借鉴学习链接:https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/flyweight-pattern.html
享元模式
享元模式(Flyweight Pattern)主要用于减少创建对象的数量,以减少内存占用和提高性能。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它提供了减少对象数量从而改善应用所需的对象结构的方式。
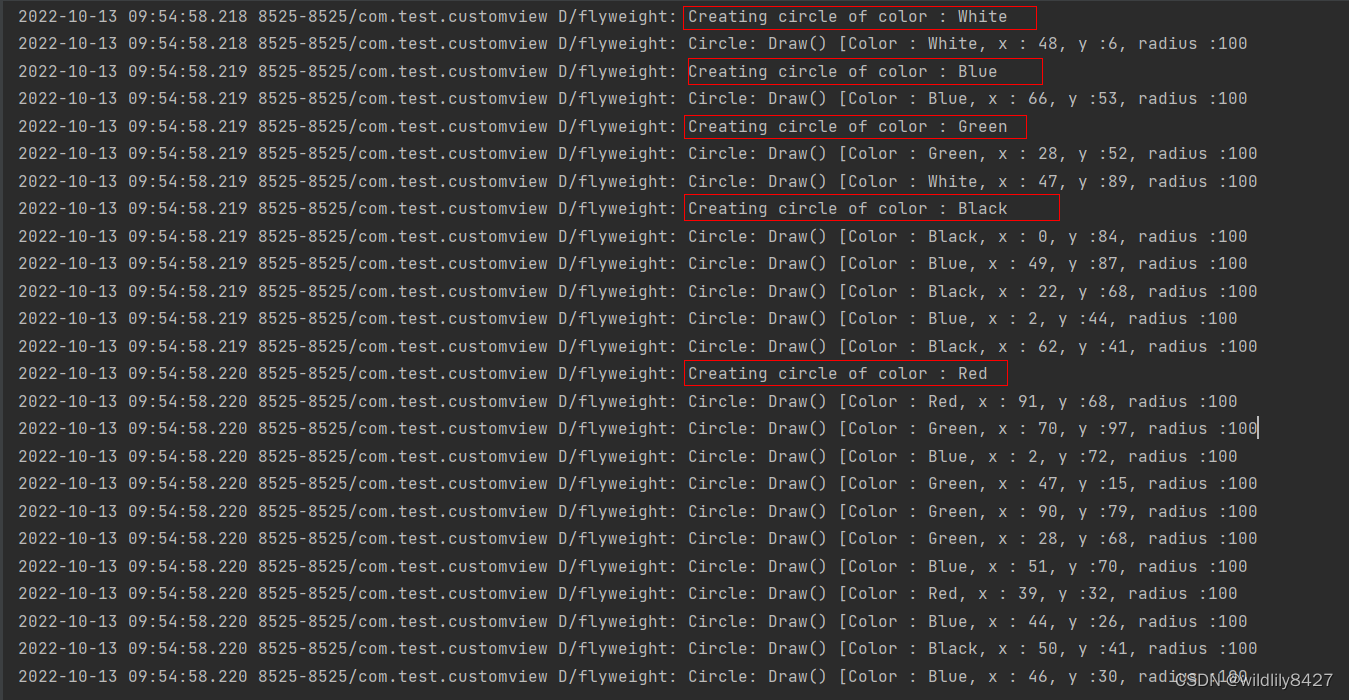
享元模式尝试重用现有的同类对象,如果未找到匹配的对象,则创建新对象。我们将通过创建 5 个对象来画出 20 个分布于不同位置的圆来演示这种模式。由于只有 5 种可用的颜色,所以 color 属性被用来检查现有的 Circle 对象。
介绍
意图:运用共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度的对象。
主要解决:在有大量对象时,有可能会造成内存溢出,我们把其中共同的部分抽象出来,如果有相同的业务请求,直接返回在内存中已有的对象,避免重新创建。
何时使用: 1、系统中有大量对象。 2、这些对象消耗大量内存。 3、这些对象的状态大部分可以外部化。 4、这些对象可以按照内蕴状态分为很多组,当把外蕴对象从对象中剔除出来时,每一组对象都可以用一个对象来代替。 5、系统不依赖于这些对象身份,这些对象是不可分辨的。
如何解决:用唯一标识码判断,如果在内存中有,则返回这个唯一标识码所标识的对象。
关键代码:用 HashMap 存储这些对象。
应用实例: 1、JAVA 中的 String,如果有则返回,如果没有则创建一个字符串保存在字符串缓存池里面。 2、数据库的数据池。
优点:大大减少对象的创建,降低系统的内存,使效率提高。
缺点:提高了系统的复杂度,需要分离出外部状态和内部状态,而且外部状态具有固有化的性质,不应该随着内部状态的变化而变化,否则会造成系统的混乱。
使用场景: 1、系统有大量相似对象。 2、需要缓冲池的场景。
注意事项: 1、注意划分外部状态和内部状态,否则可能会引起线程安全问题。 2、这些类必须有一个工厂对象加以控制。
使用Handler发送Message消息,新建Message,推荐使用Message.obtain方式,也是用到了享元模式的原理。
Message message = Message.obtain();//更加推荐这种用法
message.arg1 = 10086;
handler.sendMessage(message);
实现
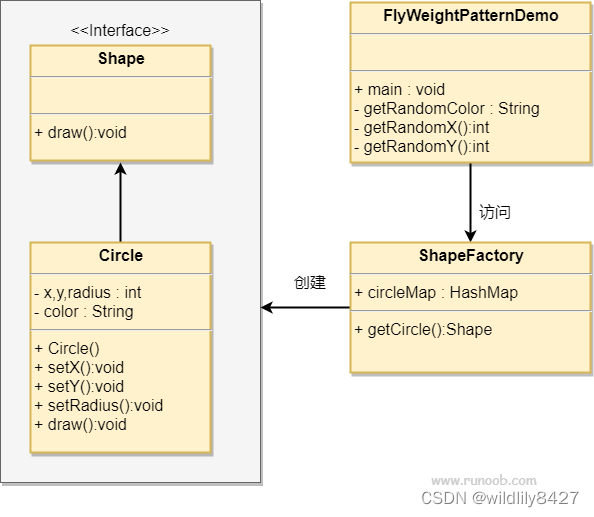
我们将创建一个 Shape 接口和实现了 Shape 接口的实体类 Circle。下一步是定义工厂类 ShapeFactory。
ShapeFactory 有一个 Circle 的 HashMap,其中键名为 Circle 对象的颜色。无论何时接收到请求,都会创建一个特定颜色的圆。ShapeFactory 检查它的 HashMap 中的 circle 对象,如果找到 Circle 对象,则返回该对象,否则将创建一个存储在 hashmap 中以备后续使用的新对象,并把该对象返回到客户端。
FlyWeightPatternDemo 类使用 ShapeFactory 来获取 Shape 对象。它将向 ShapeFactory 传递信息(red / green / blue/ black / white),以便获取它所需对象的颜色。
享元模式的 UML 图
步骤 1
创建一个接口。
//Shape.java
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
步骤 2
创建实现接口的实体类。
Circle.java
public class Circle implements Shape {
private String color;
private int x;
private int y;
private int radius;
public Circle(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void setRadius(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Circle: Draw() [Color : " + color
+", x : " + x +", y :" + y +", radius :" + radius);
}
}
步骤 3
创建一个工厂,生成基于给定信息的实体类的对象。
ShapeFactory.java
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ShapeFactory {
private static final HashMap<String, Shape> circleMap = new HashMap<>();
public static Shape getCircle(String color) {
Circle circle = (Circle)circleMap.get(color);
if(circle == null) {
circle = new Circle(color);
circleMap.put(color, circle);
System.out.println("Creating circle of color : " + color);
}
return circle;
}
}
步骤 4
使用该工厂,通过传递颜色信息来获取实体类的对象。
FlyweightPatternDemo.java
public class FlyweightPatternDemo {
private static final String colors[] =
{ "Red", "Green", "Blue", "White", "Black" };
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0; i < 20; ++i) {
Circle circle =
(Circle)ShapeFactory.getCircle(getRandomColor());
circle.setX(getRandomX());
circle.setY(getRandomY());
circle.setRadius(100);
circle.draw();
}
}
private static String getRandomColor() {
return colors[(int)(Math.random()*colors.length)];
}
private static int getRandomX() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100 );
}
private static int getRandomY() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100);
}
}
步骤5
运行程序:
// 自己编写的享元代码,参考Message Pool
//MainActivity
package com.htkj.testproject;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.GridLayoutManager;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private RecyclerView mRvPhotoList;
private CommonRecycleViewAdaper mRecycleViewAdapter;
private int mThumbWidthSmall = 80;
private int mThumbHeightSmall = 80;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
testVariablePool();
}
private void testVariablePool() {
mRvPhotoList = findViewById(R.id.rv_photo_list);
mRecycleViewAdapter = new CommonRecycleViewAdaper(this);
mRecycleViewAdapter.setThumbSize(mThumbWidthSmall,mThumbHeightSmall,14,6);
GridLayoutManager layoutManager = new GridLayoutManager(this, 14);
layoutManager.setOrientation(RecyclerView.VERTICAL);
mRvPhotoList.setLayoutManager(layoutManager);
mRvPhotoList.setAdapter(mRecycleViewAdapter);
}
}
// 适配器:CommonRecycleViewAdaper
package com.htkj.testproject;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
public class CommonRecycleViewAdaper extends RecyclerView.Adapter<CommonRecycleViewAdaper.CommonRecycleViewHolder>
{
private Context mContext;
private int mPosition;
private int width = 1150;
private int height = 600;
//设置缩略图的大小
private int thumbWidth;
private int thumbHeight;
//横排个数
private int mCountX;
private int mCountY;
public CommonRecycleViewAdaper(Context context) {
this.mContext = context;
}
public void setThumbSize(int width,int height,int countX,int countY) {
this.thumbWidth = width;
this.thumbHeight = height;
this.mCountX = countX;
this.mCountY = countY;
}
@NonNull
@Override
public CommonRecycleViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view =LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(R.layout.item_photo_list,parent,false);
view.getLayoutParams().height = height/mCountY ;
view.getLayoutParams().width = width/mCountX;
return new CommonRecycleViewHolder(view);
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull CommonRecycleViewHolder holder, @SuppressLint("RecyclerView") final int position) {
holder.itemView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
notifyDataSetChanged();
}
});
Log.d("VariablePool","position = " + position);
//优化:使用.obtain获取对象,对象使用完毕后使用recycle删除对象
VariablePool value = VariablePool.obtain();
//未优化:使用new方法创建对象
// VariablePool value = new VariablePool(MyApplication.getInstance(),"image2.jpg");
holder.photoView.setImageBitmap(value.bitmap);
value.recycle();
// 将position保存在itemView的Tag中以便点击时获取
holder.itemView.setTag(position);
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return 10000;
}
class CommonRecycleViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder{
private ImageView photoView;
private LinearLayout linearLayout;
public CommonRecycleViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
photoView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.pv_thumphoto);
linearLayout = itemView.findViewById(R.id.ll_photo_list);
}
}
}
// 享元设计,变量池
package com.htkj.testproject;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.util.Log;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* @ClassName VariablePool
* @Description //TODO
* @Author lili
* @DATE 2022/10/19 15:26
*/
public class VariablePool {
//成员
public Bitmap bitmap;
//变量池相关
public static final Object sPoolSync = new Object();
private static VariablePool sPool;
private static int sPoolSize = 0;
private int flags;
private VariablePool next;
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 50;
/**
* @Description //TODO
* @Param []
* @return com.htkj.testproject.VariablePool
**/
public static VariablePool obtain() {
synchronized (sPoolSync) {
if (sPool != null) {
VariablePool v = sPool;
sPool = v.next;
v.next = null;
v.flags = 0; // clear in-use flag
sPoolSize--;
Log.d("VariablePool","use the variablePool bitmap");
return v;
}
}
Log.d("VariablePool","variablePool is null,new the variable");
return new VariablePool(MyApplication.getInstance(),"image2.jpg");
}
public void recycle() {
recycleUnchecked();
}
void recycleUnchecked() {
// Mark the message as in use while it remains in the recycled object pool.
// Clear out all other details.
synchronized (sPoolSync) {
if (sPoolSize < MAX_POOL_SIZE) {
next = sPool;
sPool = this;
sPoolSize++;
}
}
}
public Bitmap getLoacalBitmap(Context context, String name) {
try {
InputStream fis = context.getAssets().open(name);
//把流转化为Bitmap图片
return BitmapFactory.decodeStream(fis);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public VariablePool(Context context,String str) {
this.bitmap = getLoacalBitmap(context,str);
}
}
// 布局文件:activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<!--列表-->
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/rv_photo_list"
android:layout_width="1100dp"
android:layout_height="600dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp">
</androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView>
</RelativeLayout>
//item布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/ll_photo_list"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:descendantFocusability="blocksDescendants"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/pv_thumphoto"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
运行结果:
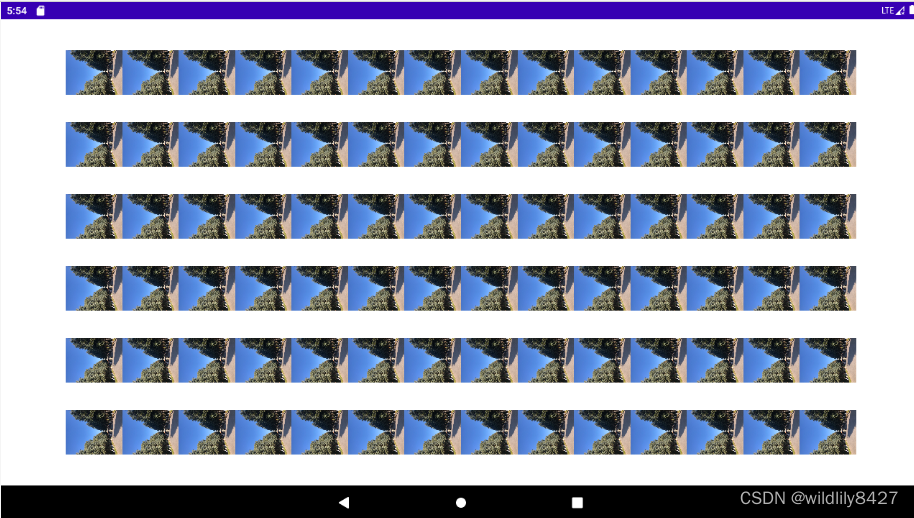
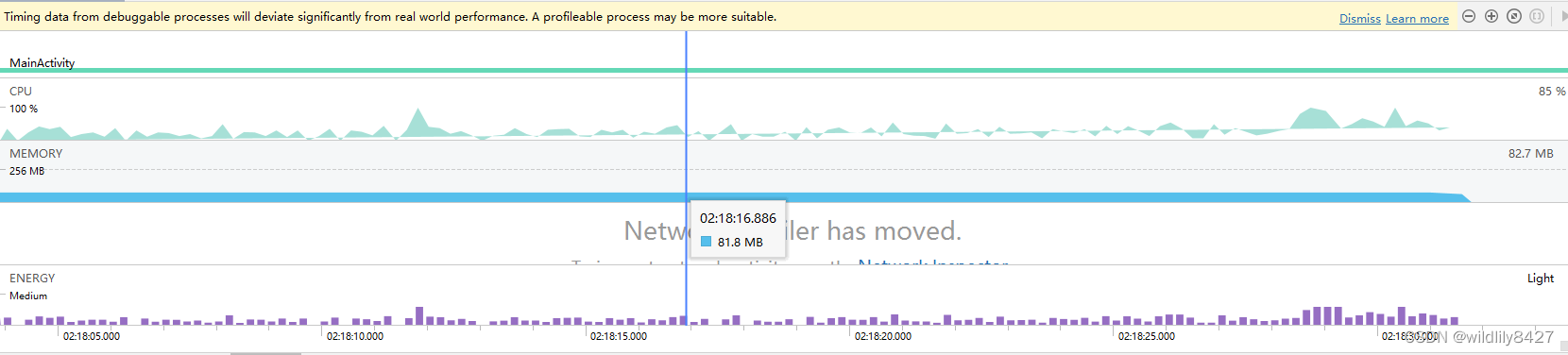
使用new方法创建,内存使用情况,大约占用0.9G内存:
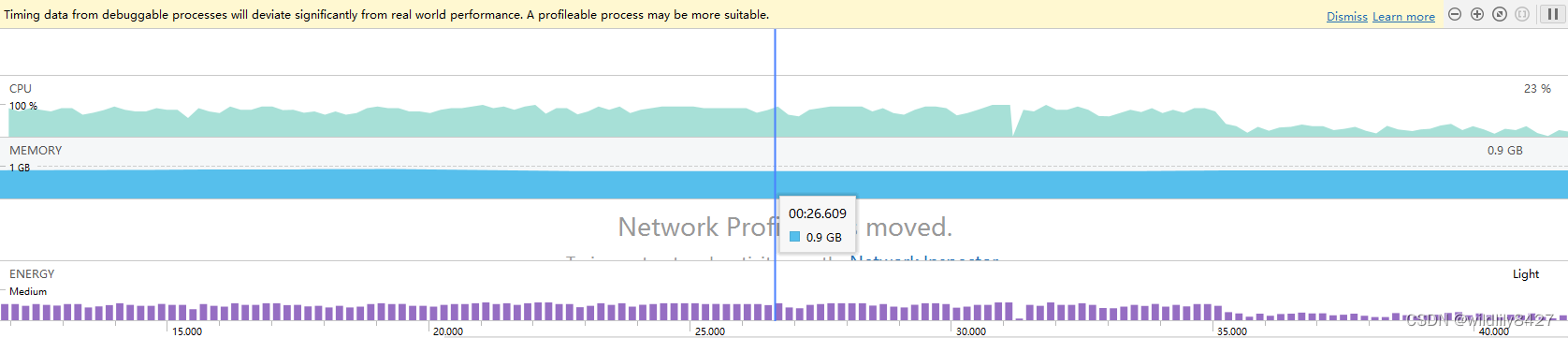
使用.obtatin的方式,内存大约占用大学82M内存,内存占用明显降低
总结
享元模式,换句话说就是共享对象,在某些对象需要重复创建,且最终只需要得到单一结果的情况下使用。因为此种模式是利用先前创建的已有对象,通过某种规则去判断当前所需对象是否可以利用原有对象做相应修改后得到想要的效果,如以上教程的实例,创建了20个不同效果的圆,但相同颜色的圆只需要创建一次便可,相同颜色的只需要引用原有对象,改变其坐标值便可。此种模式下,同一颜色的圆虽然位置不同,但其地址都是同一个,所以说此模式适用于结果注重单一结果的情况。
举一个简单例子,一个游戏中有不同的英雄角色,同一类型的角色也有不同属性的英雄,如刺客类型的英雄有很多个,按此种模式设计,利用英雄所属类型去引用原有同一类型的英雄实例,然后对其相应属性进行修改,便可得到最终想得到的最新英雄;比如说你创建了第一个刺客型英雄,然后需要设计第二个刺客型英雄,你利用第一个英雄改变属性得到第二个刺客英雄,最新的刺客英雄是诞生了,但第一个刺客英雄的属性也随之变得与第二个相同,这种情况显然是不可以的。





















 2841
2841











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








