线程
例1
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private int ticket = 200;
public MyThread(){
}
public MyThread(String name){
super(name);
}
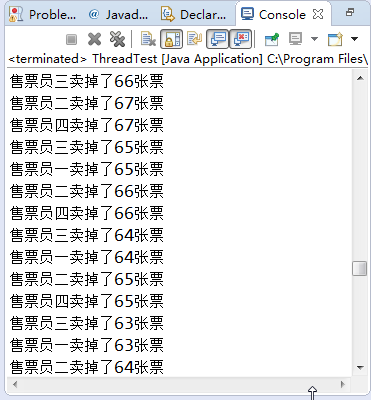
public void run() {
while (ticket >0) {
System.out.println(getName()+"卖掉了" +ticket-- + "张票");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread t1=new MyThread("售票员一");
MyThread t2=new MyThread("售票员二");
MyThread t3=new MyThread("售票员三");
MyThread t4=new MyThread("售票员四");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}例2
使用Runnable接口启动新的线程的步骤如下:
1、建立Runnable对象(建立类implements Runnable);
2、使用参数为Runnable对象的构造方法创建Thread实例;
3、调用start()方法启动线程。
Thread中有两个构造方法:
public Thread(Runnable r).
public Thread(Runnable r,String name).
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
private int i = 100;
private String s = "lock";
@Override
public void run() {
while (i > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(30);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}//1234再此等待,等到i=1来了以后123分别进入,所以有了0、-1、-2。加上if语句就解决了
synchronized (s) {//同步代码块,即锁
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖了" + i + "张票");
i--;
}
}
}
}
}
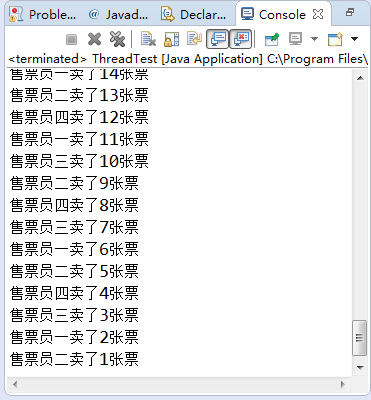
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable runnable=new MyRunnable();
Thread t1=new Thread(runnable,"售票员一");
Thread t2=new Thread(runnable,"售票员二");
Thread t3=new Thread(runnable,"售票员三");
Thread t4=new Thread(runnable,"售票员四");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}例3
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
private int i = 100;
private String s = "lock";
@Override
public void run() {
while (i > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(30);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}//1234再此等待,等到i=1来了以后123分别进入,所以有了0、-1、-2。加上if语句就解决了
synchronized (s) {//同步代码块,即锁
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖了" + i + "张票");
i--;
}
}
}
}
}
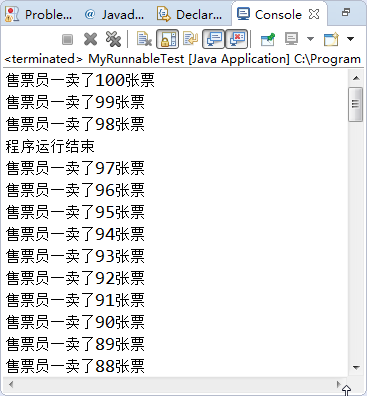
public class MyRunnableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable runnable=new MyRunnable();
Thread t1=new Thread(runnable,"售票员一");
t1.start();
try {
t1.join(100);
//直接调用join()是等待该线程运行结束后跳出,join(1000)是指主线程运行1S后就继续执行,线程继续运行到结束
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("程序运行结束");
}
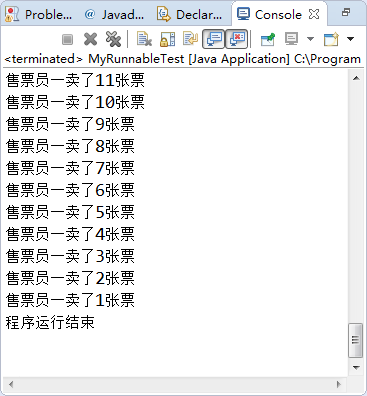
} public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable runnable=new MyRunnable();
Thread t1=new Thread(runnable,"售票员一");
t1.start();
try {
t1.join();
//直接调用join()是等待该线程运行结束后跳出,join(1000)是指主线程运行1S后就继续执行,线程继续运行到结束
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("程序运行结束");
}例4
互锁
public class DeadLockRunnable1 implements Runnable {
private String lock1 = "abc";
private String lock2 = "def";
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock1) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("麻溜把lock2的钥匙给我!");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock2) {
}
}
}
}
public class DeadLockRunnable2 implements Runnable {
private String lock1 = "abc";
private String lock2 = "def";
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock2) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("你倒是先把lock1的钥匙给我啊!");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock1) {
}
}
}
}
public class DeadLockRunnableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DeadLockRunnable1 run1=new DeadLockRunnable1();
DeadLockRunnable2 run2=new DeadLockRunnable2();
Thread t1=new Thread(run1,"张三");
Thread t2=new Thread(run2,"李四");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}





















 773
773

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








