Cesium高级教程-地形应用-修改地形数据的方式实现地形压平
修改地形数据的方式实现压平
上一节我们通过修改地形的顶点着色器代码实现的地形压平,到这里您是否会这样想?既然能够在着色器中修改地形的顶点,又因为着色器中的顶点数据是在外部传递到着色器中的,那我们是否可以直接在外面把地形数据修改好,然后将修改后的数据传递到着色器中?答案是肯定的,接下来我们介绍通过修改地形数据的方式实现地形压平。
地形数据的加载
要修改地形数据,首先您得知道地形数据在哪?如果这都不知道,那是没法进行下一步的!我们知道地形数据和影像数据都是分块数据,它是一块一块的,并不是一个整体,为了获取到地形数据,首页我们需要知道这些分块数据是从哪儿加载的。又因为在场景中添加地形是从地形服务提供者开始的,所以我们先看看地形服务提供者的文档TerrainProvider

这是一个接口定义,具体的实现由不同的子类进行,但是从该类中我们可以看到一个重要的方法requestTileGeometry(x, y, level, request) → Promise.<TerrainData>|undefined

这个方法就是用来加分块的地形数据的,因为地形服务提供者会有不同的类型,不同的类型对应不同格式的地形数据,不同类型的加载方法肯定是不一样的,我们最常用的是CesiumTerrainProvider类,所以我们打开该类的代码,看看其大致的内容。
/**
* Requests the geometry for a given tile. The result must include terrain data and
* may optionally include a water mask and an indication of which child tiles are available.
*
* @param {number} x The X coordinate of the tile for which to request geometry.
* @param {number} y The Y coordinate of the tile for which to request geometry.
* @param {number} level The level of the tile for which to request geometry.
* @param {Request} [request] The request object. Intended for internal use only.
*
* @returns {Promise<TerrainData>|undefined} A promise for the requested geometry. If this method
* returns undefined instead of a promise, it is an indication that too many requests are already
* pending and the request will be retried later.
*
*/
CesiumTerrainProvider.prototype.requestTileGeometry = function(
x,
y,
level,
request,
) {
...
// call overridden function below
return requestTileGeometry(this, x, y, level, layerToUse, request);
};
方法中调用了一个内部方法requestTileGeometry,该方法内容如下
function requestTileGeometry(provider, x, y, level, layerToUse, request) {
if (!defined(layerToUse)) {
return Promise.reject(new RuntimeError("Terrain tile doesn't exist"));
}
const urlTemplates = layerToUse.tileUrlTemplates;
if (urlTemplates.length === 0) {
return undefined;
}
// The TileMapService scheme counts from the bottom left
let terrainY;
if (!provider._scheme || provider._scheme === "tms") {
const yTiles = provider._tilingScheme.getNumberOfYTilesAtLevel(level);
terrainY = yTiles - y - 1;
} else {
terrainY = y;
}
const extensionList = [];
if (provider._requestVertexNormals && layerToUse.hasVertexNormals) {
extensionList.push(
layerToUse.littleEndianExtensionSize
? "octvertexnormals"
: "vertexnormals",
);
}
if (provider._requestWaterMask && layerToUse.hasWaterMask) {
extensionList.push("watermask");
}
if (provider._requestMetadata && layerToUse.hasMetadata) {
extensionList.push("metadata");
}
let headers;
let query;
const url = urlTemplates[(x + terrainY + level) % urlTemplates.length];
const resource = layerToUse.resource;
if (
defined(resource._ionEndpoint) &&
!defined(resource._ionEndpoint.externalType)
) {
// ion uses query parameters to request extensions
if (extensionList.length !== 0) {
query = { extensions: extensionList.join("-") };
}
headers = getRequestHeader(undefined);
} else {
//All other terrain servers
headers = getRequestHeader(extensionList);
}
const promise = resource
.getDerivedResource({
url: url,
templateValues: {
version: layerToUse.version,
z: level,
x: x,
y: terrainY,
},
queryParameters: query,
headers: headers,
request: request,
})
.fetchArrayBuffer();
if (!defined(promise)) {
return undefined;
}
return promise.then(function(buffer) {
if (!defined(buffer)) {
return Promise.reject(new RuntimeError("Mesh buffer doesn't exist."));
}
if (defined(provider._heightmapStructure)) {
return createHeightmapTerrainData(provider, buffer, level, x, y);
}
return createQuantizedMeshTerrainData(
provider,
buffer,
level,
x,
y,
layerToUse,
);
});
}
可以看到最后是调用了createQuantizedMeshTerrainData方法并将其执行结果作为返回值,我们再看看该方法的内容
function createQuantizedMeshTerrainData(provider, buffer, level, x, y, layer) {
const littleEndianExtensionSize = layer.littleEndianExtensionSize;
let pos = 0;
const cartesian3Elements = 3;
const boundingSphereElements = cartesian3Elements + 1;
const cartesian3Length = Float64Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * cartesian3Elements;
const boundingSphereLength =
Float64Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * boundingSphereElements;
const encodedVertexElements = 3;
const encodedVertexLength =
Uint16Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * encodedVertexElements;
const triangleElements = 3;
let bytesPerIndex = Uint16Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
let triangleLength = bytesPerIndex * triangleElements;
const view = new DataView(buffer);
const center = new Cartesian3(
view.getFloat64(pos, true),
view.getFloat64(pos + 8, true),
view.getFloat64(pos + 16, true),
);
pos += cartesian3Length;
const minimumHeight = view.getFloat32(pos, true);
pos += Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
const maximumHeight = view.getFloat32(pos, true);
pos += Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
const boundingSphere = new BoundingSphere(
new Cartesian3(
view.getFloat64(pos, true),
view.getFloat64(pos + 8, true),
view.getFloat64(pos + 16, true),
),
view.getFloat64(pos + cartesian3Length, true),
);
pos += boundingSphereLength;
const horizonOcclusionPoint = new Cartesian3(
view.getFloat64(pos, true),
view.getFloat64(pos + 8, true),
view.getFloat64(pos + 16, true),
);
pos += cartesian3Length;
const vertexCount = view.getUint32(pos, true);
pos += Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
const encodedVertexBuffer = new Uint16Array(buffer, pos, vertexCount * 3);
pos += vertexCount * encodedVertexLength;
if (vertexCount > 64 * 1024) {
// More than 64k vertices, so indices are 32-bit.
bytesPerIndex = Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
triangleLength = bytesPerIndex * triangleElements;
}
// Decode the vertex buffer.
const uBuffer = encodedVertexBuffer.subarray(0, vertexCount);
const vBuffer = encodedVertexBuffer.subarray(vertexCount, 2 * vertexCount);
const heightBuffer = encodedVertexBuffer.subarray(
vertexCount * 2,
3 * vertexCount,
);
AttributeCompression.zigZagDeltaDecode(uBuffer, vBuffer, heightBuffer);
// skip over any additional padding that was added for 2/4 byte alignment
if (pos % bytesPerIndex !== 0) {
pos += bytesPerIndex - (pos % bytesPerIndex);
}
const triangleCount = view.getUint32(pos, true);
pos += Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
const indices = IndexDatatype.createTypedArrayFromArrayBuffer(
vertexCount,
buffer,
pos,
triangleCount * triangleElements,
);
pos += triangleCount * triangleLength;
// High water mark decoding based on decompressIndices_ in webgl-loader's loader.js.
// https://code.google.com/p/webgl-loader/source/browse/trunk/samples/loader.js?r=99#55
// Copyright 2012 Google Inc., Apache 2.0 license.
let highest = 0;
const length = indices.length;
for (let i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
const code = indices[i];
indices[i] = highest - code;
if (code === 0) {
++highest;
}
}
const westVertexCount = view.getUint32(pos, true);
pos += Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
const westIndices = IndexDatatype.createTypedArrayFromArrayBuffer(
vertexCount,
buffer,
pos,
westVertexCount,
);
pos += westVertexCount * bytesPerIndex;
const southVertexCount = view.getUint32(pos, true);
pos += Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
const southIndices = IndexDatatype.createTypedArrayFromArrayBuffer(
vertexCount,
buffer,
pos,
southVertexCount,
);
pos += southVertexCount * bytesPerIndex;
const eastVertexCount = view.getUint32(pos, true);
pos += Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
const eastIndices = IndexDatatype.createTypedArrayFromArrayBuffer(
vertexCount,
buffer,
pos,
eastVertexCount,
);
pos += eastVertexCount * bytesPerIndex;
const northVertexCount = view.getUint32(pos, true);
pos += Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
const northIndices = IndexDatatype.createTypedArrayFromArrayBuffer(
vertexCount,
buffer,
pos,
northVertexCount,
);
pos += northVertexCount * bytesPerIndex;
let encodedNormalBuffer;
let waterMaskBuffer;
while (pos < view.byteLength) {
const extensionId = view.getUint8(pos, true);
pos += Uint8Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
const extensionLength = view.getUint32(pos, littleEndianExtensionSize);
pos += Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
if (
extensionId === QuantizedMeshExtensionIds.OCT_VERTEX_NORMALS &&
provider._requestVertexNormals
) {
encodedNormalBuffer = new Uint8Array(buffer, pos, vertexCount * 2);
} else if (
extensionId === QuantizedMeshExtensionIds.WATER_MASK &&
provider._requestWaterMask
) {
waterMaskBuffer = new Uint8Array(buffer, pos, extensionLength);
} else if (
extensionId === QuantizedMeshExtensionIds.METADATA &&
provider._requestMetadata
) {
const stringLength = view.getUint32(pos, true);
if (stringLength > 0) {
const metadata = getJsonFromTypedArray(
new Uint8Array(buffer),
pos + Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT,
stringLength,
);
const availableTiles = metadata.available;
if (defined(availableTiles)) {
for (let offset = 0; offset < availableTiles.length; ++offset) {
const availableLevel = level + offset + 1;
const rangesAtLevel = availableTiles[offset];
const yTiles =
provider._tilingScheme.getNumberOfYTilesAtLevel(availableLevel);
for (
let rangeIndex = 0;
rangeIndex < rangesAtLevel.length;
++rangeIndex
) {
const range = rangesAtLevel[rangeIndex];
const yStart = yTiles - range.endY - 1;
const yEnd = yTiles - range.startY - 1;
provider.availability.addAvailableTileRange(
availableLevel,
range.startX,
yStart,
range.endX,
yEnd,
);
layer.availability.addAvailableTileRange(
availableLevel,
range.startX,
yStart,
range.endX,
yEnd,
);
}
}
}
}
layer.availabilityTilesLoaded.addAvailableTileRange(level, x, y, x, y);
}
pos += extensionLength;
}
const skirtHeight = provider.getLevelMaximumGeometricError(level) * 5.0;
// The skirt is not included in the OBB computation. If this ever
// causes any rendering artifacts (cracks), they are expected to be
// minor and in the corners of the screen. It's possible that this
// might need to be changed - just change to `minimumHeight - skirtHeight`
// A similar change might also be needed in `upsampleQuantizedTerrainMesh.js`.
const rectangle = provider._tilingScheme.tileXYToRectangle(x, y, level);
const orientedBoundingBox = OrientedBoundingBox.fromRectangle(
rectangle,
minimumHeight,
maximumHeight,
provider._tilingScheme.ellipsoid,
);
return new QuantizedMeshTerrainData({
center: center,
minimumHeight: minimumHeight,
maximumHeight: maximumHeight,
boundingSphere: boundingSphere,
orientedBoundingBox: orientedBoundingBox,
horizonOcclusionPoint: horizonOcclusionPoint,
quantizedVertices: encodedVertexBuffer,
encodedNormals: encodedNormalBuffer,
indices: indices,
westIndices: westIndices,
southIndices: southIndices,
eastIndices: eastIndices,
northIndices: northIndices,
westSkirtHeight: skirtHeight,
southSkirtHeight: skirtHeight,
eastSkirtHeight: skirtHeight,
northSkirtHeight: skirtHeight,
childTileMask: provider.availability.computeChildMaskForTile(level, x, y),
waterMask: waterMaskBuffer,
credits: provider._tileCredits,
});
}
现在可以得出结论,就是调用地形服务提供者的requestTileGeometry方法,会获得一个QuantizedMeshTerrainData类型的实例,当然因为地形数据和影像数据类似都是分块的,所以会传入分块的索引level,x,y,该索引值是Cesium自动计算的,此处我们不需要关注,我们要关注的是这个QuantizedMeshTerrainData类型的实例,因为这就是一块地形数据,我们看看该类的定义
/**
* Terrain data for a single tile where the terrain data is represented as a quantized mesh. A quantized
* mesh consists of three vertex attributes, longitude, latitude, and height. All attributes are expressed
* as 16-bit values in the range 0 to 32767. Longitude and latitude are zero at the southwest corner
* of the tile and 32767 at the northeast corner. Height is zero at the minimum height in the tile
* and 32767 at the maximum height in the tile.
*
* @alias QuantizedMeshTerrainData
* @constructor
*
* @param {object} options Object with the following properties:
* @param {Uint16Array} options.quantizedVertices The buffer containing the quantized mesh.
* @param {Uint16Array|Uint32Array} options.indices The indices specifying how the quantized vertices are linked
* together into triangles. Each three indices specifies one triangle.
* @param {number} options.minimumHeight The minimum terrain height within the tile, in meters above the ellipsoid.
* @param {number} options.maximumHeight The maximum terrain height within the tile, in meters above the ellipsoid.
* @param {BoundingSphere} options.boundingSphere A sphere bounding all of the vertices in the mesh.
* @param {OrientedBoundingBox} [options.orientedBoundingBox] An OrientedBoundingBox bounding all of the vertices in the mesh.
* @param {Cartesian3} options.horizonOcclusionPoint The horizon occlusion point of the mesh. If this point
* is below the horizon, the entire tile is assumed to be below the horizon as well.
* The point is expressed in ellipsoid-scaled coordinates.
* @param {number[]} options.westIndices The indices of the vertices on the western edge of the tile.
* @param {number[]} options.southIndices The indices of the vertices on the southern edge of the tile.
* @param {number[]} options.eastIndices The indices of the vertices on the eastern edge of the tile.
* @param {number[]} options.northIndices The indices of the vertices on the northern edge of the tile.
* @param {number} options.westSkirtHeight The height of the skirt to add on the western edge of the tile.
* @param {number} options.southSkirtHeight The height of the skirt to add on the southern edge of the tile.
* @param {number} options.eastSkirtHeight The height of the skirt to add on the eastern edge of the tile.
* @param {number} options.northSkirtHeight The height of the skirt to add on the northern edge of the tile.
* @param {number} [options.childTileMask=15] A bit mask indicating which of this tile's four children exist.
* If a child's bit is set, geometry will be requested for that tile as well when it
* is needed. If the bit is cleared, the child tile is not requested and geometry is
* instead upsampled from the parent. The bit values are as follows:
* <table>
* <tr><th>Bit Position</th><th>Bit Value</th><th>Child Tile</th></tr>
* <tr><td>0</td><td>1</td><td>Southwest</td></tr>
* <tr><td>1</td><td>2</td><td>Southeast</td></tr>
* <tr><td>2</td><td>4</td><td>Northwest</td></tr>
* <tr><td>3</td><td>8</td><td>Northeast</td></tr>
* </table>
* @param {boolean} [options.createdByUpsampling=false] True if this instance was created by upsampling another instance;
* otherwise, false.
* @param {Uint8Array} [options.encodedNormals] The buffer containing per vertex normals, encoded using 'oct' encoding
* @param {Uint8Array} [options.waterMask] The buffer containing the watermask.
* @param {Credit[]} [options.credits] Array of credits for this tile.
*
*
* @example
* const data = new Cesium.QuantizedMeshTerrainData({
* minimumHeight : -100,
* maximumHeight : 2101,
* quantizedVertices : new Uint16Array([// order is SW NW SE NE
* // longitude
* 0, 0, 32767, 32767,
* // latitude
* 0, 32767, 0, 32767,
* // heights
* 16384, 0, 32767, 16384]),
* indices : new Uint16Array([0, 3, 1,
* 0, 2, 3]),
* boundingSphere : new Cesium.BoundingSphere(new Cesium.Cartesian3(1.0, 2.0, 3.0), 10000),
* orientedBoundingBox : new Cesium.OrientedBoundingBox(new Cesium.Cartesian3(1.0, 2.0, 3.0), Cesium.Matrix3.fromRotationX(Cesium.Math.PI, new Cesium.Matrix3())),
* horizonOcclusionPoint : new Cesium.Cartesian3(3.0, 2.0, 1.0),
* westIndices : [0, 1],
* southIndices : [0, 1],
* eastIndices : [2, 3],
* northIndices : [1, 3],
* westSkirtHeight : 1.0,
* southSkirtHeight : 1.0,
* eastSkirtHeight : 1.0,
* northSkirtHeight : 1.0
* });
*
* @see TerrainData
* @see HeightmapTerrainData
* @see GoogleEarthEnterpriseTerrainData
*/
function QuantizedMeshTerrainData(options) {
//>>includeStart('debug', pragmas.debug)
if (!defined(options) || !defined(options.quantizedVertices)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.quantizedVertices is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.indices)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.indices is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.minimumHeight)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.minimumHeight is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.maximumHeight)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.maximumHeight is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.maximumHeight)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.maximumHeight is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.boundingSphere)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.boundingSphere is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.horizonOcclusionPoint)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.horizonOcclusionPoint is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.westIndices)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.westIndices is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.southIndices)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.southIndices is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.eastIndices)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.eastIndices is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.northIndices)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.northIndices is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.westSkirtHeight)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.westSkirtHeight is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.southSkirtHeight)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.southSkirtHeight is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.eastSkirtHeight)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.eastSkirtHeight is required.");
}
if (!defined(options.northSkirtHeight)) {
throw new DeveloperError("options.northSkirtHeight is required.");
}
//>>includeEnd('debug');
this._quantizedVertices = options.quantizedVertices;
this._encodedNormals = options.encodedNormals;
this._indices = options.indices;
this._minimumHeight = options.minimumHeight;
this._maximumHeight = options.maximumHeight;
this._boundingSphere = options.boundingSphere;
this._orientedBoundingBox = options.orientedBoundingBox;
this._horizonOcclusionPoint = options.horizonOcclusionPoint;
this._credits = options.credits;
const vertexCount = this._quantizedVertices.length / 3;
const uValues = (this._uValues = this._quantizedVertices.subarray(
0,
vertexCount,
));
const vValues = (this._vValues = this._quantizedVertices.subarray(
vertexCount,
2 * vertexCount,
));
this._heightValues = this._quantizedVertices.subarray(
2 * vertexCount,
3 * vertexCount,
);
// We don't assume that we can count on the edge vertices being sorted by u or v.
function sortByV(a, b) {
return vValues[a] - vValues[b];
}
function sortByU(a, b) {
return uValues[a] - uValues[b];
}
this._westIndices = sortIndicesIfNecessary(
options.westIndices,
sortByV,
vertexCount,
);
this._southIndices = sortIndicesIfNecessary(
options.southIndices,
sortByU,
vertexCount,
);
this._eastIndices = sortIndicesIfNecessary(
options.eastIndices,
sortByV,
vertexCount,
);
this._northIndices = sortIndicesIfNecessary(
options.northIndices,
sortByU,
vertexCount,
);
this._westSkirtHeight = options.westSkirtHeight;
this._southSkirtHeight = options.southSkirtHeight;
this._eastSkirtHeight = options.eastSkirtHeight;
this._northSkirtHeight = options.northSkirtHeight;
this._childTileMask = defaultValue(options.childTileMask, 15);
this._createdByUpsampling = defaultValue(options.createdByUpsampling, false);
this._waterMask = options.waterMask;
this._mesh = undefined;
}
从注释中就可以看出这是封装的一块地形瓦片的数据,重点可以看看@example说明
* @example
* const data = new Cesium.QuantizedMeshTerrainData({
* minimumHeight : -100,
* maximumHeight : 2101,
* quantizedVertices : new Uint16Array([// order is SW NW SE NE
* // longitude
* 0, 0, 32767, 32767,
* // latitude
* 0, 32767, 0, 32767,
* // heights
* 16384, 0, 32767, 16384]),
* indices : new Uint16Array([0, 3, 1,
* 0, 2, 3]),
* boundingSphere : new Cesium.BoundingSphere(new Cesium.Cartesian3(1.0, 2.0, 3.0), 10000),
* orientedBoundingBox : new Cesium.OrientedBoundingBox(new Cesium.Cartesian3(1.0, 2.0, 3.0), Cesium.Matrix3.fromRotationX(Cesium.Math.PI, new Cesium.Matrix3())),
* horizonOcclusionPoint : new Cesium.Cartesian3(3.0, 2.0, 1.0),
* westIndices : [0, 1],
* southIndices : [0, 1],
* eastIndices : [2, 3],
* northIndices : [1, 3],
* westSkirtHeight : 1.0,
* southSkirtHeight : 1.0,
* eastSkirtHeight : 1.0,
* northSkirtHeight : 1.0
* });
从该注释中看到一块地形数据大致的组织结构,quantizedVertices属性中就包含了经纬度和高程信息,当然此处并不是纯粹的(lon,lat,alt)格式的经纬度,该数组中的经纬度和高程数据的组织是有规律的。
有了上面的知识点,我们要修改地形数据就有思路了,因为地形服务提供者的requestTileGeometry方法最后会返回一个解析好的QuantizedMeshTerrainData实例,该实例中包含了某一块瓦片的地形数据,我们只要拿到该地形数据,对其进行改造,就能实现压平功能。
添加数据拦截器
要获取地形数据,我们需要改造一下地形服务提供者的requestTileGeometry方法,我们为其添加一个拦截器,就是我们先拿到这个方法的返回值,然后加以改造,最后将改造后的数据作为返回值返回,拦截器代码如下
/**
* Requests the geometry for a given tile. The result must include terrain data and
* may optionally include a water mask and an indication of which child tiles are available.
*
* @param {number} x The X coordinate of the tile for which to request geometry.
* @param {number} y The Y coordinate of the tile for which to request geometry.
* @param {number} level The level of the tile for which to request geometry.
* @param {Request} [request] The request object. Intended for internal use only.
*
* @returns {Promise<TerrainData>|undefined} A promise for the requested geometry. If this method
* returns undefined instead of a promise, it is an indication that too many requests are already
* pending and the request will be retried later.
*
*/
let requestTileGeometry = function(
x,
y,
level,
request,
) {
...
// call overridden function below
return requestTileGeometry(this, x, y, level, layerToUse, request);
};
CesiumTerrainProvider.prototype.requestTileGeometry = function(
x,
y,
level,
request,
) {
const promise = this.requestTileGeometry(
x,
y,
level,
request);
if (promise) {
return promise.then(res => {
console.log(res);
return Promise.resolve(res);
})
}
return undefined;
};
将拦截的内容打印到控制台

地形数据解析
现在我们虽然拿到了请求的地形数据结果,但是还不能直接使用,因为看不懂,虽然有数据但是不是经纬度那样的,无从下收。为了知道数据是如何使用的,我们需要跟踪一下requestTileGeometry方法,看看在哪儿调用了该方法并对该方法中返回的数据进行了使用,此处可以借助浏览器调试功能,查看方法堆栈
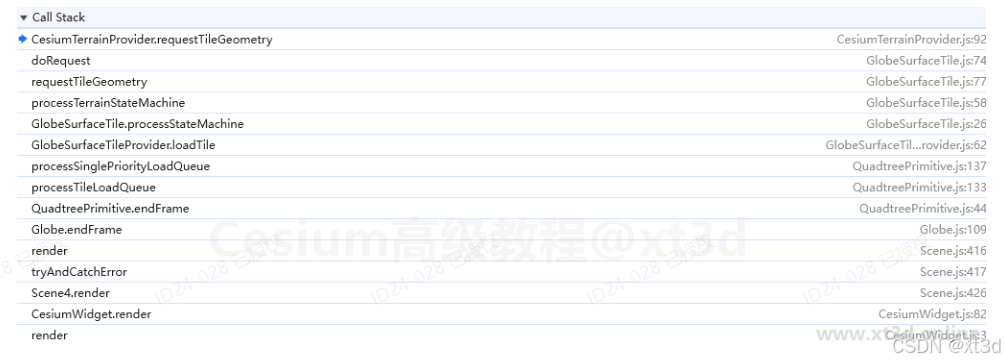
可以看到是在GlobeSurfaceTile类中调用了地形服务提供者的requestTileGeometry方法
function requestTileGeometry(surfaceTile, terrainProvider, x, y, level) {
function success(terrainData) {
if (!defined(terrainData)) {
// Throttled due to low priority - try again later.
surfaceTile.terrainState = TerrainState.UNLOADED;
surfaceTile.request = undefined;
return;
}
surfaceTile.terrainData = terrainData;
surfaceTile.terrainState = TerrainState.RECEIVED;
surfaceTile.request = undefined;
}
function failure(error) {
if (surfaceTile.request.state === RequestState.CANCELLED) {
// Cancelled due to low priority - try again later.
surfaceTile.terrainData = undefined;
surfaceTile.terrainState = TerrainState.UNLOADED;
surfaceTile.request = undefined;
return;
}
// Initially assume failure. reportError may retry, in which case the state will
// change to RECEIVING or UNLOADED.
surfaceTile.terrainState = TerrainState.FAILED;
surfaceTile.request = undefined;
const message = `Failed to obtain terrain tile X: ${x} Y: ${y} Level: ${level}. Error message: "${error}"`;
terrainProvider._requestError = TileProviderError.reportError(
terrainProvider._requestError,
terrainProvider,
terrainProvider.errorEvent,
message,
x,
y,
level,
);
if (terrainProvider._requestError.retry) {
doRequest();
}
}
function doRequest() {
// Request the terrain from the terrain provider.
const request = new Request({
throttle: false,
throttleByServer: true,
type: RequestType.TERRAIN,
});
surfaceTile.request = request;
const requestPromise = terrainProvider.requestTileGeometry(
x,
y,
level,
request,
);
// If the request method returns undefined (instead of a promise), the request
// has been deferred.
if (defined(requestPromise)) {
surfaceTile.terrainState = TerrainState.RECEIVING;
Promise.resolve(requestPromise)
.then(function (terrainData) {
success(terrainData);
})
.catch(function (e) {
failure(e);
});
} else {
// Deferred - try again later.
surfaceTile.terrainState = TerrainState.UNLOADED;
surfaceTile.request = undefined;
}
}
doRequest();
}
现在我们虽然知道了是在GlobeSurfaceTile中调用了TerrainProvider的requestTileGeometry方法,但是还是不知道数据是如何使用的,不过这里有一个重要的知识点,地形数据并不是加载完成立马就解析渲染,而是基于状态的一种管理方式,加载完成或者失败都是先标识这块数据的一个状态,当渲染时根据这个状态来决定是否加入渲染队列。
代码中还有一个关键信息,那就是将数据设置给了surfaceTile
surfaceTile.terrainData = terrainData;
surfaceTile.terrainState = TerrainState.RECEIVED;
surfaceTile.request = undefined;
我们试着全局搜索一下surfaceTile.terrainData,搜索结果如下图是所示,结果项很少,可以一个个点开看看

可以看到GlobeSurfaceTile类中有一个方法内部使用了这个数据,并且从方法的名称就可以看出是根据这个数据构建Mesh。
function transform(surfaceTile, frameState, terrainProvider, x, y, level) {
const tilingScheme = terrainProvider.tilingScheme;
const createMeshOptions = scratchCreateMeshOptions;
createMeshOptions.tilingScheme = tilingScheme;
createMeshOptions.x = x;
createMeshOptions.y = y;
createMeshOptions.level = level;
createMeshOptions.exaggeration = frameState.verticalExaggeration;
createMeshOptions.exaggerationRelativeHeight =
frameState.verticalExaggerationRelativeHeight;
createMeshOptions.throttle = true;
const terrainData = surfaceTile.terrainData;
const meshPromise = terrainData.createMesh(createMeshOptions);
if (!defined(meshPromise)) {
// Postponed.
return;
}
surfaceTile.terrainState = TerrainState.TRANSFORMING;
Promise.resolve(meshPromise)
.then(function (mesh) {
surfaceTile.mesh = mesh;
surfaceTile.terrainState = TerrainState.TRANSFORMED;
})
.catch(function () {
surfaceTile.terrainState = TerrainState.FAILED;
});
}
进入到构建Mesh的方法内
QuantizedMeshTerrainData.prototype.createMesh = function (options) {
...
const verticesPromise = createMeshTaskProcessor.scheduleTask({
minimumHeight: this._minimumHeight,
maximumHeight: this._maximumHeight,
quantizedVertices: this._quantizedVertices,
octEncodedNormals: this._encodedNormals,
includeWebMercatorT: true,
indices: this._indices,
westIndices: this._westIndices,
southIndices: this._southIndices,
eastIndices: this._eastIndices,
northIndices: this._northIndices,
westSkirtHeight: this._westSkirtHeight,
southSkirtHeight: this._southSkirtHeight,
eastSkirtHeight: this._eastSkirtHeight,
northSkirtHeight: this._northSkirtHeight,
rectangle: rectangle,
relativeToCenter: this._boundingSphere.center,
ellipsoid: ellipsoid,
exaggeration: exaggeration,
exaggerationRelativeHeight: exaggerationRelativeHeight,
});
if (!defined(verticesPromise)) {
// Postponed
return undefined;
}
const that = this;
return Promise.resolve(verticesPromise).then(function (result) {
const vertexCountWithoutSkirts = that._quantizedVertices.length / 3;
const vertexCount =
vertexCountWithoutSkirts +
that._westIndices.length +
that._southIndices.length +
that._eastIndices.length +
that._northIndices.length;
const indicesTypedArray = IndexDatatype.createTypedArray(
vertexCount,
result.indices,
);
const vertices = new Float32Array(result.vertices);
const rtc = result.center;
const minimumHeight = result.minimumHeight;
const maximumHeight = result.maximumHeight;
const boundingSphere = that._boundingSphere;
const obb = that._orientedBoundingBox;
const occludeePointInScaledSpace = defaultValue(
Cartesian3.clone(result.occludeePointInScaledSpace),
that._horizonOcclusionPoint,
);
const stride = result.vertexStride;
const terrainEncoding = TerrainEncoding.clone(result.encoding);
// Clone complex result objects because the transfer from the web worker
// has stripped them down to JSON-style objects.
that._mesh = new TerrainMesh(
rtc,
vertices,
indicesTypedArray,
result.indexCountWithoutSkirts,
vertexCountWithoutSkirts,
minimumHeight,
maximumHeight,
boundingSphere,
occludeePointInScaledSpace,
stride,
obb,
terrainEncoding,
result.westIndicesSouthToNorth,
result.southIndicesEastToWest,
result.eastIndicesNorthToSouth,
result.northIndicesWestToEast,
);
// Free memory received from server after mesh is created.
that._quantizedVertices = undefined;
that._encodedNormals = undefined;
that._indices = undefined;
that._uValues = undefined;
that._vValues = undefined;
that._heightValues = undefined;
that._westIndices = undefined;
that._southIndices = undefined;
that._eastIndices = undefined;
that._northIndices = undefined;
return that._mesh;
});
};
会看到这里使用了WebWork来对数据进行解析,所以需要找到对应的WebWork内容,您可以在Workers文件夹下找到对应的文件
function createVerticesFromQuantizedTerrainMesh(
parameters,
transferableObjects,
) {
const quantizedVertices = parameters.quantizedVertices;
const quantizedVertexCount = quantizedVertices.length / 3;
const octEncodedNormals = parameters.octEncodedNormals;
const edgeVertexCount =
parameters.westIndices.length +
parameters.eastIndices.length +
parameters.southIndices.length +
parameters.northIndices.length;
const includeWebMercatorT = parameters.includeWebMercatorT;
const exaggeration = parameters.exaggeration;
const exaggerationRelativeHeight = parameters.exaggerationRelativeHeight;
const hasExaggeration = exaggeration !== 1.0;
const includeGeodeticSurfaceNormals = hasExaggeration;
const rectangle = Rectangle.clone(parameters.rectangle);
const west = rectangle.west;
const south = rectangle.south;
const east = rectangle.east;
const north = rectangle.north;
const ellipsoid = Ellipsoid.clone(parameters.ellipsoid);
const minimumHeight = parameters.minimumHeight;
const maximumHeight = parameters.maximumHeight;
const center = parameters.relativeToCenter;
const fromENU = Transforms.eastNorthUpToFixedFrame(center, ellipsoid);
const toENU = Matrix4.inverseTransformation(fromENU, new Matrix4());
...
const uBuffer = quantizedVertices.subarray(0, quantizedVertexCount);
const vBuffer = quantizedVertices.subarray(
quantizedVertexCount,
2 * quantizedVertexCount,
);
const heightBuffer = quantizedVertices.subarray(
quantizedVertexCount * 2,
3 * quantizedVertexCount,
);
const hasVertexNormals = defined(octEncodedNormals);
const uvs = new Array(quantizedVertexCount);
const heights = new Array(quantizedVertexCount);
const positions = new Array(quantizedVertexCount);
const webMercatorTs = includeWebMercatorT
? new Array(quantizedVertexCount)
: [];
const geodeticSurfaceNormals = includeGeodeticSurfaceNormals
? new Array(quantizedVertexCount)
: [];
const minimum = scratchMinimum;
minimum.x = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
minimum.y = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
minimum.z = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
const maximum = scratchMaximum;
maximum.x = Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
maximum.y = Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
maximum.z = Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
let minLongitude = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
let maxLongitude = Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
let minLatitude = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
let maxLatitude = Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
for (let i = 0; i < quantizedVertexCount; ++i) {
const rawU = uBuffer[i];
const rawV = vBuffer[i];
const u = rawU / maxShort;
const v = rawV / maxShort;
const height = CesiumMath.lerp(
minimumHeight,
maximumHeight,
heightBuffer[i] / maxShort,
);
cartographicScratch.longitude = CesiumMath.lerp(west, east, u);
cartographicScratch.latitude = CesiumMath.lerp(south, north, v);
cartographicScratch.height = height;
minLongitude = Math.min(cartographicScratch.longitude, minLongitude);
maxLongitude = Math.max(cartographicScratch.longitude, maxLongitude);
minLatitude = Math.min(cartographicScratch.latitude, minLatitude);
maxLatitude = Math.max(cartographicScratch.latitude, maxLatitude);
const position = ellipsoid.cartographicToCartesian(cartographicScratch);
uvs[i] = new Cartesian2(u, v);
heights[i] = height;
positions[i] = position;
if (includeWebMercatorT) {
webMercatorTs[i] =
(WebMercatorProjection.geodeticLatitudeToMercatorAngle(
cartographicScratch.latitude,
) -
southMercatorY) *
oneOverMercatorHeight;
}
if (includeGeodeticSurfaceNormals) {
geodeticSurfaceNormals[i] = ellipsoid.geodeticSurfaceNormal(position);
}
Matrix4.multiplyByPoint(toENU, position, cartesian3Scratch);
Cartesian3.minimumByComponent(cartesian3Scratch, minimum, minimum);
Cartesian3.maximumByComponent(cartesian3Scratch, maximum, maximum);
}
...
}
这里面就有如何将地形数据转换为经纬度的相关算法,到此所有工作已经准备完成。我们已经知道如何获取地形数据,如何解析地形数据,接下来就只差如何修改地形数据这一关键一步了。
修改地形数据
首先在拦截器中解析地形数据,将其转为能够看得懂的经纬坐标
const tileRectangle = this.tilingScheme.tileXYToRectangle(x, y, level);
const data = terrainData;
const minimumHeight = data._minimumHeight;
const maximumHeight = data._maximumHeight;
const quantizedVertices = data._quantizedVertices;
const vertexCount = quantizedVertices.length / 3;
const positions = [];
for (let i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
const rawU = quantizedVertices[i];
const rawV = quantizedVertices[i + vertexCount];
const rawH = quantizedVertices[i + vertexCount * 2];
const u = rawU / MAX_SHORT;
const v = rawV / MAX_SHORT;
const longitude = Cesium.Math.toDegrees(Cesium.Math.lerp(tileRectangle.west, tileRectangle.east, u));
const latitude = Cesium.Math.toDegrees(Cesium.Math.lerp(tileRectangle.south, tileRectangle.north, v));
let height = Cesium.Math.lerp(minimumHeight, maximumHeight, rawH / MAX_SHORT);
positions.push([longitude, latitude, height]);
}

有了经纬度数据就可以进行关系的判断了,如果点在范围内就修改高度,判断关系参考前面通过修改着色器的方式,这里的难点在于修改范围内坐标的高度值后如何更新到地形数据里面去,其实只需要遵循如何取就如何存的原则就简单了。
let positions = [];
for (let i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
const rawU = quantizedVertices[i];
const rawV = quantizedVertices[i + vertexCount];
const rawH = quantizedVertices[i + vertexCount * 2];
const u = rawU / MAX_SHORT;
const v = rawV / MAX_SHORT;
const longitude = Cesium.Math.toDegrees(Cesium.Math.lerp(tileRectangle.west, tileRectangle.east, u));
const latitude = Cesium.Math.toDegrees(Cesium.Math.lerp(tileRectangle.south, tileRectangle.north, v));
let height = Cesium.Math.lerp(minimumHeight, maximumHeight, rawH / MAX_SHORT);
//在多边形内就修改高度值
let p=Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(longitude,latitude,0);
p=Cesium.Matrix4.multiplyByPoint(inverse,p,p);
if(p.x >= rect.x && p.x <= rect.z && p.y >= rect.y && p.y <= rect.w){
height=this.flattenHeight;
}
positions.push([longitude, latitude, height]);
}
const heights = positions.map(p => p[2]);
const newMinHeight = Math.min(...heights);
const newMaxHeight = Math.max(...heights);
const newQuantizedVertices = new Uint16Array(positions.length * 3);
positions.forEach((p, i) => {
const lonRad = Cesium.Math.toRadians(p[0]);
...
});
data._minimumHeight = newMinHeight;
data._maximumHeight = newMaxHeight;
data._quantizedVertices = newQuantizedVertices;
return Promise.resolve(data);

示例效果可到 xt3d 官网 运行查看
更多内容见 Cesium高级教程-教程简介

























 1729
1729

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










