SiLU(),
SELayer(inp, hidden_dim),
pw-linear
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
)
def forward(self, x):
if self.identity:
return x + self.conv(x)
else:
return self.conv(x)
主体模块
class EfficientNetv2(nn.Module):
def init(self, cfgs, num_classes=1000, width_mult=1.):
super(EfficientNetv2, self).init()
self.cfgs = cfgs
building first layer
input_channel = _make_divisible(24 * width_mult, 8)
layers = [conv_3x3_bn(3, input_channel, 2)]
building inverted residual blocks
block = MBConv
for t, c, n, s, fused in self.cfgs:
output_channel = _make_divisible(c * width_mult, 8)
for i in range(n):
layers.append(block(input_channel, output_channel, s if i == 0 else 1, t, fused))
input_channel = output_channel
self.features = nn.Sequential(*layers)
building last several layers
output_channel = _make_divisible(1792 * width_mult, 8) if width_mult > 1.0 else 1792
self.conv = conv_1x1_bn(input_channel, output_channel)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.classifier = nn.Linear(output_channel, num_classes)
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
m.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.001)
m.bias.data.zero_()
理解这段代码,我们还需要了解输入参数cfgs,以efficientnetv2_s为例:
def efficientnetv2_s(**kwargs):
“”"
Constructs a EfficientNetV2-S model
“”"
cfgs = [
t, c, n, s, fused
[1, 24, 2, 1, 1],
[4, 48, 4, 2, 1],
[4, 64, 4, 2, 1],
[4, 128, 6, 2, 0],
[6, 160, 9, 1, 0],
[6, 272, 15, 2, 0],
]
return EfficientNetv2(cfgs, **kwargs)
第一列“t”指的是MBConv模块和Fused-MBConv模块第一个输入后放大的倍率。
第二列“c”,channel,指的是输出的channel。
第三列“n”,指定的是MBConv模块和Fused-MBConv模块堆叠的个数。
第四列“s”,指的是卷积的步长,步长为1,图片的大小不变,步长为图片的面积缩小为原来的四分之一,实现降维。
第五列“fused”,选择MBConv模块或Fused-MBConv模块,为1这是Fused-MBConv模块,0则是MBConv模块,对应了前面摘要提过了,在浅层用Fused-MBConv代替MBConv。
完整代码
====
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
all = [‘efficientnetv2_s’, ‘efficientnetv2_m’, ‘efficientnetv2_l’, ‘efficientnetv2_xl’]
from torchsummary import summary
#这个函数的目的是确保Channel能被8整除。
def _make_divisible(v, divisor, min_value=None):
“”"
这个函数的目的是确保Channel能被8整除。
:param v:
:param divisor:
:param min_value:
:return:
“”"
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor
new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%.
if new_v < 0.9 * v:
new_v += divisor
return new_v
SiLU (Swish) activation function
if hasattr(nn, ‘SiLU’):
SiLU = nn.SiLU
else:
For compatibility with old PyTorch versions
class SiLU(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return x * torch.sigmoid(x)
class SELayer(nn.Module):
def init(self, inp, oup, reduction=4):
super(SELayer, self).init()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(oup, _make_divisible(inp // reduction, 8)),
SiLU(),
nn.Linear(_make_divisible(inp // reduction, 8), oup),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y
def conv_3x3_bn(inp, oup, stride):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
SiLU()
)
def conv_1x1_bn(inp, oup):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
SiLU()
)
class MBConv(nn.Module):
“”"
定义MBConv模块和Fused-MBConv模块,将fused设置为1或True是Fused-MBConv,否则是MBConv
:param inp:输入的channel
:param oup:输出的channel
:param stride:步长,设置为1时图片的大小不变,设置为2时,图片的面积变为原来的四分之一
:param expand_ratio:放大的倍率
:return:
“”"
def init(self, inp, oup, stride, expand_ratio, fused):
super(MBConv, self).init()
assert stride in [1, 2]
hidden_dim = round(inp * expand_ratio)
self.identity = stride == 1 and inp == oup
if fused:
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
fused
nn.Conv2d(inp, hidden_dim, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
SiLU(),
SELayer(inp, hidden_dim),
pw-linear
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
)
else:
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
pw
nn.Conv2d(inp, hidden_dim, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
SiLU(),
dw
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, 3, stride, 1, groups=hidden_dim, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
SiLU(),
SELayer(inp, hidden_dim),
pw-linear
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
)
def forward(self, x):
if self.identity:
return x + self.conv(x)
else:
return self.conv(x)
class EfficientNetv2(nn.Module):
def init(self, cfgs, num_classes=1000, width_mult=1.):
super(EfficientNetv2, self).init()
self.cfgs = cfgs
building first layer
input_channel = _make_divisible(24 * width_mult, 8)
layers = [conv_3x3_bn(3, input_channel, 2)]
building inverted residual blocks
block = MBConv
for t, c, n, s, fused in self.cfgs:
output_channel = _make_divisible(c * width_mult, 8)
for i in range(n):
layers.append(block(input_channel, output_channel, s if i == 0 else 1, t, fused))
input_channel = output_channel
self.features = nn.Sequential(*layers)
building last several layers
output_channel = _make_divisible(1792 * width_mult, 8) if width_mult > 1.0 else 1792
self.conv = conv_1x1_bn(input_channel, output_channel)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.classifier = nn.Linear(output_channel, num_classes)
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
m.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.001)
m.bias.data.zero_()
def efficientnetv2_s(**kwargs):
“”"
Constructs a EfficientNetV2-S model
“”"
cfgs = [
t, c, n, s, fused
[1, 24, 2, 1, 1],
[4, 48, 4, 2, 1],
[4, 64, 4, 2, 1],
[4, 128, 6, 2, 0],
[6, 160, 9, 1, 0],
[6, 272, 15, 2, 0],
]
return EfficientNetv2(cfgs, **kwargs)
def efficientnetv2_m(**kwargs):
“”"
Constructs a EfficientNetV2-M model
“”"
cfgs = [
t, c, n, s, fused
如果你也是看准了Python,想自学Python,在这里为大家准备了丰厚的免费学习大礼包,带大家一起学习,给大家剖析Python兼职、就业行情前景的这些事儿。
一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向路线就是把Python常用的技术点做整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
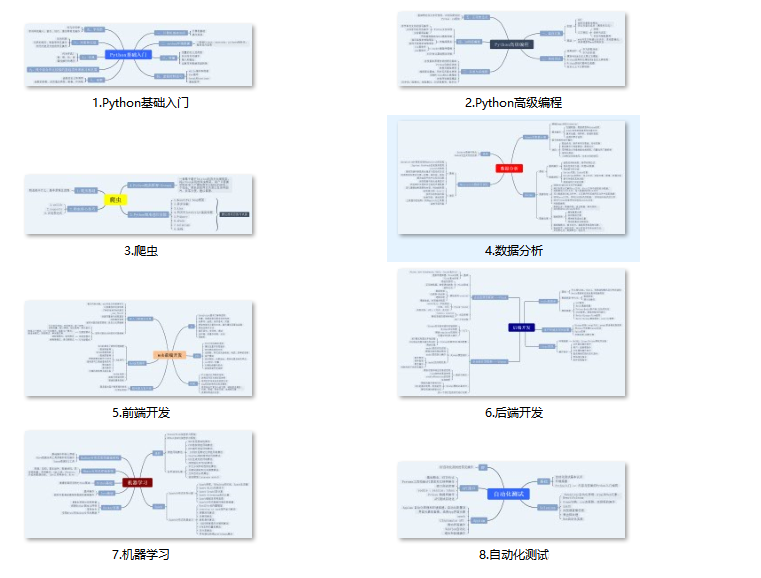
二、学习软件
工欲善其必先利其器。学习Python常用的开发软件都在这里了,给大家节省了很多时间。
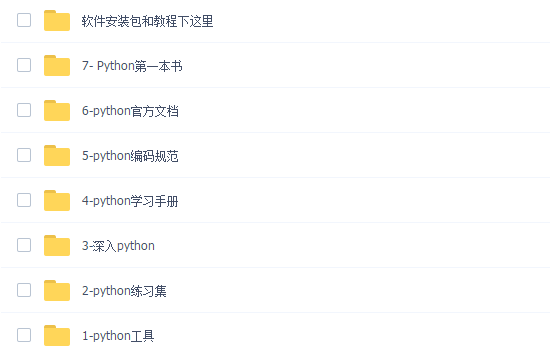
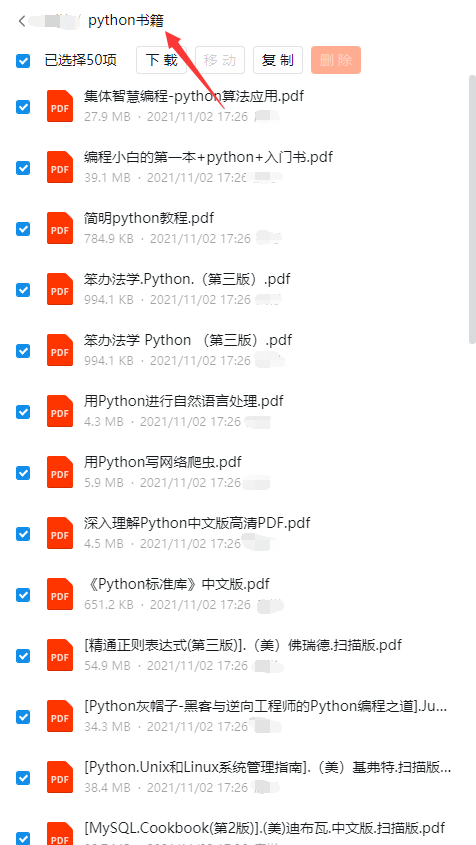
三、全套PDF电子书
书籍的好处就在于权威和体系健全,刚开始学习的时候你可以只看视频或者听某个人讲课,但等你学完之后,你觉得你掌握了,这时候建议还是得去看一下书籍,看权威技术书籍也是每个程序员必经之路。
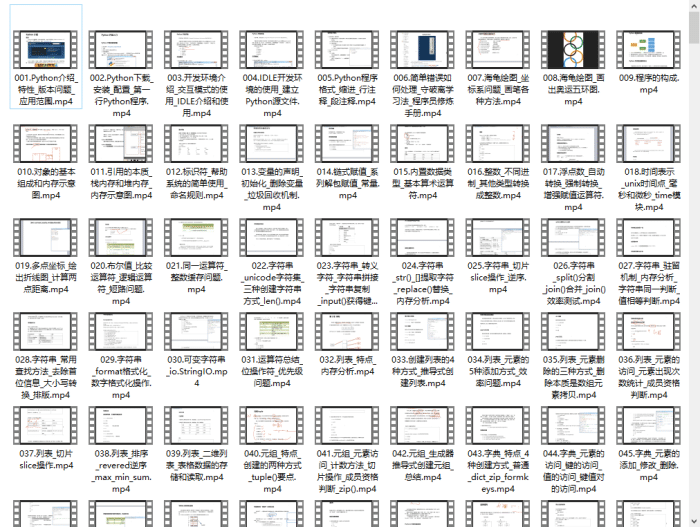
四、入门学习视频
我们在看视频学习的时候,不能光动眼动脑不动手,比较科学的学习方法是在理解之后运用它们,这时候练手项目就很适合了。
四、实战案例
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。
五、面试资料
我们学习Python必然是为了找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题是来自阿里、腾讯、字节等一线互联网大厂最新的面试资料,并且有阿里大佬给出了权威的解答,刷完这一套面试资料相信大家都能找到满意的工作。
成为一个Python程序员专家或许需要花费数年时间,但是打下坚实的基础只要几周就可以,如果你按照我提供的学习路线以及资料有意识地去实践,你就有很大可能成功!
最后祝你好运!!!
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!




















 1376
1376











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








