
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
- string是表示字符串的字符串类
- 该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
在使用string类时,必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
string和char * 区别:
- char * 是一个指针
- string是一个类,类内部封装了char*,管理这个字符串,是一个char*型的容器。
特点:
string 类内部封装了很多成员方法
例如:查找find,拷贝copy,删除delete 替换replace,插入insert
string管理char*所分配的内存,不用担心复制越界和取值越界等,由类内部进行负责
1.2 string构造函数
官方提供的所有构造函数

我们已学习的角度主要重点掌握以下几个
构造函数原型:
string();//创建一个空的字符串 例如: string str;
string(const char* s);//使用字符串s初始化string(const string& str);//使用一个string对象初始化另一个string对象string(int n, char c);//使用n个字符c初始化
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
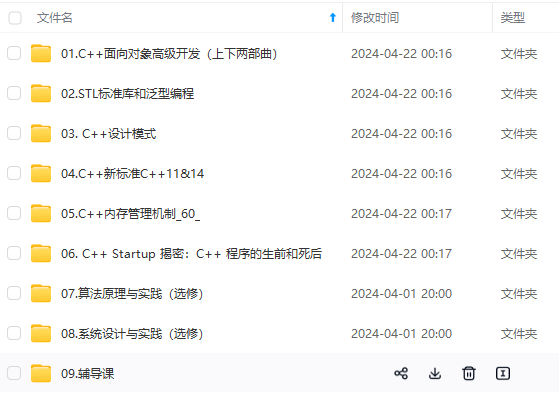
//string构造
string s1; //创建空字符串,调用无参构造函数
cout << "str1 = " << s1 << endl;
const char\* str = "hello world";
string s2(str); //把c\_string转换成了string
cout << "str2 = " << s2 << endl;
string s3(s2); //调用拷贝构造函数
cout << "str3 = " << s3 << endl;
string s4(10, 'a');
cout << "str3 = " << s3 << endl;
return 0;
}
1.3 string访问和修改
string中单个字符存取方式有两种
char& operator[](int n);//通过[]方式取字符char& at(int n);//通过at方法获取字符
示例:
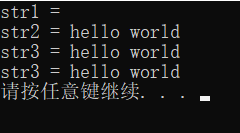
void test01()
{
string str = "hello world";
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
cout << str[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
cout << str.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//字符修改
str[0] = 'x';
str.at(1) = 'x';
cout << str << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
return 0;
}
总结:string字符串中单个字符存取有两种方式,利用 [ ] 或 at
1.4 string插入和删除
功能描述:
- 对string字符串进行插入和删除字符操作
函数原型:
string& insert(int pos, const char* s);//插入字符串string& insert(int pos, const string& str);//插入字符串string& insert(int pos, int n, char c);//在指定位置插入n个字符cstring& erase(int pos, int n = npos);//删除从Pos开始的n个字符
示例:
//字符串插入和删除
int main() {
string str = "hello";
str.insert(1, "111");
cout << str << endl;
str.erase(1, 3); //从1号位置开始3个字符
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}
**总结:**插入和删除的起始下标都是从0开始

1.5 string赋值操作
功能描述:
- 给string字符串进行赋值
赋值的函数原型:
string& operator=(const char* s);//char*类型字符串 赋值给当前的字符串string& operator=(const string &s);//把字符串s赋给当前的字符串string& operator=(char c);//字符赋值给当前的字符串string& assign(const char *s);//把字符串s赋给当前的字符串string& assign(const char *s, int n);//把字符串s的前n个字符赋给当前的字符串string& assign(const string &s);//把字符串s赋给当前字符串string& assign(int n, char c);//用n个字符c赋给当前字符串
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
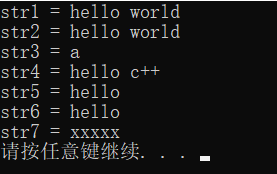
int main() {
//赋值
string str1;
str1 = "hello world";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str2;
str2 = str1;
cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
string str3;
str3 = 'a';
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
string str4;
str4.assign("hello c++");
cout << "str4 = " << str4 << endl;
string str5;
str5.assign("hello c++",5);
cout << "str5 = " << str5 << endl;
string str6;
str6.assign(str5);
cout << "str6 = " << str6 << endl;
string str7;
str7.assign(5, 'x');
cout << "str7 = " << str7 << endl;
return 0;
}
总结:
string的赋值方式很多,operator= 这种方式是比较实用的
1.5 string字符串拼接
功能描述:
- 实现在字符串末尾拼接字符串
函数原型:
string& operator+=(const char* str);//重载+=操作符string& operator+=(const char c);//重载+=操作符string& operator+=(const string& str);//重载+=操作符string& append(const char *s);//把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾string& append(const char *s, int n);//把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾string& append(const string &s);//同operator+=(const string& str)string& append(const string &s, int pos, int n);//字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//字符串拼接
string str1 = "我";
str1 += "爱玩游戏";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
str1 += ':';
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str2 = "Minecraft";
str1 += str2;
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str3 = "I";
str3.append(" love ");
str3.append("game abcde", 4);
//str3.append(str2);
str3.append(str2, 4, 3); // 从下标4位置开始 ,截取3个字符,拼接到字符串末尾
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
return 0;
}
总结:字符串拼接的重载版本很多,重点记住几种即可

注意:
- 在string尾部追加字符时,s.push_back© / s.append(1, c) / s += 'c’三种的实现方式差不多,一般
情况下string类的+=操作用的比较多,+=操作不仅可以连接单个字符,还可以连接字符串。 - 对string操作时,如果能够大概预估到放多少字符,可以先通过reserve把空间预留好。
1.7 string查找和替换
功能描述:
- 查找:查找指定字符串是否存在
- 替换:在指定的位置替换字符串
函数原型:
int find(const string& str, int pos = 0) const;//查找str第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找int find(const char* s, int pos = 0) const;//查找s第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找int find(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;//从pos位置查找s的前n个字符第一次位置int find(const char c, int pos = 0) const;//查找字符c第一次出现位置string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& str);//替换从pos开始n个字符为字符串strstring& replace(int pos, int n,const char* s);//替换从pos开始的n个字符为字符串s
示例:
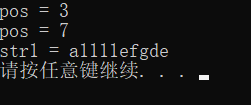
//查找和替换
void test01()
{
//查找
string str1 = "abcdefgde";
int pos = str1.find("de");
if (pos == -1)
{
cout << "未找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "pos = " << pos << endl;
}
pos = str1.rfind("de");
cout << "pos = " << pos << endl;
}
void test02()
{
//替换
string str1 = "abcdefgde";
str1.replace(1, 3, "1111");
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
总结:
- find找到字符串后返回查找的第一个字符位置,找不到返回-1
- replace在替换时,要指定从哪个位置起,多少个字符,替换成什么样的字符串
1.8 string子串
功能描述:
- 从字符串中获取想要的子串
函数原型:
string substr(int pos = 0, int n = npos) const;//返回由pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串
示例:
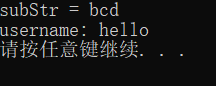
//子串
int main() {
string str = "abcdefg";
string subStr = str.substr(1, 3);
cout << "subStr = " << subStr << endl;
string email = "hello@sina.com";
int pos = email.find("@");
string username = email.substr(0, pos);
cout << "username: " << username << endl;
return 0;
}
1.9 string类对象的容量操作
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| size(重点) | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| length | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| capacity | 返回空间总大小 |
| empty (重点) | 检测字符串释放为空串,是返回true,否则返回false |
| clear (重点) | 清空有效字符 |
| reserve (重点) | 为字符串预留空间 |
| resize (重点) | 将有效字符的个数该成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充 |
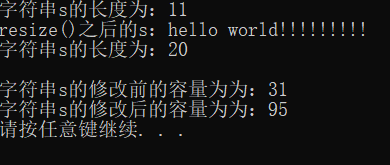
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
cout << "字符串s的长度为:"<<s.size() << endl;
s.resize(20, '!');
cout <<"resize()之后的s:"<< s << endl;
cout << "字符串s的长度为:" << s.size() << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "字符串s的修改前的容量为为:" << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(95);
cout << "字符串s的修改后的容量为为:" << s.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
注意:
- size()与length()方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入size()的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一
致,一般情况下基本都是用size()。 - clear()只是将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小。
- resize(size_t n) 与 resize(size_t n, char c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字
符个数增多时:resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的
元素空间。注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大
小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变。 - reserve(size_t res_arg=0):为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于
string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量大小。
2. string类的模拟实现
上面已经对string类进行了简单的介绍,大家只要能够正常使用即可。在面试中,面试官总喜欢让我们自己
来模拟实现string类,最主要是实现string类的构造、拷贝构造、赋值运算符重载以及析构函数。
这里主要把最主要的几个函数接口实现特殊拿出来处理,其他的完整实现就放在最下面的mini版string完整代码中
实现string的构造
string的构造有很多,我们没必要全部实现,只需实现最主要的即可!
下面我们用一个缺省的构造函数,可以实现无参和有参字符串的构造。
为了避免和C++标椎库中的string冲突,我们可以用命名空间封装起来,下面全部的模拟实现都在该命名空间中
namespace hdm
{
class string
{
public:
//构造函数
string(const char\* str = "")
{
_size = strlen(str);
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
private:
char \* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
const static size_t npos = -1;
};
}
实现string的析构函数
析构函数相对来说比较简单,我们只需要对字符串的空间进行释放即可
~string()
{
delete[]_str;
_str = nullptr;
_capacity = _size = 0;
}
实现reserve和resize
reserve是为字符串预留空间,简单来说就是用来预先开辟好空间(扩容),避免后续频繁扩容。
resize是将有效字符的个数该成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充,具体代码如下
注意:resize要分情况讨论
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char \* tem = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tem, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tem;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void resize(size_t n, const char c)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
for (size_t i = _size; i < n; ++i)
{
push\_back(c);
}
}
else if (n > _size)
{
for (size_t i = _size; i < n; ++i)
{
push\_back(c);
}
}
_size = n;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
实现string的拷贝构造
string的拷贝构造有两种写法
- 老老实实中规中矩的写法
重新开辟一个空间,将字符串拷贝到新空间上
//传统写法
string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
_capacity = s._capacity;
_size = s._size;
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
- 现代写法
可以叫工具人写法,直接用要拷贝对象的字符串来构造一个临时对象,然后用它来交换即可
//现代写法
string(const string &s)
:\_str(nullptr)
, \_size(0)
, \_capacity(0)
{
string tem(s._str);
swap(tem);
}
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
实现string赋值运算符重载
string的赋值运算符重载也有两种方式实现
- 老老实实中规中矩的写法
自己开空间,自己拷贝数据
//传统写法
string& operator=(const string &s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
char \* tem = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(tem, s._str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tem;
_capacity = s._capacity;
_size = s._size;
}
return \*this;
}
- 现代写法
也是工具人写法,本质上跟拷贝构造一个道理
//现代写法
string& operator=(string s)
{
swap(s);
return \*this;
}
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);


**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加戳这里获取](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618668825)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**
1. 老老实实中规中矩的写法
自己开空间,自己拷贝数据
//传统写法
string& operator=(const string &s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
char * tem = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(tem, s._str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tem;
_capacity = s._capacity;
_size = s._size;
}
return \*this;
}
2. 现代写法
也是工具人写法,本质上跟拷贝构造一个道理
//现代写法
string& operator=(string s)
{
swap(s);
return *this;
}
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
[外链图片转存中…(img-iFyZEfFx-1715588751762)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-HsyZPSXo-1715588751763)]
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!






















 235
235

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








