目录
一、time_t别名
time_t 用来表示时间数据类型,它是一个long(长整数)类型的别名,在time.h文件中定义,表示一个日历时间,好像是从1970年1月1日0时0分0秒到现在的秒数,感兴趣的可以自己去了解一下
typedef long time_t;二、time库函数
- time 函数的用途是返回一个值,也就是从1970年1月1日0时0分0秒到现在的秒数
- time 函数是C语言标准库中的函数,在time.h文件中声明
time_t time(time_t *t);time函数有两种调用方法:
// 将空地址传递给time函数,并将time返回值赋给变量tnow
time_t tnow = time(0);
或者
time(&tnow); // 将变量tnow的地址作为参数传递给time函数这两种方式,效果完全是一样的
举个例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
time_t tnow = time(0);
time(&tnow);
printf("%d\n",tnow);
printf("%d\n",time(&tnow));
return 0;
}
运行效果
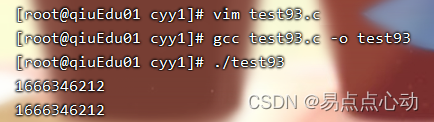
1970年1月1日到现在已经过去1666346212秒了
三、tm结构体
time_t 只是一个长整型,不符合我们的使用习惯,需要转换成可以方便表示时间的结构体,即 tm 结构体,tm结构体在 time.h 中声明
如下:
struct tm
{
int tm_sec; // 秒:取值区间为[0,59]
int tm_min; // 分:取值区间为[0,59]
int tm_hour; // 时:取值区间为[0,23]
int tm_mday; // 日期:一个月中的日期:取值区间为[1,31]
int tm_mon; // 月份:(从一月开始,0代表一月),取值区间为[0,11]
int tm_year; // 年份:其值等于实际年份减去1900
int tm_wday; // 星期:取值区间为[0,6],其中0代表星期天,1代表星期一,以此类推
int tm_yday; // 从每年的1月1日开始的天数:取值区间为[0,365],其中0代表1月1日,1代表1月2日,以此类推
int tm_isdst; // 夏令时标识符,该字段意义不大,我们不用夏令时。
};这个结构定义了年、月、日、时、分、秒、星期、当年中的某一天。用这个结构体可以很方便的显示时间
四、localtime库函数
localtime 函数用于把 time_t 表示的时间转换为 struct tm 结构体表示的时间,函数返回struct tm结构体的地址
函数声明:
struct tm * localtime(const time_t *);举个例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
time_t tnow = time(0);
struct tm *info;
info = localtime(&tnow);
printf("当前的本地时间和日期:%s", asctime(info));
return 0;
}
运行效果

你还可以这样玩
struct tm 结构体包含了时间的各要素,但还不是我们习惯的时间表达方式,我们可以用格式化输出printf、sprintf或fprintf等函数,把struct tm结构体转换为我们想要的结果
举个例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
time_t tnow = time(0);// 获取当前时间
printf("tnow=%lu\n",tnow); // 输出整数表示的时间
struct tm *sttm;
sttm = localtime(&tnow);// 把整数的时间转换为struct tm结构体的时间
// yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss格式输出,此格式用得最多
printf("%04u-%02u-%02u %02u:%02u:%02u\n",sttm->tm_year+1900,sttm->tm_mon+1,\
sttm->tm_mday,sttm->tm_hour,sttm->tm_min,sttm->tm_sec);
printf("%04u年%02u月%02u日%02u时%02u分%02u秒\n",sttm->tm_year+1900,\
sttm->tm_mon+1,sttm->tm_mday,sttm->tm_hour,sttm->tm_min,sttm->tm_sec);
// 只输出年月日
printf("%04u-%02u-%02u\n",sttm->tm_year+1900,sttm->tm_mon+1,sttm->tm_mday);
return 0;
}
运行效果

五、asctime库函数
asctime 函数返回一个指向字符串的指针,它代表了结构 struct tm 的日期和时间
函数声明:
char *asctime(const struct tm *timeptr)参数
timeptr 是指向 tm 结构的指针,包含了分解为如下各部分的日历时间:
struct tm {
int tm_sec; /* 秒,范围从 0 到 59 */
int tm_min; /* 分,范围从 0 到 59 */
int tm_hour; /* 小时,范围从 0 到 23 */
int tm_mday; /* 一月中的第几天,范围从 1 到 31 */
int tm_mon; /* 月份,范围从 0 到 11 */
int tm_year; /* 自 1900 起的年数 */
int tm_wday; /* 一周中的第几天,范围从 0 到 6 */
int tm_yday; /* 一年中的第几天,范围从 0 到 365 */
int tm_isdst; /* 夏令时 */
};返回值
该函数返回一个 C 字符串,包含了可读格式的日期和时间信息 Www Mmm dd hh:mm:ss yyyy,其中,Www 表示星期几,Mmm 是以字母表示的月份,dd 表示一月中的第几天,hh:mm:ss 表示时间,yyyy 表示年份
举个例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
struct tm t;
t.tm_sec = 10;
t.tm_min = 40;
t.tm_hour = 20;
t.tm_mday = 21;
t.tm_mon = 10-1;// 注意,要减1
t.tm_year = 2022-1900;// 注意,要减1900
t.tm_wday = 5;
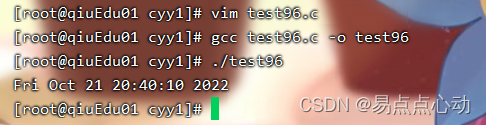
printf("%s",asctime(&t));
return(0);
}
运行效果
六、mktime库函数
- mktime 函数的功能与 localtime 函数相反
- localtime函数用于把 time_t 表示的时间转换为 struct tm 表示的时间
- mktime 函数用于把 struct tm 表示的时间转换为 time_t 表示的时间
time_t mktime(struct tm *tm);函数返回time_t的值
举个例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
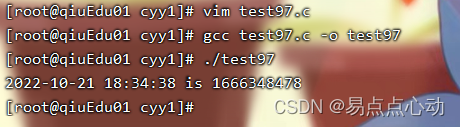
// 2022-10-21 18:34:38整数表示是1666348478
struct tm sttm;
memset(&sttm,0,sizeof(sttm));
sttm.tm_year=2022-1900; // 注意,要减1900
sttm.tm_mon=10-1; // 注意,要减1
sttm.tm_mday=21;
sttm.tm_hour=18;
sttm.tm_min=34;
sttm.tm_sec=38;
sttm.tm_isdst = 0;
printf("2022-10-21 18:34:38 is %lu\n",mktime(&sttm));
}
运行效果
七、程序睡眠
想把程序挂起一段时间,可以使用 sleep 和 usleep 两个库函数,需要包含unistd.h头文件中
函数的声明如下:
unsigned int sleep(unsigned int seconds);
int usleep(useconds_t usec);sleep函数的参数是秒,usleep函数的参数是微秒,1秒=1000000微秒
sleep(1); // 程序睡眠1秒。
sleep(10); // 程序睡眠10秒。
usleep(100000); // 程序睡眠十分之一秒。
usleep(1000000); // 程序睡眠一秒。七、获取十分钟后的时间
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
time_t tnow;
tnow=time(0); // 获取当前时间
printf("tnow=%lu\n",tnow); // 输出整数表示的时间
struct tm *sttm;
sttm=localtime(&tnow); // 把整数的时间转换为struct tm结构体的时间
// yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss格式输出,此格式用得最多
printf("%04u-%02u-%02u %02u:%02u:%02u\n",sttm->tm_year+1900,sttm->tm_mon+1,\
sttm->tm_mday,sttm->tm_hour,sttm->tm_min,sttm->tm_sec);
printf("十分钟后的时间\n");
tnow = tnow+10*60;
sttm=localtime(&tnow); // 把整数的时间转换为struct tm结构体的时间
printf("%04u-%02u-%02u %02u:%02u:%02u\n",sttm->tm_year+1900,sttm->tm_mon+1,\
sttm->tm_mday,sttm->tm_hour,sttm->tm_min,sttm->tm_sec);
return 0;
}运行效果

如果想要10分钟前的时间就 tnow = tnow-10*60 ; 想要之前的时间或者之后的可以自己设置






















 775
775











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










