从整体来看,笔者的做法与之前的模拟多态十分相似,毕竟c++多态的实现与虚函数密切相关
废话少说,see my code:
kernel.c
#include "kernel.h"
#include <stdio.h>
void shape_draw(struct shape_t* obj) {
/* Call draw of the real Instance */
obj->vtable->draw();
}
kernel.h:
#ifndef UNTITLED_KERNEL_H
#define UNTITLED_KERNEL_H
struct shape_t {
/*Virtual Method Table */
const struct shape_interface* const vtable;
};
struct shape_interface {
void (*draw)();
};
void shape_draw(struct shape_t* obj);
//obj->vtable->draw();
#endif //UNTITLED_KERNEL_H
try.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "try.h"
void draw() {
printf("error is try!\n");
}
void draw1() {
printf("error is try2!\n");
}
struct shape_t* shape_create_rectangle() {
//直接赋值,这里有个命名错误,跟gcc有关:
//static const struct shape_interface_t vtable = { draw1 } ;
//static struct shape_t base = { &vtable };
//笔者认为给结构体成员赋值,下面的写法更妥当
static const struct shape_interface vtable = {
.draw = draw1
} ;
static struct shape_t base = {
.vtable = &vtable
};
//推荐上面这种写法,因为某些编译器很有趣
struct rectangle_t* rectangle = malloc(sizeof(*rectangle));
memcpy(&rectangle->base, &base, sizeof(base));
return (struct shape_t*)(&rectangle->base);
}
顺便一提,clion的编译器相当有趣
笔者在之前曾经写错了shape_interface (_t)结构体名称,但是笔者发现:
//static const struct shape_interface_t *vtable = { draw1 } ;
//static struct shape_t base = { &vtable };
改成这样也能运行
这是为什么呢?笔者推测,gcc应该是无法找到对于结构体,就把vtable当成了数组,加上*就成为了数组。然后&vtable就成为了二级指针,由于draw1本身就是一个指针,把它转成空指针什么的可以随便赋值。gcc在找不到对应结构体后,索性为base里的vtable开辟了一段空间,由于&vatble是二级指针,但是找不到对应地址指向,可能它在编译过程中被转为了一级空指针,且等于draw1本身,这样就能解释通了。(如果有c语言高手可以留言解答一下,笔者对c语言和编译器的处理所知甚少)
try.h:
#ifndef UNTITLED_TRY_H
#define UNTITLED_TRY_H
#include "kernel.h"
struct rectangle_t {
struct shape_t* base; /* Reference to Base Class */
/* Rectangle specific Members */
int x;
int y;
};
struct shape_t* shape_create_rectangle();
#endif //UNTITLED_TRY_H
在主函数中这样调用即可:
main.c:
#include "try.h"
#include "kernel.h"
int main() {
struct shape_t* rectangle = shape_create_rectangle();
shape_draw(rectangle);
return 0;
}
接下来是重点,虚函数表的实现,可以适当改动try.c文件:
try.c:
//
// Created by el on 2024/8/16.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "try.h"
void draw() {
printf("error is try!\n");
}
void draw1() {
printf("error is try2!\n");
}
struct shape_t* shape_create_rectangle() {
//static const struct shape_interface *vtable[] = { draw , draw1 } ;
static const struct shape_interface_t *vtable[] = {
.vtable = draw
} ;
static struct shape_t base = { vtable + 1};
struct rectangle_t* rectangle = malloc(sizeof(*rectangle));
memcpy(&rectangle->base, &base, sizeof(base));
return (struct shape_t*)(&rectangle->base);
}
使用函数指针数组,就可以模拟出比较相近的虚函数表。
整个c程序的UML图如下:
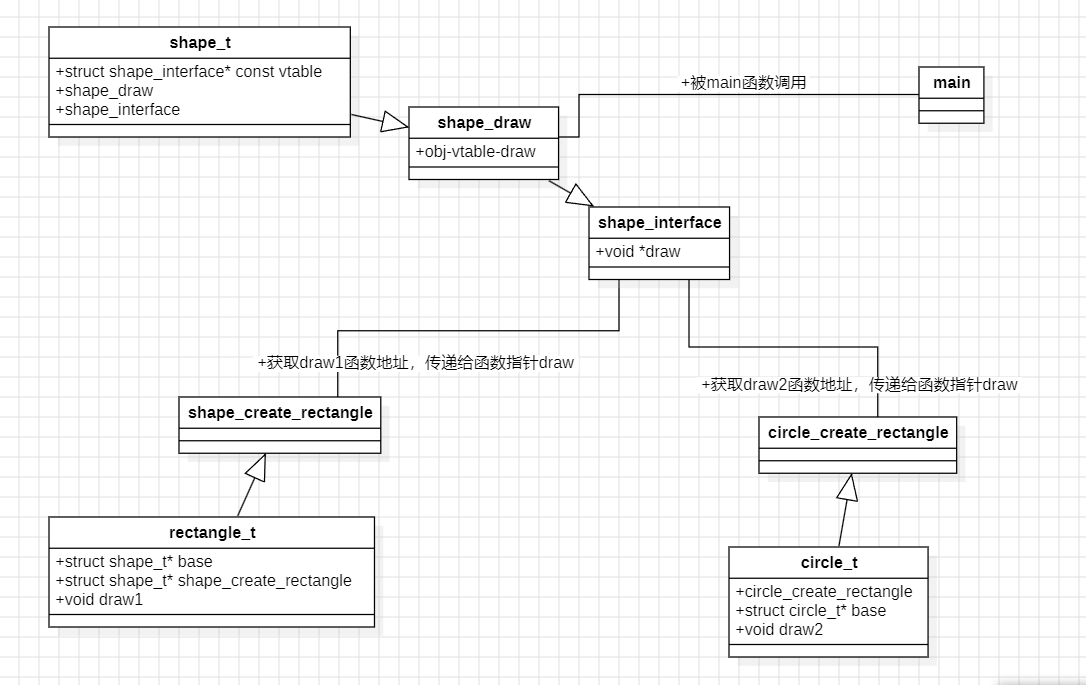
其实这张图跟笔者前一篇模拟多态的文章思想是一样的。






















 1004
1004

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








