Kruskal 算法
Kruskal算法是一种用于寻找连通图中最小生成树的算法。最小生成树是一个包含图中所有顶点的树,且边权重之和最小。Kruskal算法是一种贪心算法,它的基本思想是:每次选择边权重最小的边来扩展树,直到树包含所有的顶点。
以下是Kruskal算法的步骤:
- 按边权重从小到大排序。
- 初始时,每个顶点都是一个单独的树。
- 选择边权重最小的边,如果这条边不形成环,将其添加到树中。
- 重复步骤3,直到所有顶点都连接到一个树上。
为了确保不形成环,Kruskal算法使用了一种称为“割点”的优化技术。一个割点是这样一个顶点:删除它之后,图将分为两个或多个连通分量。在Kruskal算法中,我们首先考虑那些包含多个连通分量的顶点,并将它们作为候选的割点。然后,我们选择边权重最小的边,并确保它不连接同一个连通分量中的两个顶点。
Kruskal算法的时间复杂度是O(E log V),其中E是边的数量,V是顶点的数量。这个时间复杂度是由排序步骤决定的,因为我们需要按边权重对所有边进行排序。
Kruskal算法适用于边权重非负的连通图,并且可以用来解决一些其他的优化问题,如求解单源最短路径问题(当图中没有负权重边时)。在实际应用中,Kruskal算法常用于电信网络、计算机网络和其他需要高效传输的系统中,以确定成本最低的基础设施布局。
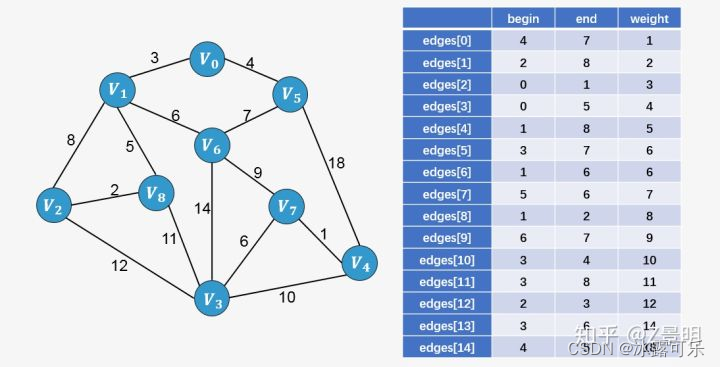
根据图片构成出图的邻接矩阵,并且根据邻接矩阵得到路径数组,写出代码如下:
并且使用sort函数,让路径数组按从小到大排序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Path{ //定义路径结构体
int start; //起点
int terminal; //终点
int values; //权值
}Path;
int g[9][9]; //路径邻接矩阵
void newGraph() {
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
g[i][j] = INT32_MAX; //最大值意味无路径
}
}
g[0][1] = 3; //为邻接矩阵赋值
g[1][0] = 3;
g[0][5] = 4;
g[5][0] = 4;
g[1][2] = 8;
g[2][1] = 8;
g[1][8] = 5;
g[8][1] = 5;
g[1][6] = 6;
g[6][1] = 6;
g[2][8] = 2;
g[8][2] = 2;
g[2][3] = 12;
g[3][2] = 12;
g[3][8] = 11;
g[8][3] = 11;
g[3][6] = 14;
g[6][3] = 14;
g[3][7] = 6;
g[7][3] = 6;
g[3][4] = 10;
g[4][3] = 10;
g[4][5] = 18;
g[5][4] = 18;
g[4][7] = 1;
g[7][4] = 1;
g[5][6] = 7;
g[6][5] = 7;
g[6][7] = 9;
g[7][6] = 9;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { //输出邻接矩阵验证
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if(g[i][j] == INT32_MAX) cout << "x ";
else cout << g[i][j] <<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
}
vector<Path> path; //存放路径的数组
void addPath() {
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
Path cur_path;
if(g[i][j] != INT32_MAX) { //倘若有路径
cur_path.start = i; //将邻接矩阵中的路径转化为路径结构体,添加到path中
cur_path.terminal = j;
cur_path.values = g[i][j];
path.push_back(cur_path);
}
}
}
sort(path.begin(), path.end(), [](const Path& a, const Path& b) {
return a.values < b.values; // 根据权值升序排序
});
for(Path i: path) { //按顺序输出路径数组
cout << i.start << "->" << i.terminal << ":" << i.values;
cout<<endl;
}
}
运行结果验证我们的代码没有错误。


这里路径重复的问题在后文会出现。。
使用队列,将路径逆向添加到队列中。
所以数组排序应该改为升序。
queue<Path> queuePath; //路径优先队列
...
sort(path.begin(), path.end(), [](const Path& a, const Path& b) {
return a.values < b.values; // 根据权值降序排序
});
for(Path i: path) { //按逆序添加路径到优先队列中
queuePath.push(i);
}
...
因为邻接矩阵中重复定义了同一条路径,如g【i】【j】和g【j】【i】是同一条路径,所以再加入路径数组(队列)中,会存在重复定义,并且本文不会添加去重部分,所以需要修改邻接矩阵中只定义一条路径即可。
后面就是Kruskal算法代码加上验证是否闭环的函数,如下:
vector<int> ans; //存放构成生成树的结点
int path_sum; //记录总路径和
bool closedTree(int i, int j) {
bool i_exited = false;
bool j_exited = false;
for(int u : ans) {
if(u == i) i_exited = true;
if(u == j) i_exited = true;
}
if(i_exited && j_exited) return false;
else return true;
}
void Kruskal(){
while(!queuePath.empty()) {
Path choice = queuePath.front();
if(closedTree(choice.start, choice.terminal)) {
ans.push_back(choice.start); //将路径的起点和终点添加到结点数组ans中
ans.push_back(choice.terminal);
path_sum += choice.values;
cout << choice.start << "," << choice.terminal <<")=" << choice.values << endl;
}
queuePath.pop();
}
}

运行结果如图,这里路径起点和终点我并没有重复要求,因为不想添加函数去重,所以这里的起点终点就是邻接矩阵中的路径坐标。
总代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Path{ //定义路径结构体
int start; //起点
int terminal; //终点
int values; //权值
}Path;
int g[9][9]; //路径邻接矩阵
void newGraph() {
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
g[i][j] = INT32_MAX; //最大值意味无路径
}
}
g[0][1] = 3; //为邻接矩阵赋值
//g[1][0] = 3;
g[0][5] = 4;
//g[5][0] = 4;
g[1][2] = 8;
//g[2][1] = 8;
g[1][8] = 5;
//g[8][1] = 5;
// g[1][6] = 6;
g[6][1] = 6;
//g[2][8] = 2;
g[8][2] = 2;
// g[2][3] = 12;
g[3][2] = 12;
// g[3][8] = 11;
g[8][3] = 11;
// g[3][6] = 14;
g[6][3] = 14;
// g[3][7] = 6;
g[7][3] = 6;
// g[3][4] = 10;
g[4][3] = 10;
// g[4][5] = 18;
g[5][4] = 18;
// g[4][7] = 1;
g[7][4] = 1;
// g[5][6] = 7;
g[6][5] = 7;
// g[6][7] = 9;
g[7][6] = 9;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { //输出邻接矩阵验证
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if(g[i][j] == INT32_MAX) cout << "x ";
else cout << g[i][j] <<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
}
vector<Path> path; //存放路径的数组
queue<Path> queuePath; //路径优先队列
void addPath() {
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
Path cur_path;
if(g[i][j] != INT32_MAX) { //倘若有路径
cur_path.start = i; //将邻接矩阵中的路径转化为路径结构体,添加到path中
cur_path.terminal = j;
cur_path.values = g[i][j];
path.push_back(cur_path);
}
}
}
sort(path.begin(), path.end(), [](const Path& a, const Path& b) {
return a.values < b.values; // 根据权值降序排序
});
for(Path i : path) {
//cout << "(" << i.start << "," << i.terminal <<")=" << i.values << endl;
}
for(Path i: path) { //按逆序添加路径到优先队列中
queuePath.push(i);
}
}
vector<int> ans; //存放构成生成树的结点
int path_sum; //记录总路径和
bool closedTree(int i, int j) {
bool i_exited = false;
bool j_exited = false;
for(int u : ans) {
if(u == i) i_exited = true;
if(u == j) i_exited = true;
}
if(i_exited && j_exited) return false;
else return true;
}
void Kruskal(){
while(!queuePath.empty()) {
Path choice = queuePath.front();
if(closedTree(choice.start, choice.terminal)) {
ans.push_back(choice.start); //将路径的起点和终点添加到结点数组ans中
ans.push_back(choice.terminal);
path_sum += choice.values;
cout << "(" <<choice.start << "," << choice.terminal <<")=" << choice.values << endl;
}
queuePath.pop();
}
cout << "cost of minimum spanning tree is :" << path_sum;
}
int main() {
newGraph();
addPath();
Kruskal();
return 0;
}





















 724
724











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








