1.连续状态马尔科夫链
我们默认本文中的马尔科夫链都是离散时间的。通常,我们所见到的马尔科夫链是离散状态的,但是为了能够模拟出连续随机变量的样本,我们必须引入连续状态马尔科夫链。通常,一个马尔科夫链由初始分布和状态转移矩阵来决定,相似的,连续状态马尔科夫链也是由这两个因素构成,只不过状态转移矩阵没办法来描述连续状态,我们再次引入转移核的概念,转移矩阵描述的是条件概率,同样,转移核描述的是条件概率,假设在
t
时刻状态值为
通常写成 ∫AK(xt,dxt+1) ,表示t+1时刻状态为A的条件概率。
同样,引出给定初始状态 x0 ,不同时刻状态的联合分布为
这和离散状态是相似的。
同样给出chapman-Kolmogorov 方程.目的就是给出n阶转移核,和离散状态n阶转移矩阵相似。For every (m,n) ∈ N2 ,
最后我们给出连续状态马尔科夫链的平稳分布和 detailed balance condition 的关系,这和MCMC联系紧密。
平稳分布. 不同时刻的状态分布相同,都为 π ,这个 π 就是平稳分布
detailed balance condition. 一个马尔科夫链,其转移核为K满足detailed balanced condition,即存在函数 f(x)
对每一个 (x,y) 成立
如何一个概率密度函数π使得马尔科夫链的转移核满足
detailedbalancedcondition ,
那么这个概率密度函数π就是该马尔科夫链的平稳分布。
(靠,写了半天,只有这个有用。。,但是。。还没完,我靠了。。。不写了,不是很影响,在下面的metropolis-hastings算法中,我会说明如何构造相关的量的)
2.MCMC method for simulation.
引用monte carlo statistical method【点这里】中的定义7.1.
Markov chain Monte Carlo method for the simulation of distribution
f
is ay method producing an ergodic markov chain (
Given
x(t)
,
1.Generate
Yt∼q(y|x(t)).
2.Take
X(t+1)=Yt
with probability
ρ(x(t),Yt)
X(t+1)=X(t)
with probability 1-
ρ(x(t),Yt)
where
ρ(x,y)=min{f(y)f(x)q(x|y)q(y|x),1}
the distribution q is called the instrumental distribution and the probability
ρ(x,y)
the metropolis-hastings acceptance proability.
结论:如果算法中的
q(y|x)
满足如下两个条件
那么如果 h∈L1(f) ,那么
μ 是初始状态分布。
4.gibbs抽样.
如果我们已知 X=x1,x2,...,xD 的联合分布 f(X) ,我们想要得到 X 的样本,我们可以用gibbs抽样的方法来得到关于
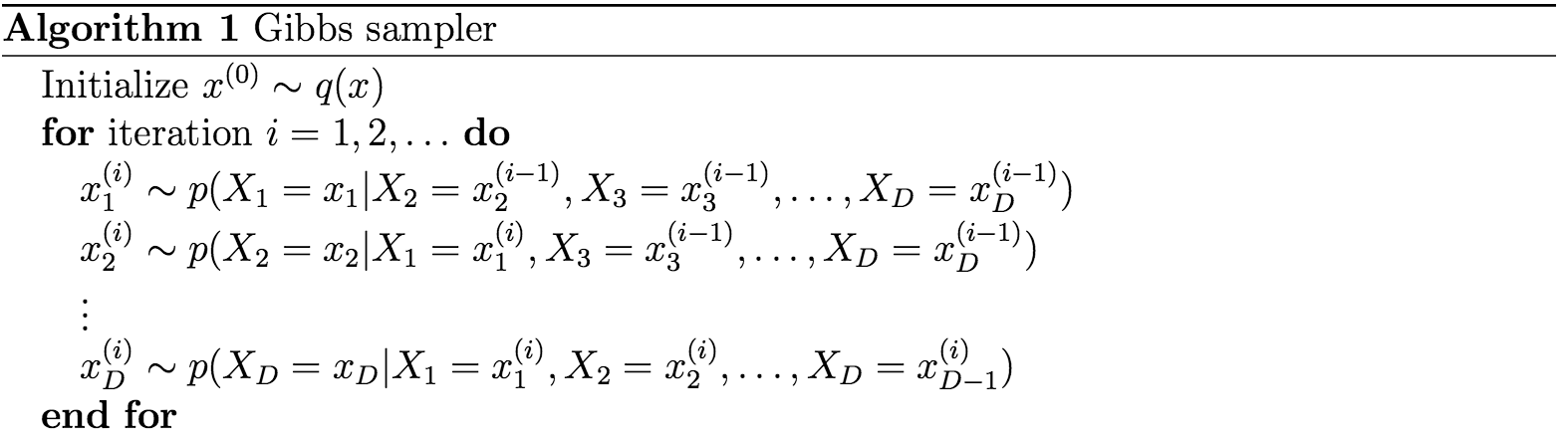
关键在于条件分布的抽样确定
我们可以用下式来
p(X1=x1|X2=x(i−1)2,...,XD=x(i−1)D)=p(X1=x1,X2=x(i−1)2,...XD=x(i−1)D)p(X2=xi−12,...,XD=x(i−1)D)
上式的右边的分母是一个标准化的东西,跟 X1 无关,所以这个条件分布是和 p(X1=x1,X2=x(i−1)2,...XD=x(i−1)D) 呈正比,所以,我们在对这个条件概率抽样的时候,是可以不用担心分布这一项的,抽样是不会用到这一项的










 本文介绍了连续状态马尔科夫链的基本概念及其转移核的定义,并探讨了平稳分布与详细平衡条件之间的关系。此外,还讨论了MCMC方法在模拟分布中的应用,包括Metropolis-Hastings算法和Gibbs抽样方法。
本文介绍了连续状态马尔科夫链的基本概念及其转移核的定义,并探讨了平稳分布与详细平衡条件之间的关系。此外,还讨论了MCMC方法在模拟分布中的应用,包括Metropolis-Hastings算法和Gibbs抽样方法。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








