_serialOpen (const char *device, const int baud)
{
struct termios options ; // 创建一个termios结构体,用于串口参数设置
speed_t myBaud ; // 创建一个速度类型的变量 myBaud,用于保存波特率
int status, fd ; // 创建整数类型的变量 status 和 fd,用于保存状态和文件描述符
switch (baud){ // 根据传入的波特率参数选择合适的波特率常数
case 9600: myBaud = B9600 ; break ;
case 115200: myBaud = B115200 ; break ;
}
if ((fd = open (device, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY | O_NONBLOCK)) == -1) // 打开串口设备,设置打开选项
return -1 ; // 如果打开失败,返回错误代码 -1
fcntl (fd, F_SETFL, O_RDWR) ; // 设置文件状态标志
// Get and modify current options: 获取并修改当前的串口参数:
tcgetattr (fd, &options) ; // 获取当前的串口参数
cfmakeraw (&options) ; // 初始化 termios 结构体为原始模式
cfsetispeed (&options, myBaud) ; // 设置输入波特率
cfsetospeed (&options, myBaud) ; // 设置输出波特率
options.c_cflag |= (CLOCAL | CREAD) ; // 本地连接和使能接收
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB ; // 禁用奇偶校验
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB ; // 1位停止位
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE ; // 用数据位掩码清空数据位设置
options.c_cflag |= CS8 ; // 设置8位数据位
options.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG) ; // 禁用规范输入
options.c_oflag &= ~OPOST ; // 禁用输出处理
options.c_cc [VMIN] = 0 ; // 读取数据的最小字符数
options.c_cc [VTIME] = 100 ; // Ten seconds (100 deciseconds) 超时等待时间(十分之一秒100ms)
tcsetattr (fd, TCSANOW, &options) ; // 设置新的串口参数
ioctl (fd, TIOCMGET, &status); // 获取串口控制模式状态
status |= TIOCM_DTR ; // 设置 DTR(数据终端就绪)位
status |= TIOCM_RTS ; // 设置 RTS(请求发送)位
ioctl (fd, TIOCMSET, &status); // 设置串口控制模式状态
usleep (10000) ; // 暂停 10 毫秒
return fd ; // 返回串口文件描述符
}
void my_serialSendstring (const int fd, const char *s)
{
int ret ;
ret = write (fd, s, strlen (s)) ;
if (ret < 0)
printf ("Serial Sendstring Error\n") ;
}
int my_serialGetstring (const int fd, char *buffer)
{
int n_read ;
n_read = read (fd, buffer, 32) ;
return n_read ;
}
基于3中的串口开发,改写
#include <pthread.h>
#include "uartTool.h"
int fd;
void* readSerial ()
{
char buffer [32] ;
while (1) {
memset (buffer, '\0', sizeof(buffer)) ;
my_serialGetstring (fd, buffer) ;
printf ("GET->%s\n", buffer) ;
}
}
void* sendSerial ()
{
char buffer [32] ;
while (1) {
memset (buffer,'\0', sizeof(buffer)) ;
scanf ("%s", buffer) ;
my_serialSendstring (fd, buffer) ;
}
}
int main (int argc, char **argv)
{
char deviceName [32] = {'\0'} ;
pthread_t readt ;
pthread_t sendt ;
if (argc < 2) {
printf ("uage:%s /dev/ttyS?\n", argv[0]) ;
return -1 ;
}
strcpy (deviceName, argv[1]) ;
if ((fd = my_serialOpen (deviceName, 115200)) == -1) {
printf ("open %s error\n", deviceName) ;
return -1;
}
pthread_create (&readt, NULL, readSerial, NULL) ;
pthread_create (&sendt, NULL, sendSerial, NULL) ;
while (1) {sleep (10);}
}
运行:
gcc uartTool.c uartTool.h uartTest.c -lpthread ./a.out /dev/ttyS5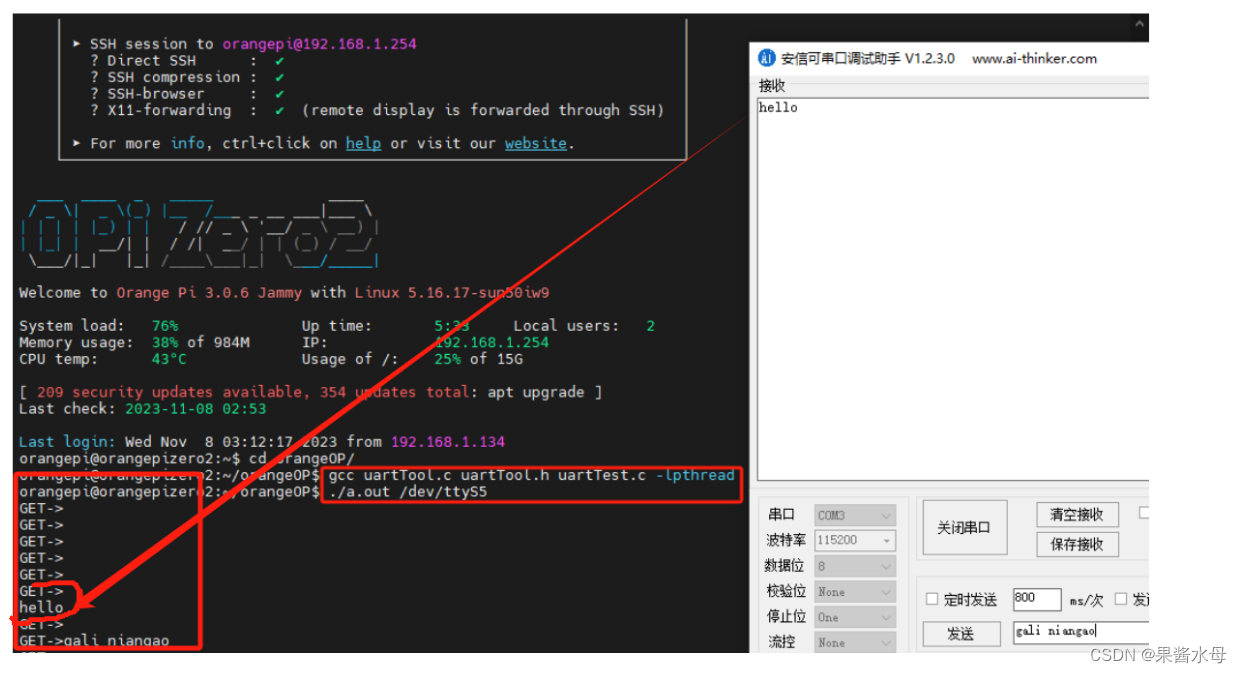






















 768
768











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








