版权声明:欢迎转载,转载请注明出处 http://blog.csdn.net/lizuobin2/
内核版本:linux2.6.32.2
硬件资源:s3c2440
参考: 韦东山SPI视频教程
内容概括:
1、I2C 驱动框架回顾
2、SPI 框架简单介绍
3、master 驱动框架
3.1 驱动侧
3.2 设备侧
4、SPI 设备驱动框架
4.1 设备册
4.2 驱动侧
5、设备驱动程序实例
1、I2C 驱动框架回顾
在前面学习 I2C 驱动程序的时候我们知道,I2C 驱动框架分为两层,一层是控制器驱动程序 i2c_adapter,它一般是由芯片厂商写好的,主要提供一个 algorithm 底层的 i2c 协议的收发函数。i2c_adapter 驱动是基于 platform 模型,在driver侧的probe函数里,取出资源信息进行设置,最后将adapter注册到i2c_bus_type,注册时会调用 i2c_scan_static_board_info,扫描并使用 i2c_new_device 创建设备(设备层的设备)。我们还提到了4种创建device的方式。
另一层是设备驱动层,基于 i2c_bus_type ,这个就很简单了,在设备驱动层 device 只需要提供一个从设备地址和名字,在 driver 里使用 i2c_smbus_read_byte_data 等类似的函数进行收发即可了,i2c_smbus_read_byte_data 等函数最终就会调用到 我们的 i2c_adapter->algorithm 里的收发函数进行收发。
2、SPI 框架简单介绍
对于SPI的大框架,与I2C是完全一致的,也分为两层,控制器驱动程序层叫 spi_master ,主要提供transfer函数,进行spi协议的收发。spi_master 也是基于 Platform 模型的,注册 spi_master 时也会扫描一个链表进行注册设备,简直太相似了。
另一层是设备驱动层,基于 spi_bus_type,相比 i2c 在device中需要提供的信息多一些,需要有名字、片选、最大速率、模式、中断号等等,在driver里则使用spi_read、spi_writer 等函数,最终也会调用到 master->transfer 函数进行发送接收。
相比 I2C ,SPI驱动的框架是要简单的,因为它少了两种注册device的方式,另外它不需要像I2C一样去发送Start信号和设备地址去探测设备,SPI只需要片选选中就行了。但是它的底层收发的控制,相对I2C要复杂一点,毕竟4根线。
3、master 驱动框架
之前,分析的驱动程序都是 S3C2410\S3C2440 平台的,由于我的开发板 Mini2440 没有SPI设备,因此厂商带的内核里关于 SPI 驱动部分不完整,而且在s3c23xx_spi_probe函数里注册master的时候写的十分复杂,干扰信息太多,不适合分析学习,因此,我搜索了一下其他平台的代码,发现 atmel_spi.c (drivers\spi),里 atmel 实现的底层控制器驱动简单清晰多了,因此就拿它开刀,分析Master驱动框架。
3.1 驱动侧
前面简介里,我提到 master 驱动框架是基于 platform 平台的(我分析的这俩都是,其它的不清楚),那么肯定就要注册platform_driver了,下面我们就开看看。
分配一个platfrom_driver结构
- static struct platform_driver atmel_spi_driver = {
- .driver = {
- .name = "atmel_spi",
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- },
- .suspend = atmel_spi_suspend,
- .resume = atmel_spi_resume,
- .remove = __exit_p(atmel_spi_remove),
- };
将 atmel_spi_driver 注册到 platform_bus_type ,匹配设备 probe
- static int __init atmel_spi_init(void)
- {
- return platform_driver_probe(&atmel_spi_driver, atmel_spi_probe);
- }
/**
* platform_driver_probe - register driver for non-hotpluggable device
* @drv: platform driver structure
* @probe: the driver probe routine, probably from an __init section
*
* Use this instead of platform_driver_register() when you know the device
* is not hotpluggable and has already been registered, and you want to
* remove its run-once probe() infrastructure from memory after the driver
* has bound to the device.
*
* One typical use for this would be with drivers for controllers integrated
* into system-on-chip processors, where the controller devices have been
* configured as part of board setup.
*
* Returns zero if the driver registered and bound to a device, else returns
* a negative error code and with the driver not registered.
*/
1、适用于非热插拔设备
2、通常Probe位于__init段3、当你知道device是非热拔插的,而且设备已经被注册了,而且你想在probe函数调用一次之后就销毁它节省空间,使用 platform_driver_probe 而非 platform_driver_register。
4、一个典型的应用是,用在完整的控制器驱动,控制器设备被当作 board setup 的一部分(在板子初始化的时候,设备就已经被注册了,放在board_info里)
5、返回0 ,如果driver注册成功且匹配到一个device ,以后再也无法被别的device probe了。
6、否则,返回一个错误,且driver未注册。
显然,我们写的正式一个控制器驱动程序,设备侧确实是早已注册(后边会讲)。
疑问:有人说使用 platform_driver_probe 时 driver 只能被一个 device 匹配绑定,之后再也无法被别的device probe,难道说,我有俩spi控制器还需要写两个控制器驱动程序么?我认为这种说法是不对的,我猜大概是driver注册时,会匹配一遍device链表,把能支持的device都probe,之后再有deivce注册进来就不行了。这个有待验证。
i2c驱动框架里,是在driver->probe 分配设置注册adapter,想必spi也是在driver->probe里分配设置注册master。
- static int __init atmel_spi_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
- {
- struct resource *regs;
- int irq;
- struct clk *clk;
- int ret;
- struct spi_master *master;
- struct atmel_spi *as;
- /* 获取 device 侧提供的Io内存以及中断 */
- regs = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
- irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);
- /* 获取 spi 时钟,一会好使能它 */
- clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "spi_clk");
- /* 分配一个spi_master结构 额外加上一个 atmel_spi 用来存放其它信息 */
- master = spi_alloc_master(&pdev->dev, sizeof *as);
- /* 设置 master */
- master->mode_bits = SPI_CPOL | SPI_CPHA | SPI_CS_HIGH; // 所支持的模式
- master->bus_num = pdev->id; // 控制器编号,用于分辨外围spi设备是连接在哪一个控制器上
- master->num_chipselect = 4; // 片选最大值+1,spi设备的片选值要小于它
- master->setup = atmel_spi_setup; // 一个控制器上可能接有多个spi设备,它们的频率和模式是不一样的,用于设备之间切换时设置这些信息。
- master->transfer = atmel_spi_transfer; // 最重要的发送函数
- master->cleanup = atmel_spi_cleanup;
- /* 将 Master 放入 pdev->dev->p->driver_data 里*/
- platform_set_drvdata(pdev, master);
- /* as 指向 master->dev->p->driver_data ,填充多出来那个 atmel_spi 结构 */
- as = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
- as->buffer = dma_alloc_coherent(&pdev->dev, BUFFER_SIZE,
- &as->buffer_dma, GFP_KERNEL);
- spin_lock_init(&as->lock);
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&as->queue);
- as->pdev = pdev;
- as->regs = ioremap(regs->start, (regs->end - regs->start) + 1);
- as->irq = irq;
- as->clk = clk;
- /* 注册中断 使能时钟 */
- ret = request_irq(irq, atmel_spi_interrupt, 0,
- dev_name(&pdev->dev), master);
- clk_enable(clk);
- /* 设置硬件寄存器 */
- spi_writel(as, CR, SPI_BIT(SWRST));
- spi_writel(as, CR, SPI_BIT(SWRST)); /* AT91SAM9263 Rev B workaround */
- spi_writel(as, MR, SPI_BIT(MSTR) | SPI_BIT(MODFDIS));
- spi_writel(as, PTCR, SPI_BIT(RXTDIS) | SPI_BIT(TXTDIS));
- spi_writel(as, CR, SPI_BIT(SPIEN));
- /* 注册master */
- ret = spi_register_master(master);
- return 0;
- }
对于master的设置过程注释已经说的很明白了,我们还得看看分配和注册过程。
- struct spi_master *spi_alloc_master(struct device *dev, unsigned size)
- {
- struct spi_master *master;
- master = kzalloc(size + sizeof *master, GFP_KERNEL);
- device_initialize(&master->dev); // 初始化设备
- master->dev.class = &spi_master_class;
- master->dev.parent = get_device(dev); // 在 sysfs 平台设备xxx目录下创建目录
- spi_master_set_devdata(master, &master[1]);
- return master;
- }
2、初始化 master->dev ,设置它的父设备等。
- int spi_register_master(struct spi_master *master)
- {
- /* 将master注册到内核中去 */
- dev_set_name(&master->dev, "spi%u", master->bus_num);
- status = device_add(&master->dev);
- /* 扫描spi设备信息,创建设备 */
- scan_boardinfo(master);
- }
2、device_add 注册设备
3、扫描spi设备信息:scan_boardinfo(master)
- static void scan_boardinfo(struct spi_master *master)
- {
- struct boardinfo *bi;
- mutex_lock(&board_lock);
- list_for_each_entry(bi, &board_list, list) {
- struct spi_board_info *chip = bi->board_info;
- unsigned n;
- /* 如果说 board_info 提供的bus_num 和 master—>bus_num 一致,则调用 spi_new_device */
- for (n = bi->n_board_info; n > 0; n--, chip++) {
- if (chip->bus_num != master->bus_num)
- continue;
- (void) spi_new_device(master, chip); // 我们放到设备驱动层,在分析它
- }
- }
- mutex_unlock(&board_lock);
- }
3.2 设备侧
有 platform_driver 必然有 platform_device 与之对应,At91sam9260_devices.c 中定义
- static struct resource spi0_resources[] = {
- [0] = {
- .start = AT91SAM9260_BASE_SPI0,
- .end = AT91SAM9260_BASE_SPI0 + SZ_16K - 1,
- .flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
- },
- [1] = {
- .start = AT91SAM9260_ID_SPI0,
- .end = AT91SAM9260_ID_SPI0,
- .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ,
- },
- };
- static struct platform_device at91sam9260_spi0_device = {
- .name = "atmel_spi", // 名字与driver一致
- .id = 0,
- .dev = {
- .dma_mask = &spi_dmamask,
- .coherent_dma_mask = DMA_BIT_MASK(32),
- },
- .resource = spi0_resources, // 资源文件
- .num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(spi0_resources),
- };
既然分配了 platform_device 那么肯定会在某个地方调用 platform_device_register 将它注册到 platform_bus_type , 就是在 at91_add_device_spi 。
- void __init at91_add_device_spi(struct spi_board_info *devices, int nr_devices)
- {
- ...
- spi_register_board_info(devices, nr_devices);
- /* Configure SPI bus(es) */
- if (enable_spi0) {
- ...
- platform_device_register(&at91sam9260_spi0_device);
- }
- if (enable_spi1) {
- ...
- platform_device_register(&at91sam9260_spi1_device);
- }
- }
2、将我们的 master 的设备侧 at91sam9260_spi0_device 注册到 platform_bus_type
思考:这样做有什么好处呢?
这样可以保证,master driver 与 device 匹配成功调用 probe 函数 scan_boardinfo 时,spi设备已经被添加到board_list中去~!如果先注册成功了 master 驱动,再添加spi设备信息就无用了。根 i2c 也是一样的。
至此,Master 驱动的框架就分析完了,至于 master 的那些设置,我们到下篇文件写 master 驱动里细究。
4、SPI 设备驱动框架
设备驱动层,参考韦东山老师的 SPI Flash 驱动来分析,设备驱动层,device driver 都是注册到spi_bus_type的,因此,我们现在看看 spi_bus_type->match 函数,看看它们如何匹配。
- static int spi_match_device(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
- {
- const struct spi_device *spi = to_spi_device(dev);
- const struct spi_driver *sdrv = to_spi_driver(drv);
- if (sdrv->id_table)
- return !!spi_match_id(sdrv->id_table, spi);
- return strcmp(spi->modalias, drv->name) == 0;
- }
4.1 设备层
设备层比较简单,先来分析它吧,目的只有一个分配 spi_board_info 设置 注册。
- static struct spi_board_info spi_info_jz2440[] = {
- {
- .modalias = "100ask_spi_flash", /* 对应的spi_driver名字也是"oled" */
- .max_speed_hz = 80000000, /* max spi clock (SCK) speed in HZ */
- .bus_num = 1, /* jz2440里OLED接在SPI CONTROLLER 1 */
- .mode = SPI_MODE_0,
- .chip_select = S3C2410_GPG(2), /* flash_cs, 它的含义由spi_master确定 */
- }
- };
- static int spi_info_jz2440_init(void)
- {
- return spi_register_board_info(spi_info_jz2440, ARRAY_SIZE(spi_info_jz2440)); // list_add_tail(&bi->list, &board_list);
- }
注册 list_add_tail(&spi_info_jz2440->list, &board_list)
前面我们提到,master注册成功时会扫描 board_list 注册 spi 设备,现在来看看 spi 设备的注册过程,虽然没有啥重要的。
- struct spi_device *spi_new_device(struct spi_master *master,
- struct spi_board_info *chip)
- {
- struct spi_device *proxy;
- int status;
- proxy = spi_alloc_device(master);
- proxy->chip_select = chip->chip_select;
- proxy->max_speed_hz = chip->max_speed_hz;
- proxy->mode = chip->mode;
- proxy->irq = chip->irq;
- strlcpy(proxy->modalias, chip->modalias, sizeof(proxy->modalias));
- proxy->dev.platform_data = (void *) chip->platform_data;
- proxy->controller_data = chip->controller_data;
- proxy->controller_state = NULL;
- status = spi_add_device(proxy);
- return proxy;
- }
- struct spi_device *spi_alloc_device(struct spi_master *master)
- {
- struct spi_device *spi;
- struct device *dev = master->dev.parent;
- spi = kzalloc(sizeof *spi, GFP_KERNEL);
- spi->master = master;
- spi->dev.parent = dev;
- spi->dev.bus = &spi_bus_type;
- spi->dev.release = spidev_release;
- device_initialize(&spi->dev);
- return spi;
- }
- int spi_add_device(struct spi_device *spi)
- {
- static DEFINE_MUTEX(spi_add_lock);
- struct device *dev = spi->master->dev.parent;
- int status;
- /* 片选限制 */
- if (spi->chip_select >= spi->master->num_chipselect) {
- dev_err(dev, "cs%d >= max %d\n",
- spi->chip_select,
- spi->master->num_chipselect);
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- /* Set the bus ID string */
- dev_set_name(&spi->dev, "%s.%u", dev_name(&spi->master->dev),
- spi->chip_select);
- status = spi_setup(spi);
- /*
- if (!spi->bits_per_word)
- spi->bits_per_word = 8;
- status = spi->master->setup(spi);
- */
- status = device_add(&spi->dev);
- }
有一点,需要留意的吧,我们在写 master 驱动时,master->num_chipselect 要大于我们将要注册进来的spi设备的 chip_select 。
4.2 驱动侧
- static struct spi_driver spi_flash_drv = {
- .driver = {
- .name = "100ask_spi_flash",
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- },
- .probe = spi_flash_probe,
- .remove = __devexit_p(spi_flash_remove),
- };
- static int spi_flash_init(void)
- {
- return spi_register_driver(&spi_flash_drv);
- }
- static int __devinit spi_flash_probe(struct spi_device *spi)
- {
- int mid, did;
- spi_flash = spi;
- s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(spi->chip_select, S3C2410_GPIO_OUTPUT);
- SPIFlashInit();
- SPIFlashReadID(&mid, &did);
- printk("SPI Flash ID: %02x %02x\n", mid, did);
- memset(&spi_flash_dev, 0, sizeof(spi_flash_dev));
- /* 构造注册一个mtd_info
- * mtd_device_register(master, parts, nr_parts)
- *
- */
- /* Setup the MTD structure */
- spi_flash_dev.name = "100ask_spi_flash";
- spi_flash_dev.type = MTD_NORFLASH;
- spi_flash_dev.flags = MTD_CAP_NORFLASH;
- spi_flash_dev.size = 0x200000; /* 2M */
- spi_flash_dev.writesize = 1;
- spi_flash_dev.writebufsize = 4096; /* 没有用到 */
- spi_flash_dev.erasesize = 4096; /* 擦除的最小单位 */
- spi_flash_dev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
- spi_flash_dev._erase = spi_flash_erase;
- spi_flash_dev._read = spi_flash_read;
- spi_flash_dev._write = spi_flash_write;
- mtd_device_register(&spi_flash_dev, NULL, 0);
- return 0;
- }
- static inline int spi_write(struct spi_device *spi, const u8 *buf, size_t len)
- {
- struct spi_transfer t = {
- .tx_buf = buf,
- .len = len,
- };
- struct spi_message m;
- spi_message_init(&m);
- spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m);
- return spi_sync(spi, &m);
- }
还记得,i2c 是通过构造 i2c_msg ,然后传递多个 i2c_msg 给底层的发送函数,多个i2c_msg 组成start信号和p信号之间的发送过程,每一个i2c_msg 都有一个start信号。大概 i2c_msg 就类比于spi里的 spi_transfer ,但是通常情况下,整个 spi_messgae 传输过程我们只片选一次就够了。下面看个实例分析。
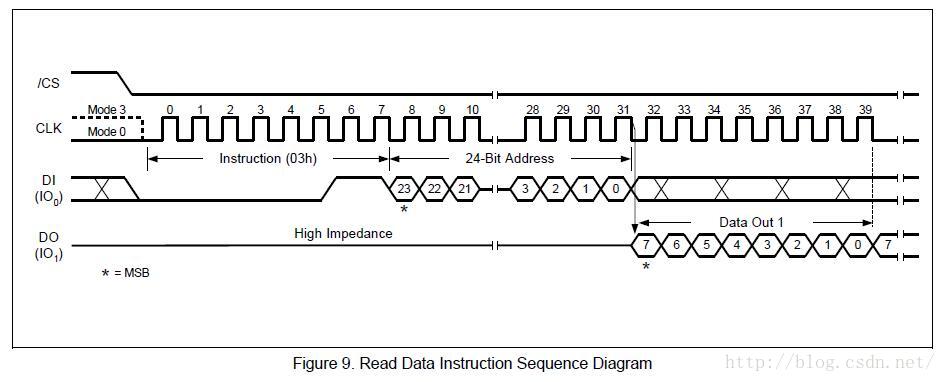
- void SPIFlashRead(unsigned int addr, unsigned char *buf, int len)
- {
- unsigned char tx_buf[4];
- struct spi_transfer t[] = {
- {
- .tx_buf = tx_buf,
- .len = 4,
- },
- {
- .rx_buf = buf,
- .len = len,
- },
- };
- struct spi_message m;
- tx_buf[0] = 0x03;
- tx_buf[1] = addr >> 16;
- tx_buf[2] = addr >> 8;
- tx_buf[3] = addr & 0xff;
- spi_message_init(&m);
- spi_message_add_tail(&t[0], &m);
- spi_message_add_tail(&t[1], &m);
- spi_sync(spi_flash, &m);
- }
纸上谈兵一大堆,现在来看看,我们在写一个spi设备驱动的时候需要做哪些工作。
设备侧:
1、分配一个 spi_board_info 结构体
2、设置 spi_board_info 里的名字、最大频率、控制器编号、模式、片选
3、注册 spi_register_board_info
驱动侧:
1、分配一个 spi_driver 结构
2、设置名字、probe等函数
3、注册 spi_register_driver
4、使用spi_write等系统调用,搞明白 spi_transfer spi_message ,会使用它们进行收发
一个 spi_message 对应于一个不可打断的spi传输过程,可以理解为片选选中直到取消选中的过程(特殊情况下,一个spi_message里面是可以取消片选再选中的),而 spi_message 由 spi_transfer 组成,根据 tx_buf rx_buf 是否为空来判断是 写还是读 操作。
至此,整个 spi 的框架分析完毕
5、设备驱动程序实例
- #include <linux/init.h>
- #include <linux/fs.h>
- #include <linux/slab.h>
- #include <linux/module.h>
- #include <linux/kernel.h>
- #include <linux/device.h>
- #include <sound/core.h>
- #include <linux/spi/spi.h>
- #include <asm/uaccess.h>
- #include <linux/timer.h>
- #include <mach/hardware.h>
- #include <mach/regs-gpio.h>
- #include <linux/gpio.h>
- #include <plat/gpio-cfg.h>
- #include <linux/mtd/cfi.h>
- #include <linux/mtd/mtd.h>
- #include <linux/mtd/partitions.h>
- /* 参考:
- * drivers\mtd\devices\mtdram.c
- * drivers/mtd/devices/m25p80.c
- */
- static struct spi_device *spi_flash;
- /*
- *
- */
- void SPIFlashReadID(int *pMID, int *pDID)
- {
- unsigned char tx_buf[4];
- unsigned char rx_buf[2];
- tx_buf[0] = 0x90;
- tx_buf[1] = 0;
- tx_buf[2] = 0;
- tx_buf[3] = 0;
- spi_write_then_read(spi_flash, tx_buf, 4, rx_buf, 2);
- *pMID = rx_buf[0];
- *pDID = rx_buf[1];
- }
- static void SPIFlashWriteEnable(int enable)
- {
- unsigned char val = enable ? 0x06 : 0x04;
- spi_write(spi_flash, &val, 1);
- }
- static unsigned char SPIFlashReadStatusReg1(void)
- {
- unsigned char val;
- unsigned char cmd = 0x05;
- spi_write_then_read(spi_flash, &cmd, 1, &val, 1);
- return val;
- }
- static unsigned char SPIFlashReadStatusReg2(void)
- {
- unsigned char val;
- unsigned char cmd = 0x35;
- spi_write_then_read(spi_flash, &cmd, 1, &val, 1);
- return val;
- }
- static void SPIFlashWaitWhenBusy(void)
- {
- while (SPIFlashReadStatusReg1() & 1)
- {
- /* 休眠一段时间 */
- /* Sector erase time : 60ms
- * Page program time : 0.7ms
- * Write status reg time : 10ms
- */
- set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
- schedule_timeout(HZ/100); /* 休眠10MS后再次判断 */
- }
- }
- static void SPIFlashWriteStatusReg(unsigned char reg1, unsigned char reg2)
- {
- unsigned char tx_buf[4];
- SPIFlashWriteEnable(1);
- tx_buf[0] = 0x01;
- tx_buf[1] = reg1;
- tx_buf[2] = reg2;
- spi_write(spi_flash, tx_buf, 3);
- SPIFlashWaitWhenBusy();
- }
- static void SPIFlashClearProtectForStatusReg(void)
- {
- unsigned char reg1, reg2;
- reg1 = SPIFlashReadStatusReg1();
- reg2 = SPIFlashReadStatusReg2();
- reg1 &= ~(1<<7);
- reg2 &= ~(1<<0);
- SPIFlashWriteStatusReg(reg1, reg2);
- }
- static void SPIFlashClearProtectForData(void)
- {
- /* cmp=0,bp2,1,0=0b000 */
- unsigned char reg1, reg2;
- reg1 = SPIFlashReadStatusReg1();
- reg2 = SPIFlashReadStatusReg2();
- reg1 &= ~(7<<2);
- reg2 &= ~(1<<6);
- SPIFlashWriteStatusReg(reg1, reg2);
- }
- /* erase 4K */
- void SPIFlashEraseSector(unsigned int addr)
- {
- unsigned char tx_buf[4];
- tx_buf[0] = 0x20;
- tx_buf[1] = addr >> 16;
- tx_buf[2] = addr >> 8;
- tx_buf[3] = addr & 0xff;
- SPIFlashWriteEnable(1);
- spi_write(spi_flash, tx_buf, 4);
- SPIFlashWaitWhenBusy();
- }
- /* program */
- void SPIFlashProgram(unsigned int addr, unsigned char *buf, int len)
- {
- unsigned char tx_buf[4];
- struct spi_transfer t[] = {
- {
- .tx_buf = tx_buf,
- .len = 4,
- },
- {
- .tx_buf = buf,
- .len = len,
- },
- };
- struct spi_message m;
- tx_buf[0] = 0x02;
- tx_buf[1] = addr >> 16;
- tx_buf[2] = addr >> 8;
- tx_buf[3] = addr & 0xff;
- SPIFlashWriteEnable(1);
- spi_message_init(&m);
- spi_message_add_tail(&t[0], &m);
- spi_message_add_tail(&t[1], &m);
- spi_sync(spi_flash, &m);
- SPIFlashWaitWhenBusy();
- }
- void SPIFlashRead(unsigned int addr, unsigned char *buf, int len)
- {
- /* spi_write_then_read规定了tx_cnt+rx_cnt < 32
- * 所以对于大量数据的读取,不能使用该函数
- */
- unsigned char tx_buf[4];
- struct spi_transfer t[] = {
- {
- .tx_buf = tx_buf,
- .len = 4,
- },
- {
- .rx_buf = buf,
- .len = len,
- },
- };
- struct spi_message m;
- tx_buf[0] = 0x03;
- tx_buf[1] = addr >> 16;
- tx_buf[2] = addr >> 8;
- tx_buf[3] = addr & 0xff;
- spi_message_init(&m);
- spi_message_add_tail(&t[0], &m);
- spi_message_add_tail(&t[1], &m);
- spi_sync(spi_flash, &m);
- }
- static void SPIFlashInit(void)
- {
- SPIFlashClearProtectForStatusReg();
- SPIFlashClearProtectForData();
- }
- /* 构造注册一个mtd_info
- * mtd_device_register(master, parts, nr_parts)
- *
- */
- /* 首先: 构造注册spi_driver
- * 然后: 在spi_driver的probe函数里构造注册mtd_info
- */
- static struct mtd_info spi_flash_dev;
- static int spi_flash_erase(struct mtd_info *mtd, struct erase_info *instr)
- {
- unsigned int addr = instr->addr;
- unsigned int len = 0;
- /* 判断参数 */
- if ((addr & (spi_flash_dev.erasesize - 1)) || (instr->len & (spi_flash_dev.erasesize - 1)))
- {
- printk("addr/len is not aligned\n");
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- for (len = 0; len < instr->len; len += 4096)
- {
- SPIFlashEraseSector(addr);
- addr += 4096;
- }
- instr->state = MTD_ERASE_DONE;
- mtd_erase_callback(instr);
- return 0;
- }
- static int spi_flash_read(struct mtd_info *mtd, loff_t from, size_t len,
- size_t *retlen, u_char *buf)
- {
- SPIFlashRead(from, buf, len);
- *retlen = len;
- return 0;
- }
- static int spi_flash_write(struct mtd_info *mtd, loff_t to, size_t len,
- size_t *retlen, const u_char *buf)
- {
- unsigned int addr = to;
- unsigned int wlen = 0;
- /* 判断参数 */
- if ((to & (spi_flash_dev.erasesize - 1)) || (len & (spi_flash_dev.erasesize - 1)))
- {
- printk("addr/len is not aligned\n");
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- for (wlen = 0; wlen < len; wlen += 256)
- {
- SPIFlashProgram(addr, (unsigned char *)buf, 256);
- addr += 256;
- buf += 256;
- }
- *retlen = len;
- return 0;
- }
- static int __devinit spi_flash_probe(struct spi_device *spi)
- {
- int mid, did;
- spi_flash = spi;
- s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(spi->chip_select, S3C2410_GPIO_OUTPUT);
- SPIFlashInit();
- SPIFlashReadID(&mid, &did);
- printk("SPI Flash ID: %02x %02x\n", mid, did);
- memset(&spi_flash_dev, 0, sizeof(spi_flash_dev));
- /* 构造注册一个mtd_info
- * mtd_device_register(master, parts, nr_parts)
- *
- */
- /* Setup the MTD structure */
- spi_flash_dev.name = "100ask_spi_flash";
- spi_flash_dev.type = MTD_NORFLASH;
- spi_flash_dev.flags = MTD_CAP_NORFLASH;
- spi_flash_dev.size = 0x200000; /* 2M */
- spi_flash_dev.writesize = 1;
- spi_flash_dev.writebufsize = 4096; /* 没有用到 */
- spi_flash_dev.erasesize = 4096; /* 擦除的最小单位 */
- spi_flash_dev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
- spi_flash_dev._erase = spi_flash_erase;
- spi_flash_dev._read = spi_flash_read;
- spi_flash_dev._write = spi_flash_write;
- mtd_device_register(&spi_flash_dev, NULL, 0);
- return 0;
- }
- static int __devexit spi_flash_remove(struct spi_device *spi)
- {
- mtd_device_unregister(&spi_flash_dev);
- return 0;
- }
- static struct spi_driver spi_flash_drv = {
- .driver = {
- .name = "100ask_spi_flash",
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- },
- .probe = spi_flash_probe,
- .remove = __devexit_p(spi_flash_remove),
- };
- static int spi_flash_init(void)
- {
- return spi_register_driver(&spi_flash_drv);
- }
- static void spi_flash_exit(void)
- {
- spi_unregister_driver(&spi_flash_drv);
- }
- module_init(spi_flash_init);
- module_exit(spi_flash_exit);
- MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Flash SPI Driver");
- MODULE_AUTHOR("weidongshan@qq.com,www.100ask.net");
- MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
- <strong style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">
- </strong>























 1067
1067

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








