点击蓝字

关注我们
AI TIME欢迎每一位AI爱好者的加入!

哔哩哔哩直播通道
扫码关注AI TIME哔哩哔哩官方账号预约直播
✦+
+
活动时间
2023年5月27日9:30-11:30

Bio
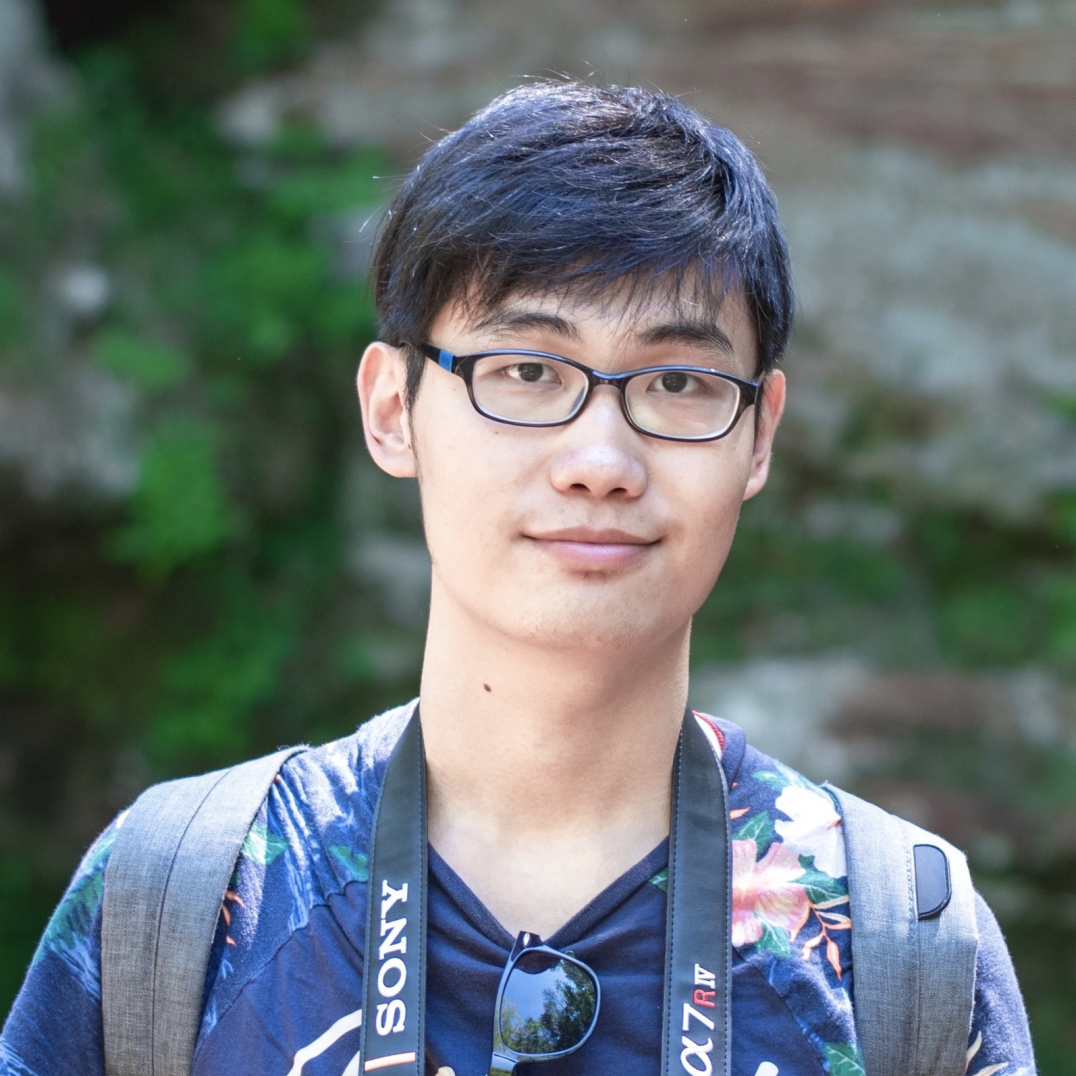
Xiang Yue:
Xiang Yue is now a 5th-year Ph.D. candidate at The Ohio State University. He has broad research interests in Natural Language Processing (NLP) with an emphasis on building Responsible and Trustworthy NLP systems, which covers aspects like generalizability, privacy and faithfulness. He has published more than 20 peer-reviewed research papers, among which 8 are (co)first-author on the top conferences or journals, and has ∼1000 citations according to Google Scholar. He won the Best Paper Award at the IEEE BIBM 2021 conference. He was a core member of the OSU TacoBot team which won third place in the first Alexa Prize TaskBot challenge. He interned at Microsoft Research (Redmond) and Tencent AI Lab (Seattle), where he gained hands-on experience in building machine learning and NLP models for large-scale real-world data.
Title
Mitigating Privacy Risks in Large Language Models: A Synthetic Data Generation Perspective
Abstract
Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable progress in natural language processing tasks, but their success raises privacy concerns as they may inadvertently leak sensitive information of training data. Generating synthetic versions of training data with a formal privacy guarantee such as differential privacy (DP) is considered to be a solution to address privacy concerns. In this direction, we show a simple, practical, and effective recipe in the text domain: simply fine-tuning a generative language model with DP allows us to generate useful synthetic text while mitigating privacy concerns. Through extensive empirical analyses, we demonstrate that our method produces synthetic data that is competitive in terms of utility with its non-private counterpart and meanwhile provides strong protection against potential privacy leakages.

Bio
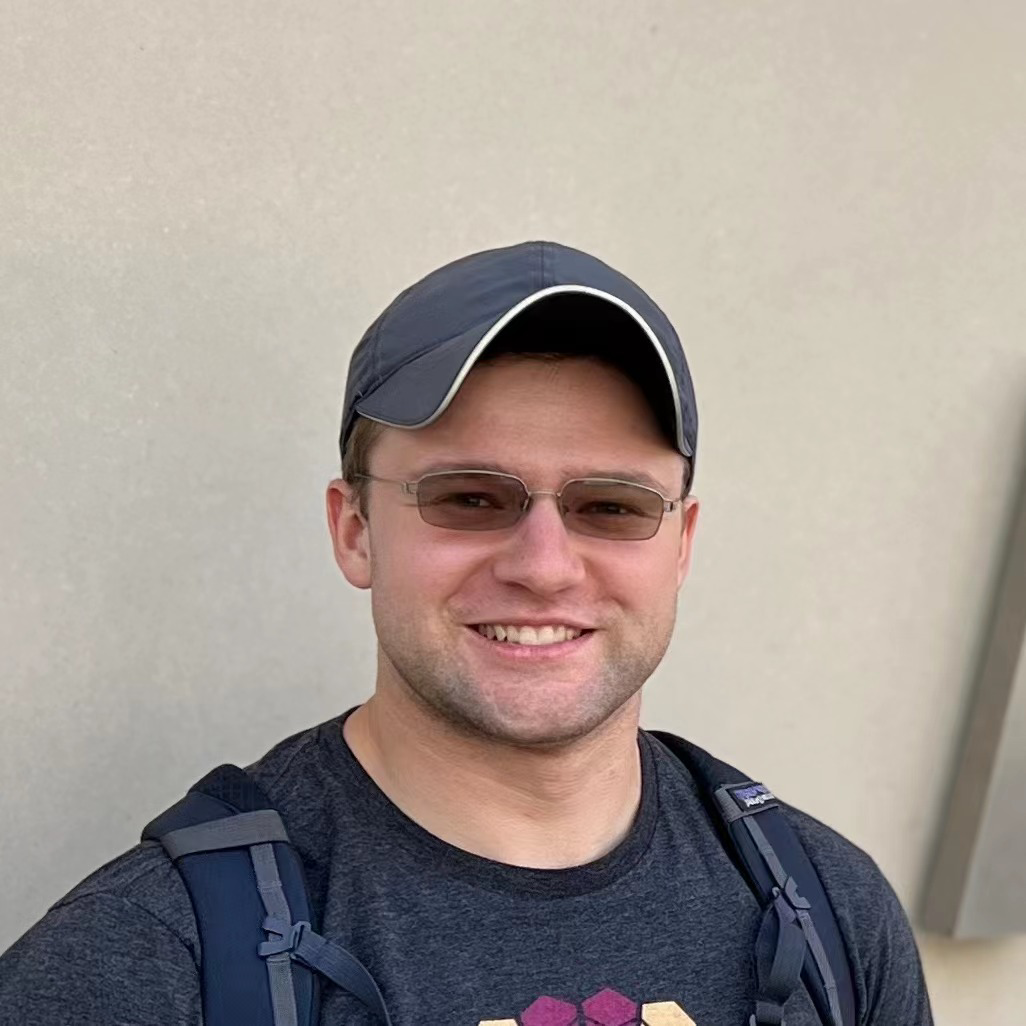
Sam Stevens:
Sam Stevens is a 2nd-year PhD student at The Ohio State University with interests in foundation-scale models in natural language processing and computer vision. His work is often cross-disciplinary, bringing large pre-trained models to fields like encryption and biology. He was a member of OSU's third-place Alexa Prize Taskbot team and will be interning at Meta AI the summer of 2023.
Title
Memorization for Good: Encryption with Autoregressive Language Models
Abstract
Over-parameterized neural language models (LMs) can memorize and recite long sequences of training data. While such memorization is normally associated with undesired properties such as overfitting and information leaking, our work casts memorization as an unexplored capability of LMs. We propose the first symmetric encryption algorithm with autoregressive language models (SELM). We show that autoregressive LMs can encode arbitrary data into a compact real-valued vector (i.e., encryption) and then losslessly decode the vector to the original message (i.e., decryption) via random subspace optimization and greedy decoding. While SELM is not amenable to conventional cryptanalysis, we investigate its security through a novel empirical variant of the classic IND-CPA (indistinguishability under chosen-plaintext attack) game.

Bio
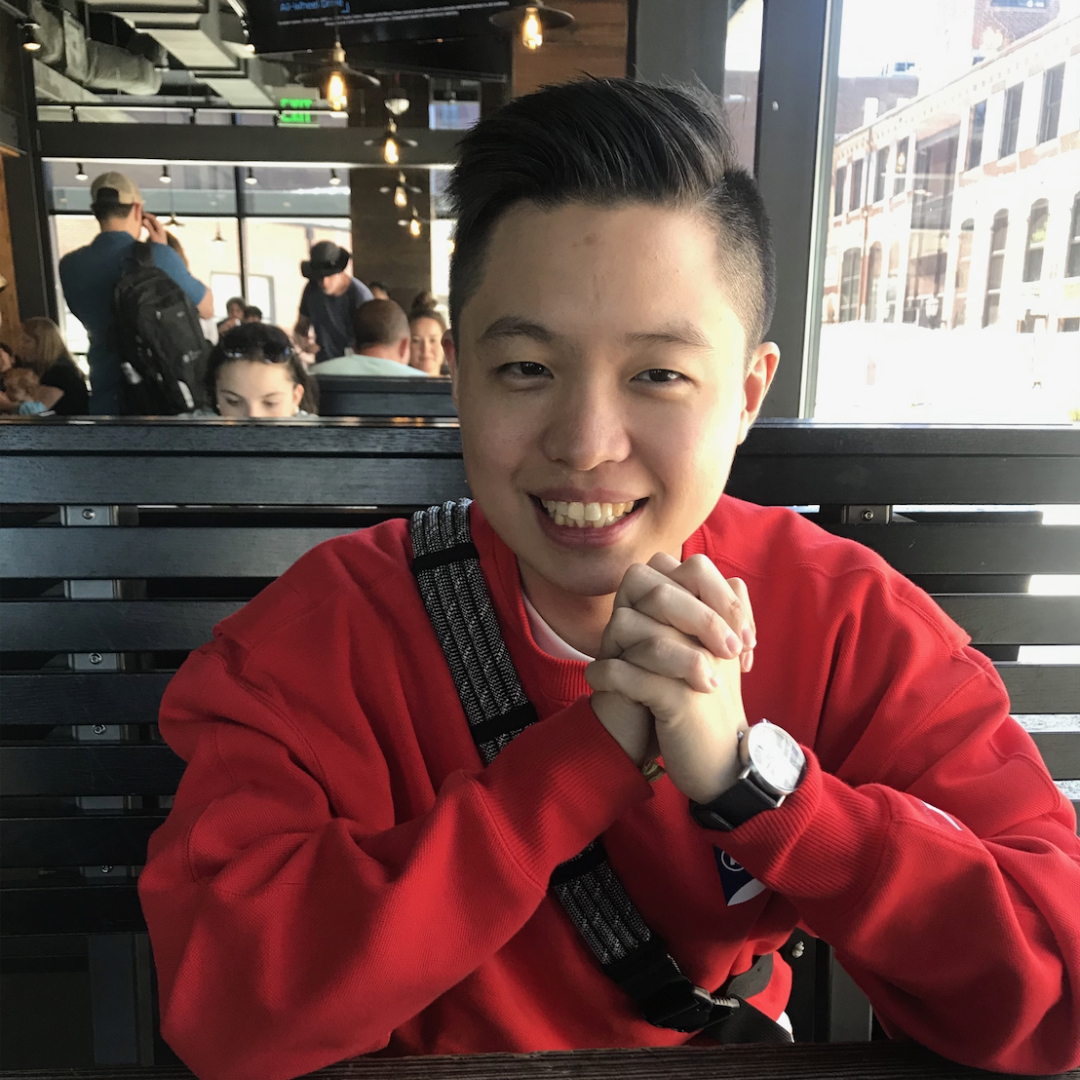
Chan Hee (Luke) Song:
Chan Hee (Luke) Song is a 3rd-year PhD student at The Ohio State University. He has broad research interests in the interaction between text and image with an emphasis on embodied AI, which is a multi-disciplinary field that spans across foundation models, dialogue systems, and knowledge bases/graphs. He has published papers in conferences such as CVPR, AAAI and is the team lead in the ongoing 1st Alexa Prize Simbot Challenge. He will be interning at Adobe Research in the summer of 2023.
Title
LLM-Planner: Few-Shot Grounded Planning for Embodied Agents with Large Language Models
Abstract
This study focuses on using large language models (LLMs) as a planner for embodied agents that can follow natural language instructions to complete complex tasks in a visually-perceived environment. The high data cost and poor sample efficiency of existing methods hinders the development of versatile agents that are capable of many tasks and can learn new tasks quickly. In this work, we propose a novel method, LLM-Planner, that harnesses the power of large language models to do few-shot planning for embodied agents. We further propose a simple but effective way to enhance LLMs with physical grounding to generate and update plans that are grounded in the current environment. Experiments on the ALFRED dataset show that our method can achieve very competitive few-shot performance: Despite using less than 0.5% of paired training data, LLM-Planner achieves competitive performance with recent baselines that are trained using the full training data. Existing methods can barely complete any task successfully under the same few-shot setting. Our work opens the door for developing versatile and sample-efficient embodied agents that can quickly learn many tasks.

Bio
Boshi Wang:
Boshi Wang is a 2nd-year PhD at The Ohio State University. He has broad research interests in Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning, and is currently focusing on understanding and improving the reasoning abilities of language models. He has published papers in top NLP/ML conferences such as EMNLP, ICLR and ICML. He previously interned at Microsoft Research Asia.
Title
Towards Reasoning in Large Language Models: The Curious Case of Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Abstract
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting can dramatically improve the complex reasoning abilities of large language models (LLMs). CoT explicitly encourages the LLM to generate intermediate rationales for solving a problem, by providing a series of reasoning steps in the demonstrations. Despite its success, there is still little understanding of what makes CoT effective and which aspects of the demonstrated reasoning steps contribute to its performance. In this talk, I will introduce our recent work towards better understanding CoT prompting. Specifically, we find that CoT reasoning is possible even with invalid demonstrations - prompting with invalid reasoning steps can achieve over 80-90% of the performance obtained using CoT under various metrics, while still generating coherent lines of reasoning during inference. Further experiments show that other aspects of the rationales, such as being relevant to the query and correctly ordering the reasoning steps, are much more important for effective CoT reasoning. Overall, these findings lead to new questions regarding LLMs' capability to learn to reason in context, and reflections on benchmarking few-shot reasoning.

Bio
Yu Gu:
Yu Gu is a fourth-year Ph.D. student at The Ohio State University working with Prof. Yu Su. His research is primarily focused on natural language processing and knowledge bases, with a particular emphasis on developing natural language interfaces for structured data and services. He has published at conferences including ACL, WWW, WSDM, and NAACL, and his research has won the COLING Outstanding Paper Award. He previously interned at Microsoft Research.
Title
Don't Generate, Discriminate: A Proposal for Grounding Language Models to Real-World Environments
Abstract
A key missing ability of current language models (LMs) is grounding to real-world environments. Most existing work for grounded language understanding uses LMs to directly generate plans that can be executed in the environment to achieve the desired effects. It casts the burden of ensuring grammaticality, faithfulness, and controllability all on the LMs. We propose Pangu, a generic framework for grounded language understanding that capitalizes on the discriminative ability of LMs instead of their generative ability. Pangu consists of a symbolic agent and a neural LM working in a concerted fashion: the agent explores the environment to incrementally construct valid candidate plans, and the LM evaluates the plausibility of the candidate plans to guide the search process. A case study on the challenging problem of knowledge base question answering (KBQA), which features a massive environment, demonstrates the remarkable effectiveness and flexibility of Pangu: A BERT-base LM is sufficient for achieving a new state of the art on standard KBQA datasets, and larger LMs further improve the performance by a large margin. Pangu also enables, for the first time, effective few-shot in-context learning for KBQA with large LMs such as Codex.

Bio
张 凯:
张凯是俄亥俄州立大学一年级博士生,研究兴趣是自然语言处理及其现实世界应用,例如信息抽取和问答,目前专注于知识与大模型的相互作用。他曾于顶级会议ACL, EMNLP, NAACL等发表多篇工作。此外,他曾在清华自然语言处理实验室,达特茅斯学院,和微软担任研究实习生。
个人主页 https://drogozhang.github.io
Title
指令任务对齐解锁大模型的零样本关系抽取能力(Aligning Instruction Tasks Unlocks Large Language Models as Zero-Shot Relation Extractors)
Abstract
大规模的指令微调 (instruction-tuning) 被证明可以显着提高大型语言模型 (LLMs) 在各种 NLP 任务上的性能,尤其是在零样本场景中。然而,即使是最先进的两个指令微调LLMs (text-davinci-003和FLAN-T5 XXL)在关系提取任务上也无法胜过小的零样本基线。我们假设这一反直觉现象是因为关系抽取任务在指令调优数据集中的比例很低,占所有任务的不到0.5%。对此,我们提出QA4RE框架将关系抽取与问答任务对齐。
QA4RE在四个关系抽取数据集和GPT-3.5以及FLAN-T5两个系列的总共六个指令调优LLMs上取得了非常显著的提升。此外,QA4RE具有鲁棒性、小样本有效性、和模型大小的可迁移性等优点。我们的工作说明,通过把指令微调阶段少见的任务(如关系抽取)与在更常见的任务(如问答)对齐,可以更好的让LLMs解决下游任务。
请添加“AI TIME小助手(微信号:AITIME_HY)”,回复“大模型”,将拉您进群!
AI TIME微信小助手

往期精彩文章推荐
记得关注我们呀!每天都有新知识!
关于AI TIME
AI TIME源起于2019年,旨在发扬科学思辨精神,邀请各界人士对人工智能理论、算法和场景应用的本质问题进行探索,加强思想碰撞,链接全球AI学者、行业专家和爱好者,希望以辩论的形式,探讨人工智能和人类未来之间的矛盾,探索人工智能领域的未来。
迄今为止,AI TIME已经邀请了1000多位海内外讲者,举办了逾550场活动,超600万人次观看。

我知道你
在看
哦
~
点击 阅读原文 预约直播!






















 1
1











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








