原创文章,转载请注明:转载自 周岳飞博客(http://zhou-yuefei.iteye.com/)
Spark streaming 程序的运行过程是将DStream的操作转化成RDD的操作,Spark Streaming 和 Spark Core 的关系如下图(图片来自spark官网)
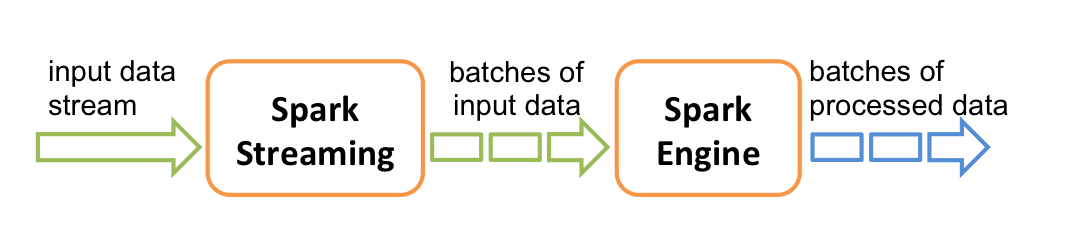

Spark Streaming 会按照程序设定的时间间隔不断动态生成Job来处理输入数据,这里的Job生成是指将Spark Streaming 的程序翻译成Spark内核的RDD操作,翻译的过程并不会触发Job的运行,Spark Streaming 会将翻译的处理逻辑封装在Job对象中,最后会将Job提交到集群上运行。这就是Spark Streaming 运行的基本过程。下面详细介绍Job动态生成和提交过程。
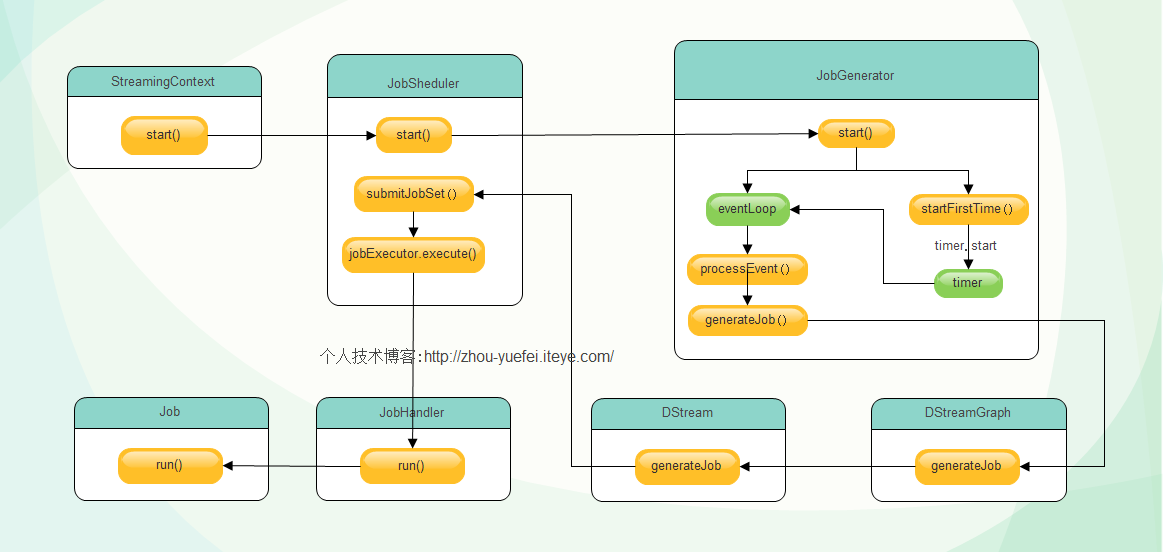
首先,当SparkStreaming的start方法调用后,整个Spark Streaming 程序开始运行,按照指定的时间间隔生成Job并提交给集群运行,在生成Job的工程中主要核心对象有
1.JobScheduler
2.JobGenerator
3.DStreamGraph
4.DStream
其中,
JobScheduler
负责启动
JobGenerator生成Job,并提交生成的Job到集群运行,这里的Job不是在spark core 中提到的job,它只是作业运行的代码模板,是逻辑级别的,可以类比java线程中的Runnable接口实现,不是真正运行的作业,
它封装了由DStream转化而来的RDD操作.JobGenerator负责定时调用
DStreamingGraph的generateJob方法生成Job和清理Dstream的元数据,
DStreamGraph持有构成DStream图的所有DStream对象,并调用
DStream的generateJob方法生成具体Job对象.DStream生成最终的Job交给
JobScheduler
调度执行。整体过程如下图所示:

下面结合源码分析每一步过程 (源码中黄色背景部分为核心逻辑代码,例如 :
scheduler
.start()
) :
首先,StreamingContext起动时调用start方法
try{
validate()
// Start the streaming scheduler in a new thread, so that thread local properties
// like call sites and job groups can be reset without affecting those of the
// current thread.
ThreadUtils.runInNewThread("streaming-start"){
sparkContext.setCallSite(startSite.get)
sparkContext.clearJobGroup()
sparkContext.setLocalProperty(SparkContext.SPARK_JOB_INTERRUPT_ON_CANCEL,"false")
savedProperties.set(SerializationUtils.clone(
sparkContext.localProperties.get()).asInstanceOf[Properties])
scheduler.start()
}
state =StreamingContextState.ACTIVE
}catch{
caseNonFatal(e)=>
logError("Error starting the context, marking it as stopped", e)
scheduler.stop(false)
state =StreamingContextState.STOPPED
throw e
}
其中调用了scheduler的start方法,此处的scheduler 就是
org.apache.spark.streaming.scheduler.JobScheduler
对象,
StreamingContext持有
org.apache.spark.streaming.scheduler.JobScheduler
对象的引用。
下面看一下
JobScheduler的start方法:
eventLoop =newEventLoop[JobSchedulerEvent]("JobScheduler"){
override protected def onReceive(event:JobSchedulerEvent):Unit= processEvent(event)
override protected def onError(e:Throwable):Unit= reportError("Error in job scheduler", e)
}
eventLoop.start()
// attach rate controllers of input streams to receive batch completion updates
for{
inputDStream <- ssc.graph.getInputStreams
rateController <- inputDStream.rateController
} ssc.addStreamingListener(rateController)
listenerBus.start()
receiverTracker =newReceiverTracker(ssc)
inputInfoTracker =newInputInfoTracker(ssc)
executorAllocationManager =ExecutorAllocationManager.createIfEnabled(
ssc.sparkContext,
receiverTracker,
ssc.conf,
ssc.graph.batchDuration.milliseconds,
clock)
executorAllocationManager.foreach(ssc.addStreamingListener)
receiverTracker.start()
jobGenerator.start()
executorAllocationManager.foreach(_.start())
logInfo("Started JobScheduler")
可以看到
JobScheduler调用了
jobGenerator的start方法和
eventLoop的start方法,eventLoop用来接收
JobSchedulerEvent消息,并交给
processEvent函数进行处理
代码如下:
private def processEvent(event:JobSchedulerEvent){
try{
event match {
caseJobStarted(job, startTime)=> handleJobStart(job, startTime)
caseJobCompleted(job, completedTime)=> handleJobCompletion(job, completedTime)
caseErrorReported(m, e)=> handleError(m, e)
}
}catch{
case e:Throwable=>
reportError("Error in job scheduler", e)
}
}
可以看到
JobScheduler中的eventLoop只处理JobStarted,JobCompleted和ErrorReported 三类消息,这三类消息的处理不是Job动态生成的核心逻辑代码先略过,(注意:后面
JobGenerator中也有个eventLoop不要和这里的eventLoop混淆。)
JobGenerator的start方法首先new了一个EventLoop对象eventLoop,并复
写onReceive(),将收到的JobGeneratorEvent 消息交给 processEvent 方法处理.源码如下:
/** Start generation of jobs */ def start(): Unit = synchronized { if (eventLoop != null) return // generator has already been started // Call checkpointWriter here to initialize it before eventLoop uses it to avoid a deadlock. // See SPARK-10125 checkpointWriter eventLoop = new EventLoop[JobGeneratorEvent]("JobGenerator") { override protected def onReceive(event: JobGeneratorEvent): Unit = processEvent(event) override protected def onError(e: Throwable): Unit = { jobScheduler.reportError("Error in job generator", e) } } eventLoop.start() if (ssc.isCheckpointPresent) { restart() } else { startFirstTime() } }
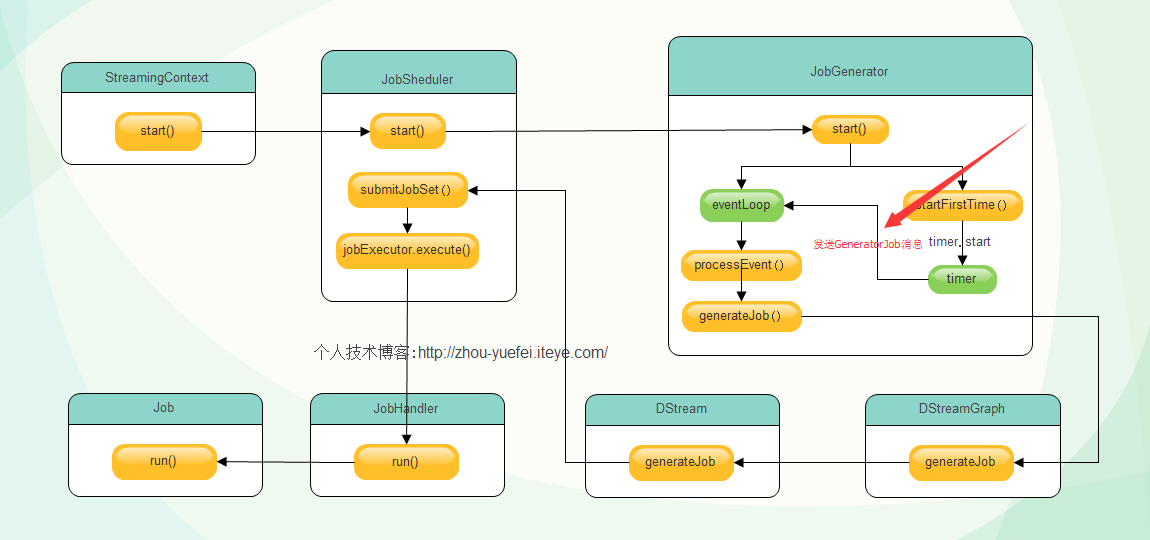
JobGenerator创建了eventLoop对象之后调用该对象的start方法,启动监听进程,准备接收JobGeneratorEvent类型消息交给processEvent函数处理,然后调用了startFirstTime方法,该方法启动DStreamGraph和定时器,定时器启动后根据程序设定的时间间隔给eventLoop对象发送GenerateJobs消息,如下图:

eventLoop对象收到
GenerateJobs 消息交个processEvent方法处理,processEvent收到该消息,调用generateJobs方法处理,源码如下:
/** Generate jobs and perform checkpoint for the given `time`. */
private def generateJobs(time:Time){
// Checkpoint all RDDs marked for checkpointing to ensure their lineages are
// truncated periodically. Otherwise, we may run into stack overflows (SPARK-6847).
ssc.sparkContext.setLocalProperty(RDD.CHECKPOINT_ALL_MARKED_ANCESTORS,"true")
Try{
jobScheduler.receiverTracker.allocateBlocksToBatch(time)// allocate received blocks to batch
graph.generateJobs(time)// generate jobs using allocated block
} match {
caseSuccess(jobs)=>
val streamIdToInputInfos = jobScheduler.inputInfoTracker.getInfo(time)
jobScheduler.submitJobSet(JobSet(time, jobs, streamIdToInputInfos))
caseFailure(e)=>
jobScheduler.reportError("Error generating jobs for time "+ time, e)
}
eventLoop.post(DoCheckpoint(time, clearCheckpointDataLater =false))
}
JobGenerator中的generateJobs方法主要关注两行代码,首先调用graph的generateJobs方法,给方法返回Success(jobs) 或者 Failure(e),其中的jobs就是该方法返回的Job对象集合,如果Job创建成功,再调用JobScheduler的submitJobSet方法将job提交给集群执行。
首先分析Job对象的产生,DStreamGraph 的start方法源码:
def generateJobs(time:Time):Seq[Job]={
logDebug("Generating jobs for time "+ time)
val jobs =this.synchronized{
outputStreams.flatMap { outputStream =>
val jobOption = outputStream.generateJob(time)
jobOption.foreach(_.setCallSite(outputStream.creationSite))
jobOption
}
}
logDebug("Generated "+ jobs.length +" jobs for time "+ time)
jobs
}
DStreamGraph 的start方法源码调用了outputStream对象的generateJob方法,ForeachDStream重写了该方法:
override def generateJob(time:Time):Option[Job]={
parent.getOrCompute(time) match {
caseSome(rdd)=>
val jobFunc =()=> createRDDWithLocalProperties(time, displayInnerRDDOps){
foreachFunc(rdd, time)
}
Some(newJob(time, jobFunc))
caseNone=>None
}
}
ForeachDStream的
generateJob 将用户编写的DStream处理函数封装在jobFunc中,并将其传入Job对象,至此Job的生成。
接下来分析Job提交过程,JobScheduler负责Job的提交,核心代码在submitJobSet方法中:
def submitJobSet(jobSet:JobSet){
if(jobSet.jobs.isEmpty){
logInfo("No jobs added for time "+ jobSet.time)
}else{
listenerBus.post(StreamingListenerBatchSubmitted(jobSet.toBatchInfo))
jobSets.put(jobSet.time, jobSet)
jobSet.jobs.foreach(job => jobExecutor.execute(newJobHandler(job)))
logInfo("Added jobs for time "+ jobSet.time)
}
}
其中jobExecutor对象是一个线程池,JobHandler实现了
Runnable接口,在JobHandler 的run方法中会调用传入的job对象的run方法。
疑问:Job的run方法执行是如何触发RDD的Action操作从而出发job的真正运行的呢?我们下次再具体分析,请随时关注博客更新!






















 1419
1419

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








