本期文章将讲述常用智能优化算法改进策略---变异篇,一共包含五种常见的变异策略:
高斯变异,t分布扰动变异,自适应t分布扰动变异,柯西变异,差分变异。
五种策略可以方便移植到其他智能算法的改进中!
为了方便大家对变异策略的深入了解,作者将在简单易懂的粒子群算法教大家如何运用这五种策略,今后也方便大家移植到别的智能算法中。
高斯变异:
高斯函数如下:

带入粒子群算法中如下:
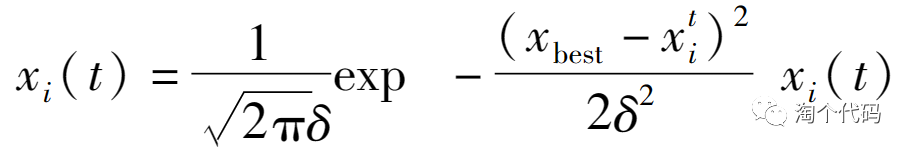
t分布扰动变异:

带入粒子群算法中如下:

自适应t分布扰动变异;
对C_Iter进行自适应变化,可以在算法前期进行全局搜索,在后期进行局部搜索,从而达到收敛。
freen = exp(4.*(l/iter).^2);
然后再带入此式当中:

柯西变异:
柯西概率密度函数如下:

带入粒子群算法中:
xnewbest=xbest+xbest×Cauchy(0,1)
随机差分变异:

Xα是全局最优粒子,X‘(t)是随机粒子,r是一个[0,1]的随机数。
结果展示
在CEC2005函数集进行展示,设置迭代次数1000次,种群个数100个。
其中PSO为原始粒子群,GPSO是高斯变异的粒子群,t-PSO是t分布变异的粒子群,self_adaption_t_PSO是自适应t分布变异的粒子群,CPSO是柯西变异的粒子群,DE-PSO是差分变异的粒子群。

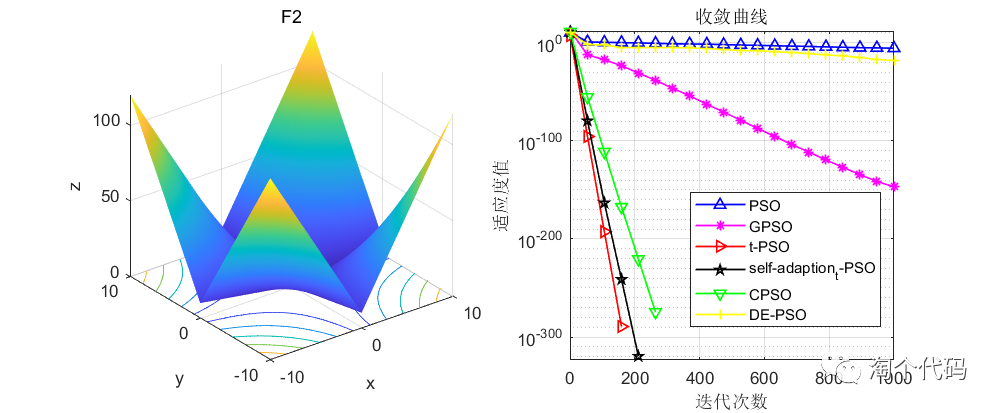
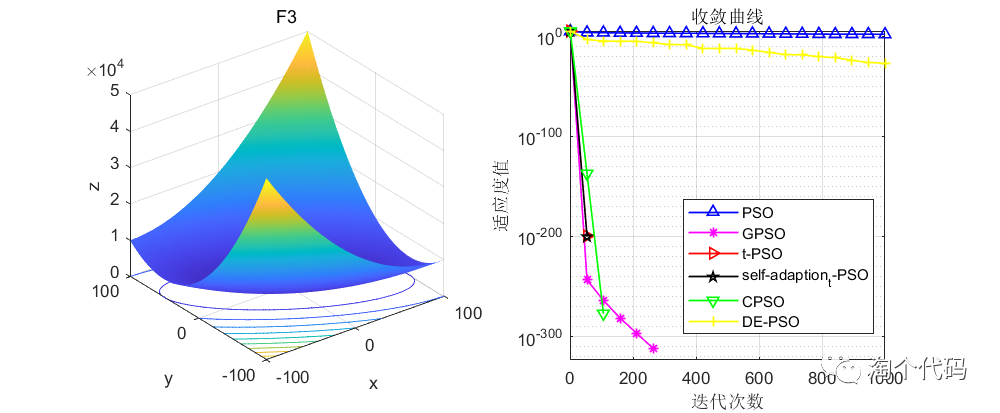

注意!本程序代码只是为了教大家如何使用这几种变异策略,如果看到改进后的算法没有原始算法效果好,请不要见怪!
这几种策略并非说用到某种算法上就一定会效果好,关键要看算法本身的原理公式适不适合!要分析其原理并不断进行尝试!
代码展示
%
clear
clc
close all
number='F'; %选定优化函数,自行替换:F1~F23
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=CEC2005(number); % [lb,ub,D,y]:下界、上界、维度、目标函数表达式
SearchAgents=100; % population members
Max_iterations=1000; % maximum number of iteration
%% 调用PSO算法
[fMin , bestX, PSO_Convergence_curve ] = PSO(SearchAgents, Max_iterations,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by PSO for ' [num2str(number)],' is : ', num2str(fMin)]);
fprintf ('Best solution obtained by PSO: %s\n', num2str(bestX,'%e '));
%% 调用高斯变异的PSO
[Best_score,Best_pos,GPSO_curve]=GPSO(SearchAgents,Max_iterations,lb,ub,dim,fobj); % Calculating the solution of the given problem using GPSO
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by GPSO for ' [num2str(number)],' is : ', num2str(Best_score)]);
fprintf ('Best solution obtained by GPSO: %s\n', num2str(Best_pos,'%e '));
%% 调用t分布扰动的PSO算法
[Alpha_score,Alpha_pos,t_PSO_Convergence_curve]=t_PSO(SearchAgents,Max_iterations,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by t_PSO for ' [num2str(number)],' is : ', num2str(Alpha_score)]);
fprintf ('Best solution obtained by t_PSO: %s\n', num2str(Alpha_pos,'%e '));
%% 调用自适应t分布扰动的PSO算法
[Alpha_score,Alpha_pos,self_adaption_t_PSO_Convergence_curve]=self_adaption_t_PSO(SearchAgents,Max_iterations,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by self_adaption_t_PSO for ' [num2str(number)],' is : ', num2str(Alpha_score)]);
fprintf ('Best solution obtained by self_adaption_t_PSO: %s\n', num2str(Alpha_pos,'%e '));
%% 调用柯西变异扰动的PSO算法
[Alpha_score,Alpha_pos,CPSO_Convergence_curve]=CPSO(SearchAgents,Max_iterations,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by CPSO for ' [num2str(number)],' is : ', num2str(Alpha_score)]);
fprintf ('Best solution obtained by CPSO: %s\n', num2str(Alpha_pos,'%e '));
%% 调用差分变异扰动的PSO算法
[Alpha_score,Alpha_pos,DE_PSO_Convergence_curve]=DE_PSO(SearchAgents,Max_iterations,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by DE_PSO for ' [num2str(number)],' is : ', num2str(Alpha_score)]);
fprintf ('Best solution obtained by DE_PSO: %s\n', num2str(Alpha_pos,'%e '));
%% Figure
figure1 = figure('Color',[1 1 1]);
G1=subplot(1,2,1,'Parent',figure1);
func_plot(number)
title(number)
xlabel('x')
ylabel('y')
zlabel('z')
subplot(1,2,2)
G2=subplot(1,2,2,'Parent',figure1);
CNT=20;
k=round(linspace(1,Max_iterations,CNT)); %随机选CNT个点
% 注意:如果收敛曲线画出来的点很少,随机点很稀疏,说明点取少了,这时应增加取点的数量,100、200、300等,逐渐增加
% 相反,如果收敛曲线上的随机点非常密集,说明点取多了,此时要减少取点数量
iter=1:1:Max_iterations;
if ~strcmp(number,'F16')&&~strcmp(number,'F9')&&~strcmp(number,'F11') %这里是因为这几个函数收敛太快,不适用于semilogy,直接plot
semilogy(iter(k),PSO_Convergence_curve(k),'b-^','linewidth',1);
hold on
semilogy(iter(k),GPSO_curve(k),'m-*','linewidth',1);
hold on
semilogy(iter(k),t_PSO_Convergence_curve(k),'r->','linewidth',1);
hold on
semilogy(iter(k),self_adaption_t_PSO_Convergence_curve(k),'k-p','linewidth',1);
hold on
semilogy(iter(k),CPSO_Convergence_curve(k),'g-v','linewidth',1);
hold on
semilogy(iter(k),DE_PSO_Convergence_curve(k),'y-+','linewidth',1);
else
plot(iter(k),PSO_Convergence_curve(k),'b-^','linewidth',1);
hold on
plot(iter(k),GPSO_curve(k),'m-*','linewidth',1);
hold on
plot(iter(k),t_PSO_Convergence_curve(k),'r->','linewidth',1);
hold on
plot(iter(k),self_adaption_t_PSO_Convergence_curve(k),'k-p','linewidth',1);
hold on
plot(iter(k),CPSO_Convergence_curve(k),'g-v','linewidth',1);
hold on
plot(iter(k),DE_PSO_Convergence_curve(k),'y-+','linewidth',1);
end
grid on;
title('收敛曲线')
xlabel('迭代次数');
ylabel('适应度值');
box on
legend('PSO','GPSO','t-PSO','self-adaption_t-PSO','CPSO','DE-PSO')
set (gcf,'position', [300,300,800,330])代码目录

直接运行MAIN.m脚本文件即可!
点击下方卡片获取更多代码!
往期独家原创优秀算法:
后续会不定时更新哦~
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










