定义
组合模式(Composite Pattern),将对象组合成树形结构以表示‘部分-整体‘的层次结构。组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
解析:部分-整体的层次结构:
我们熟悉的计算机文件和目录。目录里面包含文件,可以看成一个整体,而文件可以看成目录的一个部分。计算机的文件系统其实是一棵巨大的文件树。Linux的ROOT看作大树的入口,而下面的/bin、/home等,当然,你也可以创建一个空文件在root下面,譬如(me)。这样,无论是/bin、/home还是me都可以被一致对待,因为它们都是数据的集合,只不够数据不同而已。在任何层次上,该层次的整体和部分都可以被一致地对待。
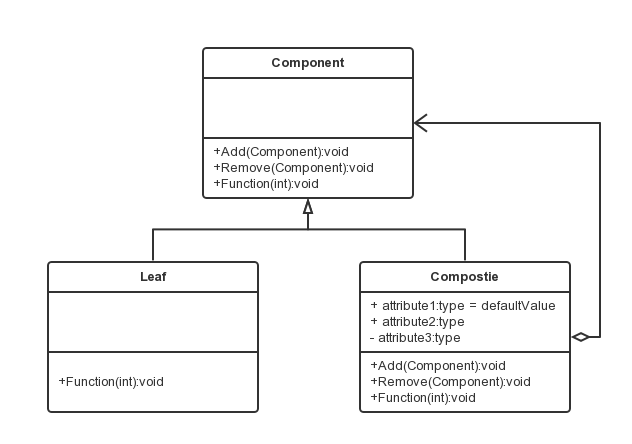
结构图
适用
1、需求中体现部分与整体的层次结构。
2、用户可以忽略组合对象与单个对象的不同,统一地使用组合结构中的所有对象。
实例
对于一些大型的公司,都会有人力资源部、财务部、技术部,子公司等。可能好多设计开始是将分公司与总公司共用一套代码,只是用id作为它们的区别。但是有个很明显不合常理的地方,总部和分部应该成树状结构,而不是平行管理的。所以,我们必须换个思维,分公司也可以看作总公司的一个部门,只不过该分公司可以有分支,而部门则看作叶子了。
首先,公司的抽象类:
abstract class Company{
protect String name;
public Company(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public abstract void Add(Company c);
public abstract void Remove(Company c);
public abstract void Function(int depth);//深度,用"-"表示,
} 部门类
class Section extends Company{
public Section(String name){
super(name);
}
@Override
public void Add(Company c){
//部门不可以再分
}
@Override
public void Remove(Company c){
//部门不可以再分
}
@Override
public void Function(int depth){
StringBuilder d = new StringBuilder("");
for(int i = 0;i < depth; i++){//输出深度线
d.append("-");
}
System.out.println(new String(d)+this.getName());
//部门不可再分,所以不能展示
}
}具体公司类:
public class ConcreteCompany extends Company {
private List<Company> cList;
public ConcreteCompany() {
cList = new ArrayList<Company>();
}
public ConcreteCompany(String name) {
super(name);
cList = new ArrayList<Company>() ;
}
@Override
protected void add(Company company) {
cList.add(company);
}
@Override
protected void Function(int depth) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) {
sb.append("-");
}
System.out.println(new String(sb) + this.getName());
//深度展示其结点的子公司或者部门
for (Company c : cList) {
c.Function(depth + 2);
}
}
@Override
protected void romove(Company company) {
cList.remove(company);
}
} 客户端调用:
public static void main(String[] args){
Section marketSectionInGuangzhou = new Section("广研市场部);
Section developingSectionInGuangzhou = new Section("广研开发部");
Section marketSectionInBeijing = new Section("腾讯北京市场部");
Section developingSectionInBeijing = new Section("腾讯北京开发部");
Section marketSectionInRoot = new Section("总部市场部);
Section developingSectionInRoot = new Section("总部工程部");
ConcreteCompany com1 = new ConcreteCompany("腾讯广州研发中心");
com1.Add(marketSectionInGuangzhou);
com1.Add(developingSectionInGuangzhou);
ConcreteCompany com2 = new ConcreteCompany("腾讯北京分公司");
com2.Add(marketSectionInBeijing);
com2.Add(developingSectionInBeijing);
ConcreteCompany root = new ConcreteCompany("腾讯深圳总部");
root.Add(marketSectionInRoot);
root.Add(developingSectionInRoot);
}结果显示:
-腾讯深圳总部
—总部市场部
—总部工程部
—腾讯广州研发中心
—–广研市场部
—–广研开发部
—腾讯北京分公司
—–腾讯北京市场部
—–腾讯北京开发部
总结
组合模式定义了包含类似上面的市场部和工程部等分部门这些基本对象,同时又定义了广研和北京分公司等组合对象。基本对象可以被组合成更复杂的组合对象,而组合对象又可以被再组合,这样不断地递归下去,客户代码无需纠结基本对象与组合对象的组织问题了。






















 453
453











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








