Java设计模式(行为型)之-策略模式
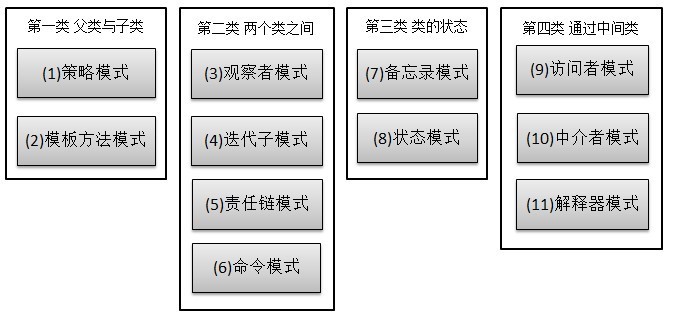
行为型模式,共11种:策略模式、模板方法模式、观察者模式、迭代子模式、责任链模式、命令模式、备忘录模式、状态模式、访问者模式、中介者模式、解释器模式。
先看看11行为型模式的关系:
策略模式(strategy)
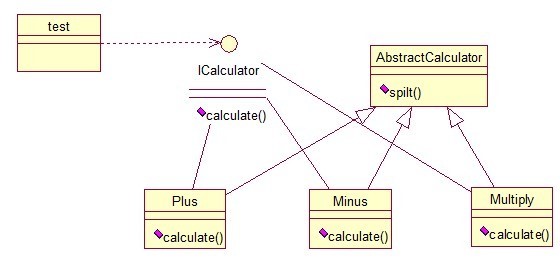
策略模式定义了一系列算法,并将每个算法封装起来,使他们可以相互替换,且算法的变化不会影响到使用算法的客户。需要设计一个接口,为一系列实现类提供统一的方法,多个实现类实现该接口,设计一个抽象类(可有可无,属于辅助类),提供辅助函数,关系图如下:
图中接口 ICalculator 提供统一的方法,
AbstractCalculator是辅助类,提供辅助方法,接下来,依次实现下每个类:
public class StrategyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String exp="2+8";
Plus plus=new Plus();
int result=plus.caculate(exp);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
// 接口,提供统一方法
interface ICaculator
{
public int caculate(String exp);
}
// 辅助类,提供辅助方法
abstract class AbstractCaculator
{
public int[] split(String exp,String opt){
String[] array=exp.split(opt);
int[] Intarray=new int[2];
Intarray[0]=Integer.parseInt(array[0]);
Intarray[1]=Integer.parseInt(array[1]);
return Intarray;
}
}
// 三个实现类
class Plus extends AbstractCaculator implements ICaculator
{
@Override
public int caculate(String exp) {
int[] IntArray=split(exp, "\\+");
return IntArray[0]+IntArray[1];
}
}
class Minus extends AbstractCaculator implements ICaculator
{
@Override
public int caculate(String exp) {
int[] IntArray=split(exp, "-");
return IntArray[0]-IntArray[1];
}
}
class Multiply extends AbstractCaculator implements ICaculator
{
@Override
public int caculate(String exp) {
int[] IntArray=split(exp, "\\*");
return IntArray[0]*IntArray[1];
}
}
输出:10
策略模式的决定权在用户,系统本身提供不同算法的实现,新增或者删除算法,对各种算法做封装。因此,策略模式多用在算法决策系统中,外部用户只需要决定用哪个算法即可。






















 400
400

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








