构造函数:实例化一个对象时调用构造函数
1) 特点
A. 函数名和类名完全相同
B. 不能定义构造函数的类型(返回类型),也不能使用void
C. 通常情况下构造函数应声明位公有函数,否则它不能像其他成员函数那样被显式地调用
D. 构造函数被声明为私有有特殊的用途
E. 构造函数可以有任意类型和任意个数的参数,一个类可以有多个构造函数(重载)
2) 默认构造函数
A. 不带参数的构造函数
B. 如果程序中未声明,则系统自动产生出一个默认构造函数
3) 构造函数的重载
示例:
[Test.h]
#ifndef_TEST_H_
#define_TEST_H_
classTest
{
public:
Test();//默认的无参构造函数
Test(int x,int y,int z); //构造函数重载
private:
int x_;
int y_;
int z_;
};
#endif
[Test.cpp]
#include"Test.h"
#include<iostream>
usingnamespace std;
Test::Test()
{
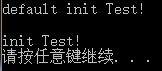
cout << "default init Test!\n"<< endl;
}
Test::Test(intx, int y, int z)
{
cout << "init Test!"<< endl;
x_ = x;
y_ = y;
z_ = z;
}
[main.cpp]
#include<iostream>
#include"Test.h"
usingnamespace std;
intmain()
{
Test t1; //调用默认构造函数Test()
Test t(1,2,3); //调用重载构造函数Test(int, int, int)
return 0;
}
4) 构造函数与new运算符
示例:
[Test.h]
#ifndef_TEST_H_
#define_TEST_H_
classTest
{
public:
Test();//默认的无参构造函数
Test(int x,int y,int z); //重载构造函数
private:
int x_;
int y_;
int z_;
};
#endif
[Test.cpp]
#include"Test.h"
#include<iostream>
usingnamespace std;
Test::Test()
{
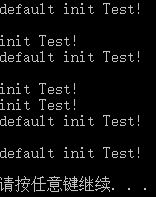
cout << "default init Test!"<< endl;
}
Test::Test(intx, int y, int z)
{
cout << "init Test!"<< endl;
x_ = x;
y_ = y;
z_ = z;
}
[main.cpp]
#include<iostream>
#include"Test.h"
usingnamespace std;
intmain()
{
Test t1;
Test t(1,2,3);
Test *p1 = newTest(); //new分配空间,调用默认构造函数
Test *p2 = new Test(3,4,5); //new分配空间,调用重载的带参构造函数
Test array[3] = { Test(7, 8, 9) }; //一个调用重载的带参的构造函数,两个调用默认构造函数
return 0;
}
5) 全局对象的构造函数先于main函数
示例:
[Test.h]:
#ifndef_TEST_H_
#define_TEST_H_
classTest
{
public:
Test(int x,int y,int z);
~Test();
private:
int x_;
int y_;
int z_;
};
#endif
[Test.cpp]:
#include"Test.h"
#include<iostream>
usingnamespace std;
Test::Test(intx, int y, int z)
{
x_ = x;
y_ = y;
z_ = z;
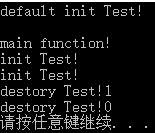
cout << "init Test!" <<x_ << endl;
}
Test::~Test()
{
cout << "destory Test!"<< x_ << endl;
}
main.c
#include<iostream>
#include"Test.h"
usingnamespace std;
Testt3; //全局对象
intmain()
{
cout << "main function!"<<endl;
Test t1();
Test t(4,5,6);
Test *p = new Test(7,8,9);
delete p;
return 0;
}






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








