4. 随机梯度下降
梯度
- 导数 (标量)
- 偏微分 (函数延某个方向的变换量 标量)
- 梯度 (函数变化量最大的方向 向量)
梯度的意义:模为变换率大小,矢量方向。
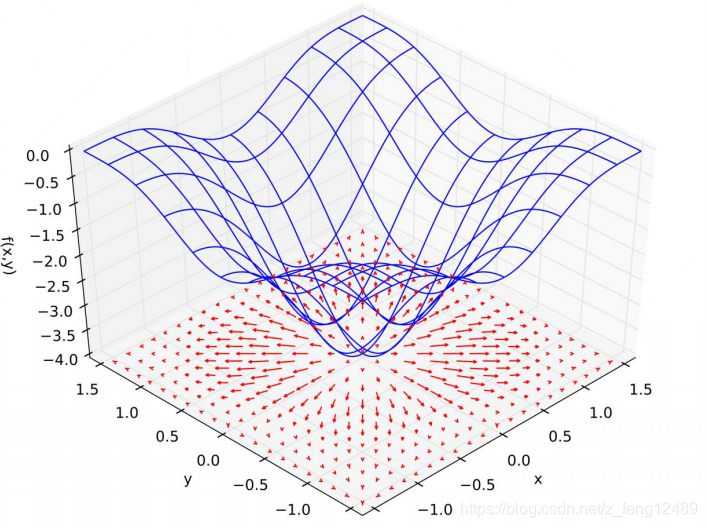
如何求取最小值:梯度下降
θ
t
+
1
=
θ
t
−
α
t
∇
f
(
θ
t
)
\theta_{t+1} = \theta_t-\alpha_t\nabla f(\theta_t)
θt+1=θt−αt∇f(θt)

影响优化器优化精度的两个重要因素:
- 局部极小值
- 鞍点
凸函数才会有全局最小值,通常情况下存在局部极小值。
(ResNet-56 论文-2018 何凯明)

影响优化器搜索过程效果的因素:
- 初始化状态
- 学习率
- 动量(逃离局部极小值)
- …
常见函数的梯度
| 函数类型 | 函数 | 导数 |
|---|---|---|
| 常函数 | c | 0 |
| 线性函数 | ax | a |
| 二次函数 | a x 2 ax^2 ax2 | 2ax |
| 幂函数 | x a x^a xa | a x a − 1 ax^{a-1} axa−1 |
| 指数函数 | a x a^x ax | a x l n a a^xlna axlna |
| 指数函数 | e x e^x ex | e x e^x ex |
| 对数函数 | l o g a ( x ) log_a(x) loga(x) | 1 / ( x l n a ) 1/(xlna) 1/(xlna) |
| 对数函数 | lnx | 1/x |
| 三角函数 | sin(x) | cos(x) |
| 三角函数 | cos(x) | sin(x) |
| 三角函数 | tan(x) | sec(x) |
激活函数
- Sigmoid/Logistic 会伴随严重的梯度弥散现象(长时间梯度的不到更新)。
f ( x ) = σ ( x ) = 1 1 + e − x [ 0 , 1 ] f(x)=\sigma(x)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}~~~~~[0,1] f(x)=σ(x)=1+e−x1 [0,1]

求导:

z = torch.linspace(-100,100,5)
z #tensor([-100., -50., 0., 50., 100.])
torch.sigmoid(z) #tensor([0.00e+00, 1.92e-22, 5.00e-01, 1.00e+00, 1.00e+00])
- tanh 常用于循环神经网络
f ( x ) = t a n h ( x ) = e x − e − x e x + e − x = 2 s i g m o i d ( 2 x ) − 1 [ − 1 , 1 ] f(x)=tanh(x)=\frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}}=2sigmoid(2x)-1~~~[-1,1] f(x)=tanh(x)=ex+e−xex−e−x=2sigmoid(2x)−1 [−1,1]

求导:
d d x t a n h ( x ) = 1 − t a n h 2 ( x ) \frac{d}{dx}tanh(x)=1-tanh^2(x) dxdtanh(x)=1−tanh2(x)
z = torch.linspace(-2, 2, 5)
z #tensor([-2., -1., 0., 1., 2.])
torch.tanh(z) #tensor([-0.9640, -0.7616, 0.0000, 0.7616, 0.9640])
- ReLu Rectified Linear Unit 整形的线性单元 (最常用的激活函数)


z = torch.linspace(-2, 2, 5)
z #tensor([-2., -1., 0., 1., 2.])
torch.relu(z) #tensor([0., 0., 0., 1., 2.])
Loss 损失函数的梯度
典型的损失函数:
- Mean Squared Error(均方误差)
- Cross Entropy Loss(交叉熵损失)
- 可用于二分类
- 可扩展为多分类
- 常与 softmax 函数搭配使用
- Mean Squared Error( 均 方 误 差 )
-
l
o
s
s
=
∑
(
y
−
(
w
∗
x
+
b
)
)
2
loss = \sum\big(y-(w*x+b)\big)^2
loss=∑(y−(w∗x+b))2
l o s s = n o r m ( y − ( w ∗ x + b ) ) 2 loss = norm\big(y-(w*x+b)\big)^2 loss=norm(y−(w∗x+b))2 - ∇ l o s s ∇ θ = 2 ∑ ( y − f θ ( x ) ) ∗ ∇ f θ ( x ) ∇ θ \frac{\nabla loss}{\nabla \theta} = 2\sum \big(y-f_\theta(x)\big)*\frac{\nabla f_\theta(x)}{\nabla \theta} ∇θ∇loss=2∑(y−fθ(x))∗∇θ∇fθ(x)
- Gradient API:
-
l
o
s
s
=
∑
(
y
−
(
w
∗
x
+
b
)
)
2
loss = \sum\big(y-(w*x+b)\big)^2
loss=∑(y−(w∗x+b))2
1.torch.autograd.grad(loss, [w1, w2, ...])
[w1 grad, w2 grad, ...]
2.loss.backward()
w1.grad
w2.grad
...
#Mean Square Error (MSE)
x = torch.ones(1)
y = torch.ones(1)
w = torch.full([1], 2, requires_grad=True)
mse = F.mse_loss(y,w*x) #(y-w*x)
mse #tensor(1., grad_fn=<MeanBackward1>)
#1.auto.grad (requires_grad)
torch.autograd.grad(mse, w) #(tensor([2.]),)
#2.backward
mse = F.mse_loss(y,w*x) #(y-w*x)
mse.backward()
w.grad #tensor([2.])
-
Cross Entropy Loss( 交 叉 熵 损 失)
-
Softmax
p i = e a i ∑ k = 1 N e a k p_i=\frac{e^{a_i}}{\sum_{k=1}^{N}e^{a_k}} pi=∑k=1Neakeai

- 转移成概率值
- 拉大值之间的差距
Softmax 求导:

得到:


∂
p
i
∂
a
j
=
p
i
(
δ
i
j
−
p
j
)
\frac{\partial p_i}{\partial a_j}=p_i(\delta_{ij}-p_j)
∂aj∂pi=pi(δij−pj)
from torch.nn import functional as F
a = torch.rand(3, requires_grad=True)
p = F.softmax(a, dim=0)
a #tensor([0.4588, 0.0768, 0.0897], requires_grad=True)
p #tensor([0.4212, 0.2875, 0.2912], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward>)
torch.autograd.grad(p[0], a, retain_graph=True) #output scalar
#(tensor([ 0.2438, -0.1211, -0.1227]),)

























 1331
1331











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










