-
4 3 2 0 0 1 0 1.2 0 2 2 0 0 1 0 2 1 0 0 1.2 0 2 1 0 0 1 0
样例输出
-
1 2 1 -1
描述
In Yan Yuan, the Peking University campus, there are many homeless cats. They all live happy lives because students founded a Cat Association to take care of them. Students not only feed them, but also treat their illness and sterilize some of them. Students make many feeding spots for the cats and cats always gather around those spots and make a lot of noise at night. Now the university authorities decide to restrict the number of feeding spots. This is the conversation between an officer and Rose Li, the director of Cat Association, and also a ACMer.
"Rose, From now on, you can't build any new feeding spots any more. But I want you to keep exactly N feeding spots, and you should make the area which contains the feeding spots as small as possible!"
"Oh, do you mean that we should find a smallest convex hull which contains N spots?"
"Convex hull? What is a convex hull? Please speak Chinese!"
"All right, forget the convex hull. So what do you mean the 'area', what's its shape?"
"It means... and the shape? Oh... let's do it this way: you can choose any feeding spot as center, and then draw a circle which includes exactly N spots. You should find the smallest circle of such kind, and then we remove all feeding spots outside that circle."
Although this way sounds a little bit ridiculous, Rose still writes a program to solve the problem. Can you write the program?
输入
The first line is an integer T (T <= 50), meaning the number of test cases.
Then T lines follow, each describing a test case.
For each test case:
Two integer M and N go first(1 <= M, N <= 100), meaning that there are M feeding spots originally and Rose Li has to keep exactly N spots.
Then M pairs of real numbers follow, each means a coordinate of a feeding spot in Yan Yuan. The range of coordinates is between [-1000,1000]
输出
For each test case, print the radius of the smallest circle. Please note that the radius must be an POSITIVE INTEGER and no feeding spots should be located just on the circle because it's hard for the campus gardeners to judge whether they are inside or outside the circle. If there are no solution, print "-1" instead.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#define LL long long
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define RR freopen("in.txt","r",stdin)
#define WW freopen("in.txt","w",stdout);
#define eps 1e-12
using namespace std;
struct node
{
double x, y;
} q[110];
double ou_dis(node a, node b)
{
double ans;
ans = (a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x) + (a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y);
return sqrt(ans);
}
double g[110][110];
int main()
{
// RR;
int tg;
scanf("%d", &tg);
int m, n;
int ans;
bool ok;
int i, j;
while(tg--)
{
ok=false;
scanf("%d %d", &m, &n);
for(i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
scanf("%lf %lf", &q[i].x, &q[i].y);
}
for(i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
for(j=1; j<=m; j++)
{
if(i!=j)
{
g[i][j] = ou_dis(q[i], q[j]);
}
else
{
g[i][j] = 0.0;
}
}
}
if(m == 1 && n == 1)
{
cout<<1<<endl;
continue;
}
if(n > m)
{
cout<<-1<<endl;
continue;
}
if(m == n)
{
int dd = INF;
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
int dt = -INF;
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++)
{
dt = max(dt,(int )g[i][j]+1);
}
dd = min(dt,dd);
}
cout<<dd<<endl;
continue;
}
double cur[110];
for(i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
for(j=1; j<=m; j++)
{
cur[j]=g[i][j];
}
sort(cur+1, cur+m+1);
/* for(int k=1; k<=m; k++){
printf("%lf ", cur[k]);
}printf("\n\n"); */
double dd=cur[n];
int ff=ceil(dd+eps);
// printf("ff = %d**\n", ff);
double gg=(double)ff;
bool z=true;
for(j=n+1; j<=m; j++)
{
if( gg-cur[j] >= -eps )
{
//false;
z=false;
break;
}
}
if(z==true)
{
if(ok==true)
{
if(ans > ff) ans=ff;
}
else
{
ans = ff;
ok=true;
}
}
}
if(ok)
printf("%d\n", ans);
else
printf("-1\n");
}
return 0;
}Fractal
时间限制: 1000ms-
3 0.375 0.001 0.478
样例输出
-
-1 4 20
描述
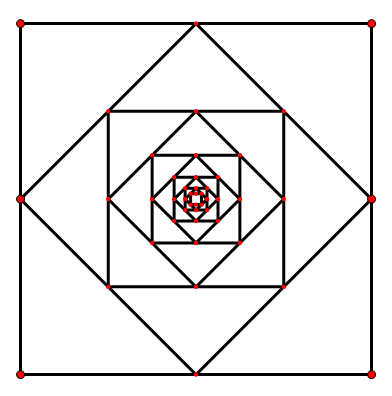
This is the logo of PKUACM 2016. More specifically, the logo is generated as follows:
1. Put four points A0(0,0), B0(0,1), C0(1,1), D0(1,0) on a cartesian coordinate system.
2. Link A0B0, B0C0, C0D0, D0A0 separately, forming square A0B0C0D0.
3. Assume we have already generated square AiBiCiDi, then square Ai+1Bi+1Ci+1Di+1 is generated by linking the midpoints of AiBi, BiCi, CiDi and DiAi successively.
4. Repeat step three 1000 times.
Now the designer decides to add a vertical line x=k to this logo( 0<= k < 0.5, and for k, there will be at most 8 digits after the decimal point). He wants to know the number of common points between the new line and the original logo.
输入
In the first line there’s an integer T( T < 10,000), indicating the number of test cases.
Then T lines follow, each describing a test case. Each line contains an float number k, meaning that you should calculate the number of common points between line x = k and the logo.
输出
For each test case, print a line containing one integer indicating the answer. If there are infinity common points, print -1.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#define LL long long
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define RR freopen("in.txt","r",stdin)
#define WW freopen("in.txt","w",stdout);
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
double x,key;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%lf",&key);
int cnt=0;
x=0;
while(1)
{
if(x==key)
{
printf("-1\n");
break;
}
else if(key<x)
{
printf("%d\n",cnt*4);
break;
}
x+=(0.5-x)/2;
cnt++;
}
}
return 0;
}




















 5297
5297

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








