目录
Introduction
在真实世界应用程序中渲染的3D网格通常会在多个三角形之间共享顶点。即使是像绘制矩形这样简单的事情,这种情况也已经发生了:
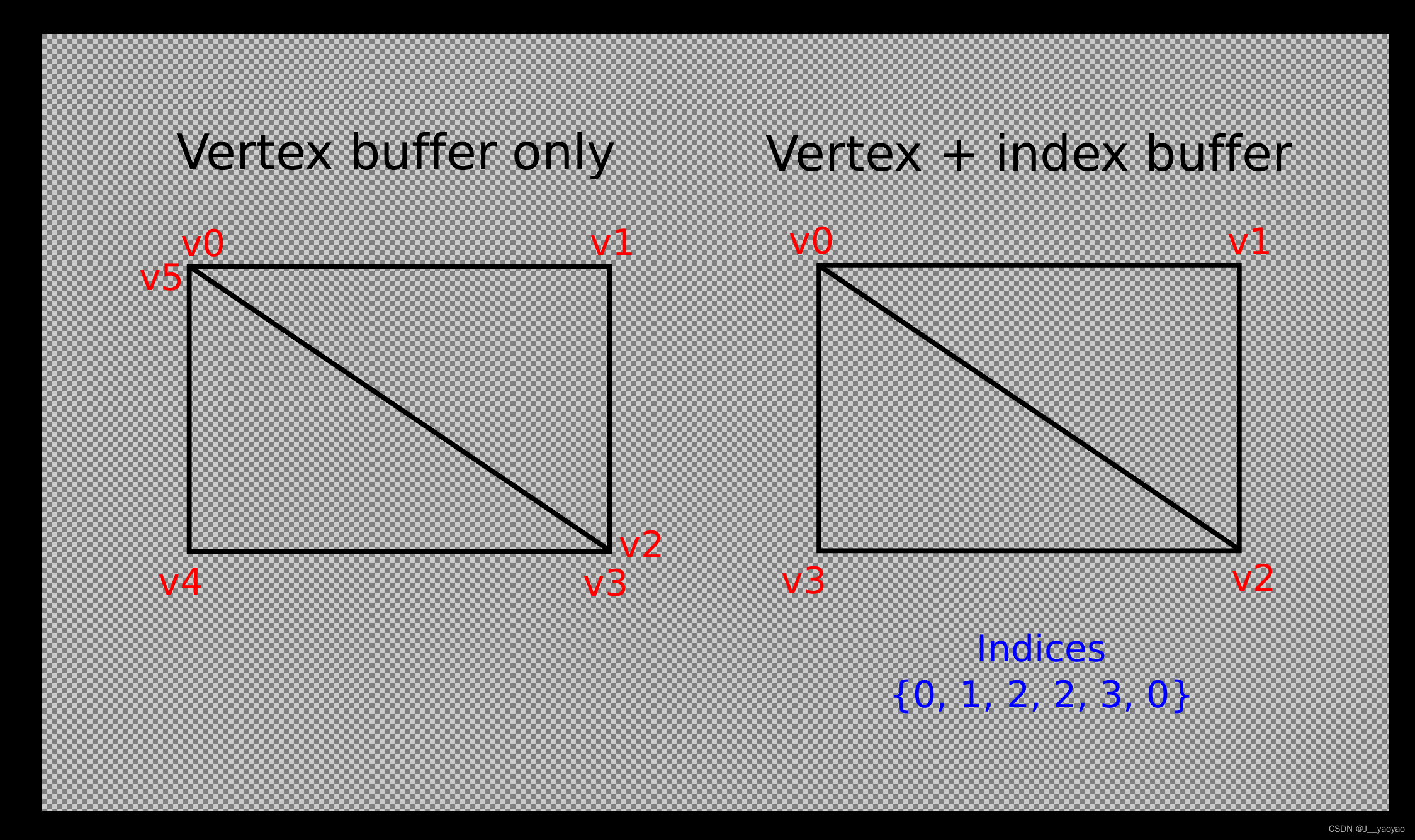
绘制矩形需要两个三角形,这意味着我们需要一个包含6个顶点的顶点缓冲区。问题是需要复制两个顶点的数据,导致50%的冗余。这只会在更复杂的网格中变得更糟,其中顶点在平均3个三角形中重复使用。解决这个问题的方法是使用索引缓冲区。
索引缓冲区本质上是指向顶点缓冲区的指针数组。它允许您重新排序顶点数据,并为多个顶点重用现有数据。上图演示了如果我们有一个包含四个唯一顶点的顶点缓冲区,那么矩形的索引缓冲区会是什么样子。前三个索引定义右上三角形,后三个索引为左下三角形定义顶点。
Index buffer creation
在本章中,我们将修改顶点数据并添加索引数据,以绘制一个如图所示的矩形。修改顶点数据以表示四个角:
const std::vector<Vertex> vertices = {
{{-0.5f, -0.5f}, {1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f}},
{{0.5f, -0.5f}, {0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f}},
{{0.5f, 0.5f}, {0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f}},
{{-0.5f, 0.5f}, {1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f}}
};左上角为红色,右上角为绿色,右下角为蓝色,左下角为白色。我们将添加一个新的数组索引来表示索引缓冲区的内容。它应该与插图中的索引相匹配,以绘制右上三角和左下三角。
const std::vector<uint16_t> indices = {
0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 0
};根据顶点中的条目数量,可以为索引缓冲区使用uint16_t或uint32_t。我们现在可以坚持uint16_t,因为我们使用的唯一顶点少于65535个。
就像顶点数据一样,索引需要上传到VkBuffer中,GPU才能访问它们。定义两个新的类成员以保存索引缓冲区的资源:
VkBuffer vertexBuffer;
VkDeviceMemory vertexBufferMemory;
VkBuffer indexBuffer;
VkDeviceMemory indexBufferMemory;我们现在要添加的createIndexBuffer函数几乎与createVertexBuffer相同:
void initVulkan() {
...
createVertexBuffer();
createIndexBuffer();
...
}
void createIndexBuffer() {
VkDeviceSize bufferSize = sizeof(indices[0]) * indices.size();
VkBuffer stagingBuffer;
VkDeviceMemory stagingBufferMemory;
createBuffer(bufferSize, VK_BUFFER_USAGE_TRANSFER_SRC_BIT, VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_VISIBLE_BIT | VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_COHERENT_BIT, stagingBuffer, stagingBufferMemory);
void* data;
vkMapMemory(device, stagingBufferMemory, 0, bufferSize, 0, &data);
memcpy(data, indices.data(), (size_t) bufferSize);
vkUnmapMemory(device, stagingBufferMemory);
createBuffer(bufferSize, VK_BUFFER_USAGE_TRANSFER_DST_BIT | VK_BUFFER_USAGE_INDEX_BUFFER_BIT, VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_DEVICE_LOCAL_BIT, indexBuffer, indexBufferMemory);
copyBuffer(stagingBuffer, indexBuffer, bufferSize);
vkDestroyBuffer(device, stagingBuffer, nullptr);
vkFreeMemory(device, stagingBufferMemory, nullptr);
}只有两个显著的差异。bufferSize现在等于索引数乘以索引类型的大小,uint16_t或uint32_t。indexBuffer的用法应该是VK_BUFFER_USAGE_INDEX_BUFFER_BIT,而不是VK_BUFFER_USAGE_VERTEX_BUFFER_BIT,这是有意义的。除此之外,过程完全相同。我们创建一个暂存缓冲区,将内容复制到索引,然后将其复制到最终的设备本地索引缓冲区。
索引缓冲区应该在程序结束时清理,就像顶点缓冲区一样:
void cleanup() {
cleanupSwapChain();
vkDestroyBuffer(device, indexBuffer, nullptr);
vkFreeMemory(device, indexBufferMemory, nullptr);
vkDestroyBuffer(device, vertexBuffer, nullptr);
vkFreeMemory(device, vertexBufferMemory, nullptr);
...
}Using an index buffer
使用索引缓冲区进行绘图涉及对recordCommandBuffer的两个更改。我们首先需要绑定索引缓冲区,就像我们对顶点缓冲区所做的那样。不同的是,只能有一个索引缓冲区。不幸的是,不可能为每个顶点属性使用不同的索引,因此即使只有一个属性发生变化,我们仍然必须完全复制顶点数据。
vkCmdBindVertexBuffers(commandBuffer, 0, 1, vertexBuffers, offsets);
vkCmdBindIndexBuffer(commandBuffer, indexBuffer, 0, VK_INDEX_TYPE_UINT16);索引缓冲区与vkCmdBindIndexBuffer绑定,其中包含索引缓冲区、其中的字节偏移量和索引数据类型作为参数。如前所述,可能的类型是VK_INDEX_TYPE_UINT16和VK_INDX_TYPE_UINT32。
仅仅绑定索引缓冲区还没有改变任何东西,我们还需要改变绘图命令,告诉Vulkan使用索引缓冲区。删除vkCmdDraw行并将其替换为vkCmdDrawIndexed:
vkCmdDrawIndexed(commandBuffer, static_cast<uint32_t>(indices.size()), 1, 0, 0, 0);对该函数的调用与vkCmdDraw非常相似。前两个参数指定索引的数量和实例的数量。我们没有使用实例,所以只需指定一个实例。索引数表示将传递给顶点着色器的顶点数。下一个参数指定索引缓冲区中的偏移量,使用值1将导致显卡开始读取第二个索引。倒数第二个参数指定要添加到索引缓冲区中的索引的偏移量。最后一个参数指定实例化的偏移量,我们不使用该偏移量。
现在运行程序,您应该看到以下内容:
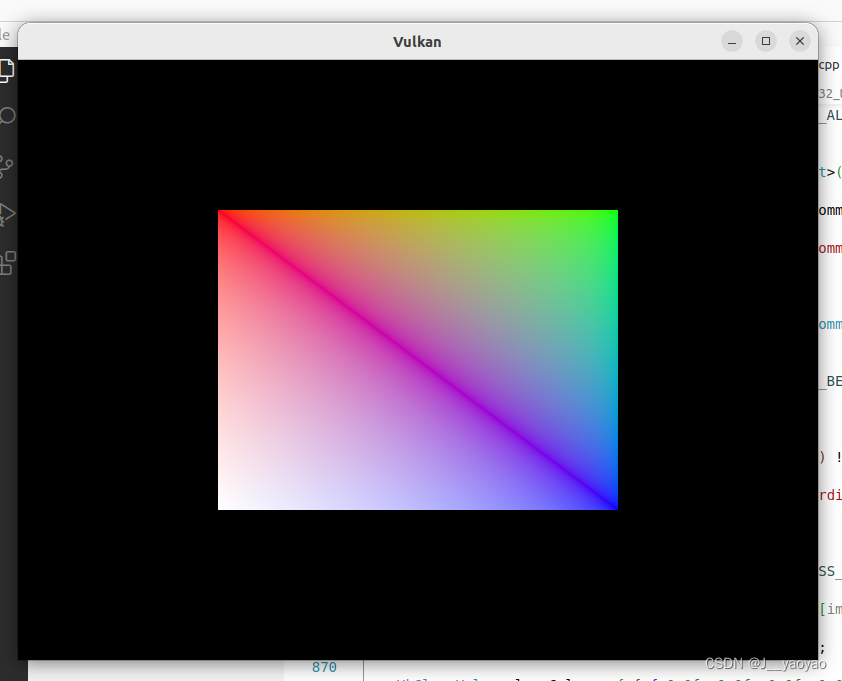
现在您知道如何通过使用索引缓冲区重用顶点来节省内存。在我们将要加载复杂3D模型的未来章节中,这将变得尤为重要。
上一章已经提到,您应该从单个内存分配中分配多个资源,如缓冲区,但实际上您应该更进一步。驱动程序开发人员建议您也将多个缓冲区(如顶点和索引缓冲区)存储到单个VkBuffer中,并在vkCmdBindVertexBuffers等命令中使用偏移量。优点是在这种情况下,您的数据更易于缓存,因为它们更靠近。当然,如果在相同的渲染操作期间没有使用多个资源,甚至可以将相同的内存块重新用于多个资源(前提是刷新了它们的数据)。这被称为别名,一些Vulkan函数具有显式标志来指定要执行此操作。





















 368
368

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








