缓动函数 Easing Functions
缓动函数 自定义参数随时间变化的速率。
常见效果
Linear:无缓动效果;
Quadratic:二次方的缓动(t^2);
Sinusoidal:正弦曲线的缓动(sin(t));
Exponential:指数曲线的缓动(2^t);
Circular:圆形曲线的缓动(sqrt(1-t^2));
Cubic:三次方的缓动(t^3);
Quartic:四次方的缓动(t^4);
Quintic:五次方的缓动(t^5);
Elastic:指数衰减的正弦曲线缓动;
Back:超过范围的三次方缓动((s+1)t^3 - st^2);
Bounce:指数衰减的反弹缓动。
缓动方式
每个效果都分三个缓动方式(方法),分别是:
easeIn:从0开始加速的缓动;
easeOut:减速到0的缓动;
easeInOut:前半段从0开始加速,后半段减速到0的缓动。
具体如图所示:

函数参数说明
每个函数包含 t、b、c 和 d 四个参数
- t = Time - 表示动画开始以来经过的时间。通常从0开始,通过游戏循环或update函数来缓慢增加。
- b = Beginning value - 动画的起点,默认从0开始。
- c = Change in value - 从起点到终点的差值。
- d = Duration - 完成动画所需的时间。
使用示例
t = 0 - 动画从0s开始
b = 200 - 对象 x 坐标的起始位置为200
c = 300 - 对象必须向右移动 300,到500 结束
d = 1 - 对象用 1 秒时间来完成从 200 到 500 的移动
Linear 线性
function easeLinear (t, b, c, d) {
return c * t / d + b;
}
Quadratic 二次渐变

Quadratic easing in
function easeInQuad (t, b, c, d) {
return c * (t /= d) * t + b;
}
Quadratic easing out
function easeOutQuad (t, b, c, d) {
return -c * (t /= d) * (t - 2) + b;
}
Quadratic easing in and out
function easeInOutQuad (t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t + b;
return -c / 2 * ((--t) * (t - 2) - 1) + b;
}
Sinusoidal 正弦渐变
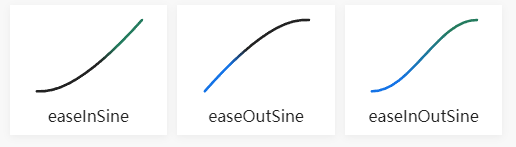
Sinusoidal easing in
function easeInSine (t, b, c, d) {
return -c * Math.cos(t / d * (Math.PI / 2)) + c + b;
}
Sinusoidal easing out
function easeOutSine (t, b, c, d) {
return c * Math.sin(t / d * (Math.PI / 2)) + b;
}
Sinusoidal easing in and out
function easeInOutSine (t, b, c, d) {
return -c / 2 * (Math.cos(Math.PI * t / d) - 1) + b;
}
Exponential 指数渐变

Exponential easing in
function easeInExpo (t, b, c, d) {
return (t == 0) ? b : c * Math.pow(2, 10 * (t / d - 1)) + b;
}
Exponential easing out
function easeOutExpo (t, b, c, d) {
return (t == d) ? b + c : c * (-Math.pow(2, -10 * t / d) + 1) + b;
}
Exponential easing in and out
function easeInOutExpo (t, b, c, d) {
if (t == 0) return b;
if (t == d) return b + c;
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * Math.pow(2, 10 * (t - 1)) + b;
return c / 2 * (-Math.pow(2, -10 * --t) + 2) + b;
}
Circular 圆形曲线

Circular easing in
function easeInCirc (t, b, c, d) {
return -c * (Math.sqrt(1 - (t /= d) * t) - 1) + b;
}
Circular easing out
function easeOutCirc (t, b, c, d) {
return c * Math.sqrt(1 - (t = t / d - 1) * t) + b;
}
Circular easing in and out
function easeInOutCirc (t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return -c / 2 * (Math.sqrt(1 - t * t) - 1) + b;
return c / 2 * (Math.sqrt(1 - (t -= 2) * t) + 1) + b;
}
Cubic 三次方

Cubic easing in
function easeInCubic (t, b, c, d) {
return c * (t /= d) * t * t + b;
}
Cubic easing out
function easeOutCubic (t, b, c, d) {
return c * ((t = t / d - 1) * t * t + 1) + b;
}
Cubic easing in and out
function easeInOutCubic (t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t * t + b;
return c / 2 * ((t -= 2) * t * t + 2) + b;
}
Quartic 四次方

Quartic easing in
function easeInQuart (t, b, c, d) {
return c * (t /= d) * t * t * t + b;
}
Quartic easing out
function easeOutQuart (t, b, c, d) {
return -c * ((t = t / d - 1) * t * t * t - 1) + b;
}
Quartic easing in and out
function easeInOutQuart (t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t * t * t + b;
return -c / 2 * ((t -= 2) * t * t * t - 2) + b;
}
Quintic 五次方

Quintic easing in
function easeInQuint (t, b, c, d) {
return c * (t /= d) * t * t * t * t + b;
}
Quintic easing out
function easeOutQuint (t, b, c, d) {
return c * ((t = t / d - 1) * t * t * t * t + 1) + b;
}
Quintic easing in and out
function easeInOutQuint (t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t * t * t * t + b;
return c / 2 * ((t -= 2) * t * t * t * t + 2) + b;
}
Elastic 指数衰减正弦曲线

Elastic easing in
function easeInElastic (t, b, c, d) {
var s = 1.70158;
var p = 0;
var a = c;
if (t == 0) return b;
if ((t /= d) == 1) return b + c;
if (!p) p = d * .3;
if (a < Math.abs(c)) {
a = c;
var s = p / 4;
}
else var s = p / (2 * Math.PI) * Math.asin(c / a);
return -(a * Math.pow(2, 10 * (t -= 1)) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p)) + b;
}
Elastic easing out
function easeOutElastic (t, b, c, d) {
var s = 1.70158;
var p = 0;
var a = c;
if (t == 0) return b;
if ((t /= d) == 1) return b + c;
if (!p) p = d * .3;
if (a < Math.abs(c)) {
a = c;
var s = p / 4;
}
else var s = p / (2 * Math.PI) * Math.asin(c / a);
return a * Math.pow(2, -10 * t) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p) + c + b;
}
Elastic easing in and out
function easeInOutElastic (t, b, c, d) {
var s = 1.70158;
var p = 0;
var a = c;
if (t == 0) return b;
if ((t /= d / 2) == 2) return b + c;
if (!p) p = d * (.3 * 1.5);
if (a < Math.abs(c)) {
a = c;
var s = p / 4;
}
else var s = p / (2 * Math.PI) * Math.asin(c / a);
if (t < 1) return -.5 * (a * Math.pow(2, 10 * (t -= 1)) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p)) + b;
return a * Math.pow(2, -10 * (t -= 1)) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p) * .5 + c + b;
}
Back

Back easing in
function easeInBack (t, b, c, d) {
if (s == undefined) s = 1.70158;
return c * (t /= d) * t * ((s + 1) * t - s) + b;
}
Back easing out
function easeOutBack (t, b, c, d) {
if (s == undefined) s = 1.70158;
return c * ((t = t / d - 1) * t * ((s + 1) * t + s) + 1) + b;
}
Back easing in and out
function easeInOutBack (t, b, c, d) {
if (s == undefined) s = 1.70158;
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * (t * t * (((s *= (1.525)) + 1) * t - s)) + b;
return c / 2 * ((t -= 2) * t * (((s *= (1.525)) + 1) * t + s) + 2) + b;
}
Bounce
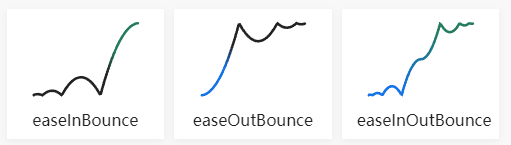
Bounce easing in
function easeInBounce(t, b, c, d) {
return c - easeOutBounce(d - t, 0, c, d) + b;
}
Bounce easing out
function easeOutBounce(t, b, c, d) {
if ((t/=d) < (1/2.75)) {
return c*(7.5625*t*t) + b;
} else if (t < (2/2.75)) {
return c*(7.5625*(t-=(1.5/2.75))*t + .75) + b;
} else if (t < (2.5/2.75)) {
return c*(7.5625*(t-=(2.25/2.75))*t + .9375) + b;
} else {
return c*(7.5625*(t-=(2.625/2.75))*t + .984375) + b;
}
}
Bounce easing in and out
function easeInOutBounce(t, b, c, d) {
if (t < d/2) return easeInBounce (t*2, 0, c, d) * .5 + b;
return easeOutBounce (t*2-d, 0, c, d) * .5 + c*.5 + b;
}


























 794
794

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








