接着上面的写,下面就说到整个协议栈的主循环来了,一个osal_start_system()函数,进入这个函数可以看到是一个死循环
for(;;) 以后,整个程序就一直在这里面不停的轮询查找,进行各种处理操作。
我们跳转到osal_run_system()函数,看看里面的内容
void osal_run_system( void )
{
uint8 idx = 0;
osalTimeUpdate();//见1.1
Hal_ProcessPoll(); // This replaces MT_SerialPoll() and osal_check_timer().
//这部分是对串口啊这些进行处理,暂时不做介绍//这部分
do {
if (tasksEvents[idx]) // Task is highest priority that is ready.
{
break;
}
} while (++idx < tasksCnt);//见1.2
if (idx < tasksCnt)
{
uint16 events;
halIntState_t intState;
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
events = tasksEvents[idx];
tasksEvents[idx] = 0; // Clear the Events for this task.
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
events = (tasksArr[idx])( idx, events );
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
tasksEvents[idx] |= events; // Add back unprocessed events to the current task.
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
}
#if defined( POWER_SAVING )
else // Complete pass through all task events with no activity?
{
osal_pwrmgr_powerconserve(); // Put the processor/system into sleep
}
#endif
/* Yield in case cooperative scheduling is being used. */
#if defined (configUSE_PREEMPTION) && (configUSE_PREEMPTION == 0)
{
osal_task_yield();
}
#endif
}1.1、函数osalTimeUpdate()
void osalTimeUpdate( void )
{
uint32 tmp;
uint32 ticks320us;
uint16 elapsedMSec = 0;
// Get the free-running count of 320us timer ticks
tmp = macMcuPrecisionCount();
//每320us定时器2溢出一次,tmp里计的溢出次数
if ( tmp != previousMacTimerTick )
{
// Calculate the elapsed ticks of the free-running timer.
ticks320us = tmp - previousMacTimerTick;
// Store the MAC Timer tick count for the next time through this function.
previousMacTimerTick = tmp;
// update converted number with remaining ticks from loop and the
// accumulated remainder from loop
tmp = (ticks320us * 8) + remUsTicks;//*8/25其实是*320/1000,转换成ms
// Convert the 320 us ticks into milliseconds and a remainder
CONVERT_320US_TO_MS_ELAPSED_REMINDER( tmp, elapsedMSec, remUsTicks );
//这个里面除以25了。temp是被除数,elapsedMSec商,remUsTicks是余数
// Update OSAL Clock and Timers
//判断时间是否到了1ms,如果等于或者超过1ms(elapsedMSec >= 1),则需要轮询任务列表
{
osalClockUpdate( elapsedMSec );
osalTimerUpdate( elapsedMSec );
}
}
}在上面代码部分,大部分已经做出注释了,大家可以结合cc2530的T2定时器看看,涉及到具体的硬件。下面我们需要知道的是上面代码结束时候的函数:
osalTimerUpdate( elapsedMSec );这个部分涉及到osal中一个非常重要的数据链表,是对每个任务的时间操作计时。当有一个事件触发的时候,该事件对应的数据就被添加到这个数据链表中,包括它的任务id,轮询时间,以及事件id,重新加载时间,以及next
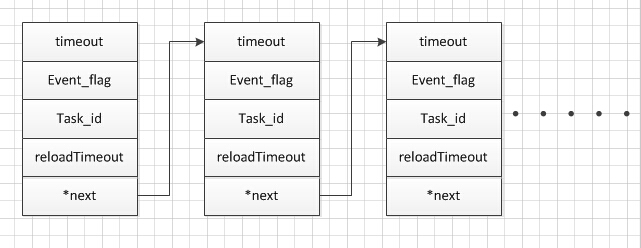
OK,现在我们看看osalTimerUpdata里的内容:
void osalTimerUpdate( uint16 updateTime )
{
halIntState_t intState;
osalTimerRec_t *srchTimer;
osalTimerRec_t *prevTimer;
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Hold off interrupts.
// Update the system time
osal_systemClock += updateTime;
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Re-enable interrupts.
// Look for open timer slot
if ( timerHead != NULL )
{
// Add it to the end of the timer list
srchTimer = timerHead;
prevTimer = (void *)NULL;
// Look for open timer slot
while ( srchTimer )//从头到尾遍历这个链表
{
osalTimerRec_t *freeTimer = NULL;
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Hold off interrupts.
if (srchTimer->timeout <= updateTime)
{
srchTimer->timeout = 0;//timeout时间置0,下面设置事件
}
else
{
srchTimer->timeout = srchTimer->timeout - updateTime;//timeout时间减1
}
// Check for reloading
if ( (srchTimer->timeout == 0) && (srchTimer->reloadTimeout)
&& (srchTimer->event_flag) )//这三个条件都为1
{
// Notify the task of a timeout
osal_set_event( srchTimer->task_id, srchTimer->event_flag );//设置该事件为1
// Reload the timer timeout value
srchTimer->timeout = srchTimer->reloadTimeout;
}
// When timeout or delete (event_flag == 0)
//该事件不需要看,删除事件
{
// Take out of list
if ( prevTimer == NULL )
timerHead = srchTimer->next;
else
prevTimer->next = srchTimer->next;
// Setup to free memory
freeTimer = srchTimer;
// Next
srchTimer = srchTimer->next;
}
else
{
// Get next
prevTimer = srchTimer;
srchTimer = srchTimer->next;
}
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState );
// Re-enable interrupts.
if ( freeTimer )
{
if ( freeTimer->timeout == 0 )
{
osal_set_event( freeTimer->task_id, freeTimer->event_flag );
}
osal_mem_free( freeTimer );
}
}
}
}可以看到,当运行这个函数的时候,会对这个链表进行遍历,对timeout减1,当减到0时,有选择性的重新加载时间或者从该链表中删除该成员,并且将对应的事件置1,以便后边程序处理。
1.2 事件处理操作部分
这里我们先对数组tasksEvents和tasksArr[idx]做出简要介绍。
tasksEvents是一个指针,在z-stack中使用的时候都是当数组使用的,他里面记录的是有没有事件发生,如有有,则相应的位置置1。而taskArr是与tasksEvent里面一一对应的时间处理函数,这部分是一个函数数组。当taskEvents对应位置置1的时候,taskArr相对应的函数进行处理。
在上一篇的叙述的最后,我们提到
osal_set_event(Hal_TaskID, HAL_KEY_EVENT);这个部分已经把对应的tasksEvents[Hal_TaskID]置1,然后通过这段代码
do {
if (tasksEvents[idx]) // Task is highest priority that is ready.
{
break;
}
} while (++idx < tasksCnt);发现已经置1,所以调用
events = (tasksArr[idx])( idx, events );进入Hal_ProcessEvent函数进行处理。接下来调用这段代码
if (events & HAL_KEY_EVENT)
{
#if (defined HAL_KEY) && (HAL_KEY == TRUE)
/* Check for keys */
HalKeyPoll();
/* if interrupt disabled, do next polling */
if (!Hal_KeyIntEnable)
{
osal_start_timerEx( Hal_TaskID, HAL_KEY_EVENT, 100);
}
#endif // HAL_KEY
return events ^ HAL_KEY_EVENT;
}函数HalKeyPoll()是关于按键读取及回调处理函数
void HalKeyPoll (void)
{
uint8 keys = 0;
if ((HAL_KEY_JOY_MOVE_PORT & HAL_KEY_JOY_MOVE_BIT)) /* Key is active HIGH */
{
keys = halGetJoyKeyInput();//按键AD读取,判断是哪个按键
}
/* If interrupts are not enabled, previous key status and current key status
* are compared to find out if a key has changed status.
*/
if (!Hal_KeyIntEnable)//如果不使用中断
{
if (keys == halKeySavedKeys)//如果按键没有变化
{
/* Exit - since no keys have changed */
return;
}
/* Store the current keys for comparation next time */
halKeySavedKeys = keys;
}
else
{
/* Key interrupt handled here */
}
if (HAL_PUSH_BUTTON1())
{
keys |= HAL_KEY_SW_6;
}
/* Invoke Callback if new keys were depressed */
if (keys && (pHalKeyProcessFunction))
{
(pHalKeyProcessFunction) (keys, HAL_KEY_STATE_NORMAL);//按键回调函数
}
}下面就转到回调函数
void OnBoard_KeyCallback ( uint8 keys, uint8 state )
{
uint8 shift;
(void)state;
shift = (keys & HAL_KEY_SW_6) ? true : false;
if ( OnBoard_SendKeys( keys, shift ) != ZSuccess )
{
// Process SW1 here
if ( keys & HAL_KEY_SW_1 ) // Switch 1
{
}
// Process SW2 here
if ( keys & HAL_KEY_SW_2 ) // Switch 2
{
}
// Process SW3 here
if ( keys & HAL_KEY_SW_3 ) // Switch 3
{
}
// Process SW4 here
if ( keys & HAL_KEY_SW_4 ) // Switch 4
{
}
// Process SW5 here
if ( keys & HAL_KEY_SW_5 ) // Switch 5
{
}
// Process SW6 here
if ( keys & HAL_KEY_SW_6 ) // Switch 6
{
}
}
}需要重点注意的这句代码:
nBoard_SendKeys( keys, shift ) != ZSuccess这句代码的意思就是发送数据到app层,进行数据处理
uint8 OnBoard_SendKeys( uint8 keys, uint8 state )
{
keyChange_t *msgPtr;
if ( registeredKeysTaskID != NO_TASK_ID )
{
// Send the address to the task
msgPtr = (keyChange_t *)osal_msg_allocate( sizeof(keyChange_t) );
if ( msgPtr )
{
msgPtr->hdr.event = KEY_CHANGE;
msgPtr->state = state;
msgPtr->keys = keys;
osal_msg_send( registeredKeysTaskID, (uint8 *)msgPtr );
}
return ( ZSuccess );
}
else
return ( ZFailure );
}可以看到把KEY_CHANGE,state,key保存到结构体msgPtr中,然后通过osal_msg_send传递到另外一个重要的链表中,以便应用层处理。
这个链表是用于对两个进程之间进行任务传递的,相当于信号或者邮箱机制。
通过osal_msg_send()函数调用的osal_msg_enqueue()函数,这部分可以发现这里的链表中存的成员可以是不同结构的成员,这部分代码写的比较牛逼。
void osal_msg_enqueue( osal_msg_q_t *q_ptr, void *msg_ptr )
{
void *list;
halIntState_t intState;
// Hold off interrupts
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
OSAL_MSG_NEXT( msg_ptr ) = NULL;
// If first message in queue
if ( *q_ptr == NULL )
{
*q_ptr = msg_ptr;
}
else
{
// Find end of queue
for ( list = *q_ptr; OSAL_MSG_NEXT( list ) != NULL; list = OSAL_MSG_NEXT( list ) );
// Add message to end of queue
OSAL_MSG_NEXT( list ) = msg_ptr;
}
// Re-enable interrupts
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
}
最后通过osal_msg_send()函数将sampleapp的任务置1,实现任务调度。






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








