目录(每一个环境都很重要!)
1.使用正确版本(v5.0)的yolov5进行训练得到pt模型;
2.将pt模型使用yolov5工程中的export.py转换为onnx模型;
3.将onnx模型使用rknn-toolkit2中onnx文件夹的test.py转换为rknn模型
4.在板子上使用rknpu2工具调用rknn模型,实现NPU推理加速
一、使用正确版本(v5.0)的yolov5进行训练得到pt模型;
一定一定一定要选择正确的版本进行训练,别一从头开始就走远了(抱头痛哭),官方给出的版本id如下图所示:
但是我打开之后发现资源没了,之后我选择的了yolov5-5.0版本的进行模型训练。(如果能打开的话可以参考这篇博客)https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57315535/article/details/128250096?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522169044858316800182715751%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334..%2522%257D&request_id=169044858316800182715751&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~all~sobaiduend~default-4-128250096-null-null.142^v91^insertT0,239^v3^control&utm_term=pt%E8%BD%ACrknn&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187如果没有资源的话就下载yolov5-5.0的进行训练,按照后面的流程走一般是不会出现大问题的,训练完以后保存好best.pt这个权重!至此第一部分结束。
二.将pt模型使用yolov5工程中的export.py转换为onnx模型
在yolov5-5.0代码中,将yolo.py替换为如下代码(跟官方的不太一样):
# YOLOv5 🚀 by Ultralytics, AGPL-3.0 license
"""
YOLO-specific modules
Usage:
$ python models/yolo.py --cfg yolov5s.yaml
"""
import argparse
import contextlib
import os
import platform
import sys
from copy import deepcopy
from pathlib import Path
FILE = Path(__file__).resolve()
ROOT = FILE.parents[1] # YOLOv5 root directory
if str(ROOT) not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(str(ROOT)) # add ROOT to PATH
if platform.system() != 'Windows':
ROOT = Path(os.path.relpath(ROOT, Path.cwd())) # relative
from models.common import * # noqa
from models.experimental import * # noqa
from utils.autoanchor import check_anchor_order
from utils.general import LOGGER, check_version, check_yaml, make_divisible, print_args
from utils.plots import feature_visualization
from utils.torch_utils import (fuse_conv_and_bn, initialize_weights, model_info, profile, scale_img, select_device,
time_sync)
try:
import thop # for FLOPs computation
except ImportError:
thop = None
class Detect(nn.Module):
# YOLOv5 Detect head for detection models
stride = None # strides computed during build
dynamic = False # force grid reconstruction
export = False # export mode
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors
self.grid = [torch.empty(0) for _ in range(self.nl)] # init grid
self.anchor_grid = [torch.empty(0) for _ in range(self.nl)] # init anchor grid
self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)) # shape(nl,na,2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.inplace = inplace # use inplace ops (e.g. slice assignment)
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training: # inference
if self.dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
if isinstance(self, Segment): # (boxes + masks)
xy, wh, conf, mask = x[i].split((2, 2, self.nc + 1, self.no - self.nc - 5), 4)
xy = (xy.sigmoid() * 2 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (wh.sigmoid() * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, conf.sigmoid(), mask), 4)
else: # Detect (boxes only)
xy, wh, conf = x[i].sigmoid().split((2, 2, self.nc + 1), 4)
xy = (xy * 2 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (wh * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, conf), 4)
z.append(y.view(bs, self.na * nx * ny, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), ) if self.export else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
def _make_grid(self, nx=20, ny=20, i=0, torch_1_10=check_version(torch.__version__, '1.10.0')):
d = self.anchors[i].device
t = self.anchors[i].dtype
shape = 1, self.na, ny, nx, 2 # grid shape
y, x = torch.arange(ny, device=d, dtype=t), torch.arange(nx, device=d, dtype=t)
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid(y, x, indexing='ij') if torch_1_10 else torch.meshgrid(y, x) # torch>=0.7 compatibility
grid = torch.stack((xv, yv), 2).expand(shape) - 0.5 # add grid offset, i.e. y = 2.0 * x - 0.5
anchor_grid = (self.anchors[i] * self.stride[i]).view((1, self.na, 1, 1, 2)).expand(shape)
return grid, anchor_grid
class Segment(Detect):
# YOLOv5 Segment head for segmentation models
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), nm=32, npr=256, ch=(), inplace=True):
super().__init__(nc, anchors, ch, inplace)
self.nm = nm # number of masks
self.npr = npr # number of protos
self.no = 5 + nc + self.nm # number of outputs per anchor
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.proto = Proto(ch[0], self.npr, self.nm) # protos
self.detect = Detect.forward
def forward(self, x):
p = self.proto(x[0])
x = self.detect(self, x)
return (x, p) if self.training else (x[0], p) if self.export else (x[0], p, x[1])
class BaseModel(nn.Module):
# YOLOv5 base model
def forward(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False):
return self._forward_once(x, profile, visualize) # single-scale inference, train
def _forward_once(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False):
y, dt = [], [] # outputs
for m in self.model:
if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
x = m(x) # run
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
return x
def _profile_one_layer(self, m, x, dt):
c = m == self.model[-1] # is final layer, copy input as inplace fix
o = thop.profile(m, inputs=(x.copy() if c else x, ), verbose=False)[0] / 1E9 * 2 if thop else 0 # FLOPs
t = time_sync()
for _ in range(10):
m(x.copy() if c else x)
dt.append((time_sync() - t) * 100)
if m == self.model[0]:
LOGGER.info(f"{'time (ms)':>10s} {'GFLOPs':>10s} {'params':>10s} module")
LOGGER.info(f'{dt[-1]:10.2f} {o:10.2f} {m.np:10.0f} {m.type}')
if c:
LOGGER.info(f"{sum(dt):10.2f} {'-':>10s} {'-':>10s} Total")
def fuse(self): # fuse model Conv2d() + BatchNorm2d() layers
LOGGER.info('Fusing layers... ')
for m in self.model.modules():
if isinstance(m, (Conv, DWConv)) and hasattr(m, 'bn'):
m.conv = fuse_conv_and_bn(m.conv, m.bn) # update conv
delattr(m, 'bn') # remove batchnorm
m.forward = m.forward_fuse # update forward
self.info()
return self
def info(self, verbose=False, img_size=640): # print model information
model_info(self, verbose, img_size)
def _apply(self, fn):
# Apply to(), cpu(), cuda(), half() to model tensors that are not parameters or registered buffers
self = super()._apply(fn)
m = self.model[-1] # Detect()
if isinstance(m, (Detect, Segment)):
m.stride = fn(m.stride)
m.grid = list(map(fn, m.grid))
if isinstance(m.anchor_grid, list):
m.anchor_grid = list(map(fn, m.anchor_grid))
return self
class DetectionModel(BaseModel):
# YOLOv5 detection model
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov5s.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, anchors=None): # model, input channels, number of classes
super().__init__()
if isinstance(cfg, dict):
self.yaml = cfg # model dict
else: # is *.yaml
import yaml # for torch hub
self.yaml_file = Path(cfg).name
with open(cfg, encoding='ascii', errors='ignore') as f:
self.yaml = yaml.safe_load(f) # model dict
# Define model
ch = self.yaml['ch'] = self.yaml.get('ch', ch) # input channels
if nc and nc != self.yaml['nc']:
LOGGER.info(f"Overriding model.yaml nc={self.yaml['nc']} with nc={nc}")
self.yaml['nc'] = nc # override yaml value
if anchors:
LOGGER.info(f'Overriding model.yaml anchors with anchors={anchors}')
self.yaml['anchors'] = round(anchors) # override yaml value
self.model, self.save = parse_model(deepcopy(self.yaml), ch=[ch]) # model, savelist
self.names = [str(i) for i in range(self.yaml['nc'])] # default names
self.inplace = self.yaml.get('inplace', True)
# Build strides, anchors
m = self.model[-1] # Detect()
if isinstance(m, (Detect, Segment)):
s = 256 # 2x min stride
m.inplace = self.inplace
forward = lambda x: self.forward(x)[0] if isinstance(m, Segment) else self.forward(x)
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, s, s))]) # forward
check_anchor_order(m)
m.anchors /= m.stride.view(-1, 1, 1)
self.stride = m.stride
self._initialize_biases() # only run once
# Init weights, biases
initialize_weights(self)
self.info()
LOGGER.info('')
def forward(self, x, augment=False, profile=False, visualize=False):
if augment:
return self._forward_augment(x) # augmented inference, None
return self._forward_once(x, profile, visualize) # single-scale inference, train
def _forward_augment(self, x):
img_size = x.shape[-2:] # height, width
s = [1, 0.83, 0.67] # scales
f = [None, 3, None] # flips (2-ud, 3-lr)
y = [] # outputs
for si, fi in zip(s, f):
xi = scale_img(x.flip(fi) if fi else x, si, gs=int(self.stride.max()))
yi = self._forward_once(xi)[0] # forward
# cv2.imwrite(f'img_{si}.jpg', 255 * xi[0].cpu().numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))[:, :, ::-1]) # save
yi = self._descale_pred(yi, fi, si, img_size)
y.append(yi)
y = self._clip_augmented(y) # clip augmented tails
return torch.cat(y, 1), None # augmented inference, train
def _descale_pred(self, p, flips, scale, img_size):
# de-scale predictions following augmented inference (inverse operation)
if self.inplace:
p[..., :4] /= scale # de-scale
if flips == 2:
p[..., 1] = img_size[0] - p[..., 1] # de-flip ud
elif flips == 3:
p[..., 0] = img_size[1] - p[..., 0] # de-flip lr
else:
x, y, wh = p[..., 0:1] / scale, p[..., 1:2] / scale, p[..., 2:4] / scale # de-scale
if flips == 2:
y = img_size[0] - y # de-flip ud
elif flips == 3:
x = img_size[1] - x # de-flip lr
p = torch.cat((x, y, wh, p[..., 4:]), -1)
return p
def _clip_augmented(self, y):
# Clip YOLOv5 augmented inference tails
nl = self.model[-1].nl # number of detection layers (P3-P5)
g = sum(4 ** x for x in range(nl)) # grid points
e = 1 # exclude layer count
i = (y[0].shape[1] // g) * sum(4 ** x for x in range(e)) # indices
y[0] = y[0][:, :-i] # large
i = (y[-1].shape[1] // g) * sum(4 ** (nl - 1 - x) for x in range(e)) # indices
y[-1] = y[-1][:, i:] # small
return y
def _initialize_biases(self, cf=None): # initialize biases into Detect(), cf is class frequency
# https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02002 section 3.3
# cf = torch.bincount(torch.tensor(np.concatenate(dataset.labels, 0)[:, 0]).long(), minlength=nc) + 1.
m = self.model[-1] # Detect() module
for mi, s in zip(m.m, m.stride): # from
b = mi.bias.view(m.na, -1) # conv.bias(255) to (3,85)
b.data[:, 4] += math.log(8 / (640 / s) ** 2) # obj (8 objects per 640 image)
b.data[:, 5:5 + m.nc] += math.log(0.6 / (m.nc - 0.99999)) if cf is None else torch.log(cf / cf.sum()) # cls
mi.bias = torch.nn.Parameter(b.view(-1), requires_grad=True)
Model = DetectionModel # retain YOLOv5 'Model' class for backwards compatibility
class SegmentationModel(DetectionModel):
# YOLOv5 segmentation model
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov5s-seg.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, anchors=None):
super().__init__(cfg, ch, nc, anchors)
class ClassificationModel(BaseModel):
# YOLOv5 classification model
def __init__(self, cfg=None, model=None, nc=1000, cutoff=10): # yaml, model, number of classes, cutoff index
super().__init__()
self._from_detection_model(model, nc, cutoff) if model is not None else self._from_yaml(cfg)
def _from_detection_model(self, model, nc=1000, cutoff=10):
# Create a YOLOv5 classification model from a YOLOv5 detection model
if isinstance(model, DetectMultiBackend):
model = model.model # unwrap DetectMultiBackend
model.model = model.model[:cutoff] # backbone
m = model.model[-1] # last layer
ch = m.conv.in_channels if hasattr(m, 'conv') else m.cv1.conv.in_channels # ch into module
c = Classify(ch, nc) # Classify()
c.i, c.f, c.type = m.i, m.f, 'models.common.Classify' # index, from, type
model.model[-1] = c # replace
self.model = model.model
self.stride = model.stride
self.save = []
self.nc = nc
def _from_yaml(self, cfg):
# Create a YOLOv5 classification model from a *.yaml file
self.model = None
def parse_model(d, ch): # model_dict, input_channels(3)
# Parse a YOLOv5 model.yaml dictionary
LOGGER.info(f"\n{'':>3}{'from':>18}{'n':>3}{'params':>10} {'module':<40}{'arguments':<30}")
anchors, nc, gd, gw, act = d['anchors'], d['nc'], d['depth_multiple'], d['width_multiple'], d.get('activation')
if act:
Conv.default_act = eval(act) # redefine default activation, i.e. Conv.default_act = nn.SiLU()
LOGGER.info(f"{colorstr('activation:')} {act}") # print
na = (len(anchors[0]) // 2) if isinstance(anchors, list) else anchors # number of anchors
no = na * (nc + 5) # number of outputs = anchors * (classes + 5)
layers, save, c2 = [], [], ch[-1] # layers, savelist, ch out
for i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']): # from, number, module, args
m = eval(m) if isinstance(m, str) else m # eval strings
for j, a in enumerate(args):
with contextlib.suppress(NameError):
args[j] = eval(a) if isinstance(a, str) else a # eval strings
n = n_ = max(round(n * gd), 1) if n > 1 else n # depth gain
if m in {
Conv, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, MixConv2d, Focus, CrossConv,
BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3SPP, C3Ghost, nn.ConvTranspose2d, DWConvTranspose2d, C3x}:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no: # if not output
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
if m in {BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost, C3x}:
args.insert(2, n) # number of repeats
n = 1
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:
args = [ch[f]]
elif m is Concat:
c2 = sum(ch[x] for x in f)
# TODO: channel, gw, gd
elif m in {Detect, Segment}:
args.append([ch[x] for x in f])
if isinstance(args[1], int): # number of anchors
args[1] = [list(range(args[1] * 2))] * len(f)
if m is Segment:
args[3] = make_divisible(args[3] * gw, 8)
elif m is Contract:
c2 = ch[f] * args[0] ** 2
elif m is Expand:
c2 = ch[f] // args[0] ** 2
else:
c2 = ch[f]
m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type, m_.np = i, f, t, np # attach index, 'from' index, type, number params
LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>18}{n_:>3}{np:10.0f} {t:<40}{str(args):<30}') # print
save.extend(x % i for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
ch.append(c2)
return nn.Sequential(*layers), sorted(save)
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='yolov5s.yaml', help='model.yaml')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=1, help='total batch size for all GPUs')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--profile', action='store_true', help='profile model speed')
parser.add_argument('--line-profile', action='store_true', help='profile model speed layer by layer')
parser.add_argument('--test', action='store_true', help='test all yolo*.yaml')
opt = parser.parse_args()
opt.cfg = check_yaml(opt.cfg) # check YAML
print_args(vars(opt))
device = select_device(opt.device)
# Create model
im = torch.rand(opt.batch_size, 3, 640, 640).to(device)
model = Model(opt.cfg).to(device)
# Options
if opt.line_profile: # profile layer by layer
model(im, profile=True)
elif opt.profile: # profile forward-backward
results = profile(input=im, ops=[model], n=3)
elif opt.test: # test all models
for cfg in Path(ROOT / 'models').rglob('yolo*.yaml'):
try:
_ = Model(cfg)
except Exception as e:
print(f'Error in {cfg}: {e}')
else: # report fused model summary
model.fuse()
注意,训练的时候不要修改,训练完之后转onnx模型的时候再改!
接着将训练好的best.pt文件存至与yolo.py同一级的文件夹中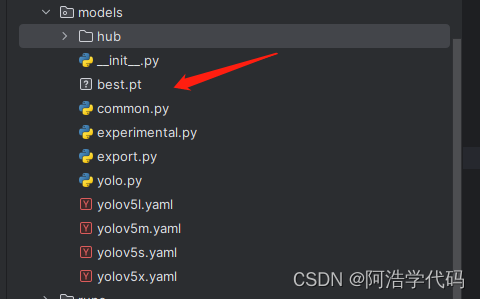
并且修改export.py的配置文件
运行export.py会得到onnx模型。到这里第二部算是大功告成了!
以上部分都是在windows系统上完成的---------------------------------------------------------------------
下面的将要在Linux系统上完成。
三.将onnx模型使用rknn-toolkit2中onnx文件夹的test.py转换为rknn模型
GitHub - rockchip-linux/rknn-toolkit2rknn-toolkit2下载链接GitHub - rockchip-linux/rknn-toolkit2

将这个文件下载下来
1.安装rknn-toolkit2的环境
其环境要求在./doc目录下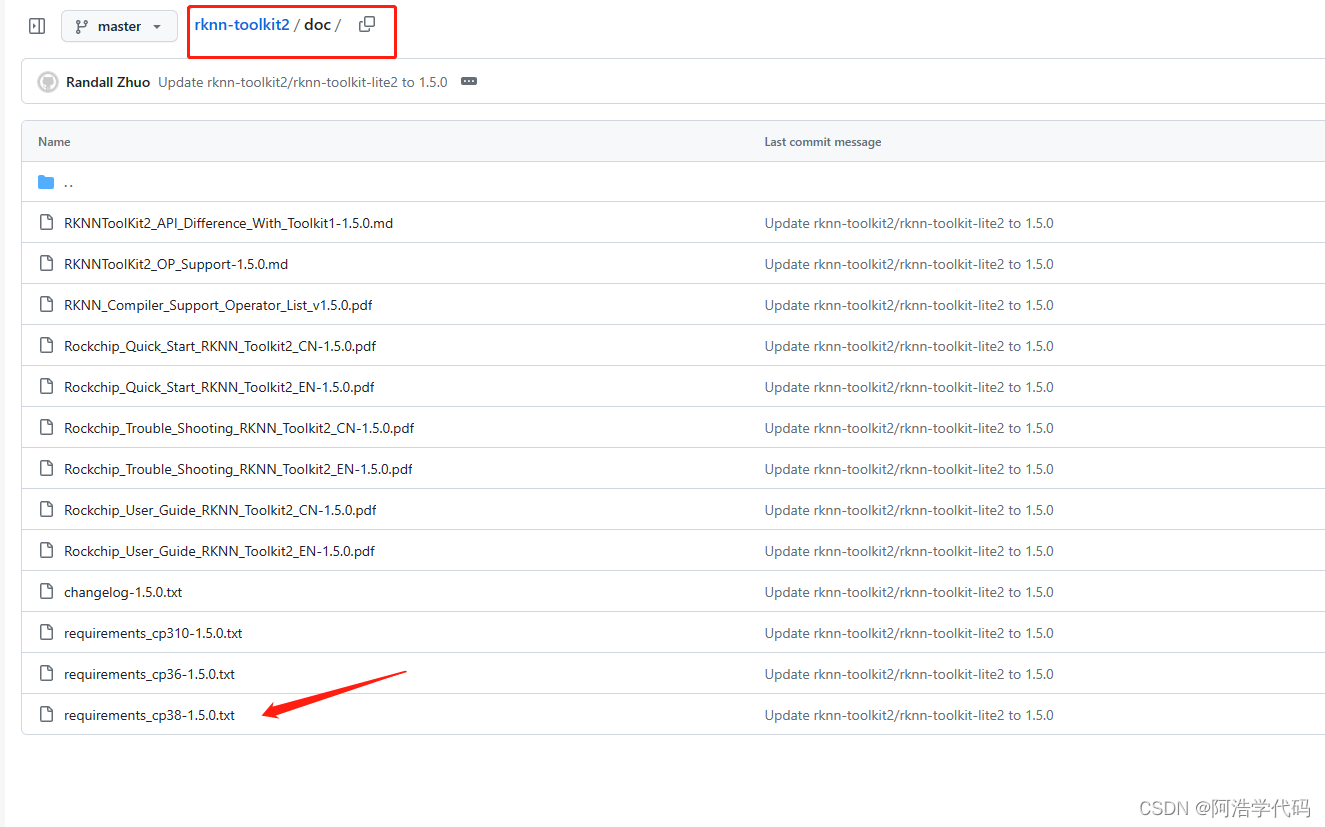
这里我使用的是anaconda创建的python3.8虚拟环境,创建环境并命名为RKnn
conda create -n RKnn python==3.8使用pip安装requirements_cp38-1.4.0.txt中的包
pip install -r requirements_cp38-1.5.0.txt别安装错了!
2.下载rknn_toolkit2-1.4.0
在./packages目录下

输入以下命令:
pip install rknn_toolkit2-1.5.0+1fa95b5c-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl提示安装完成后我们可以检查是否安装成功,在终端中运行python,输入:
from rknn.api import RKNN若不报错说明我们的工具包已经安装成功,之后便可进行rknn模型的转换了~(ctrl+D退出python)
3.onnx转换为rknn
在rknn-toolkit2工程文件夹中浏览至 ./examples/onnx/yolov5,将我们在之前转换得到的best.onnx复制到该文件夹下,修改该文件夹下的test.py中的内容为自己模型的名字,要修改的地方如下: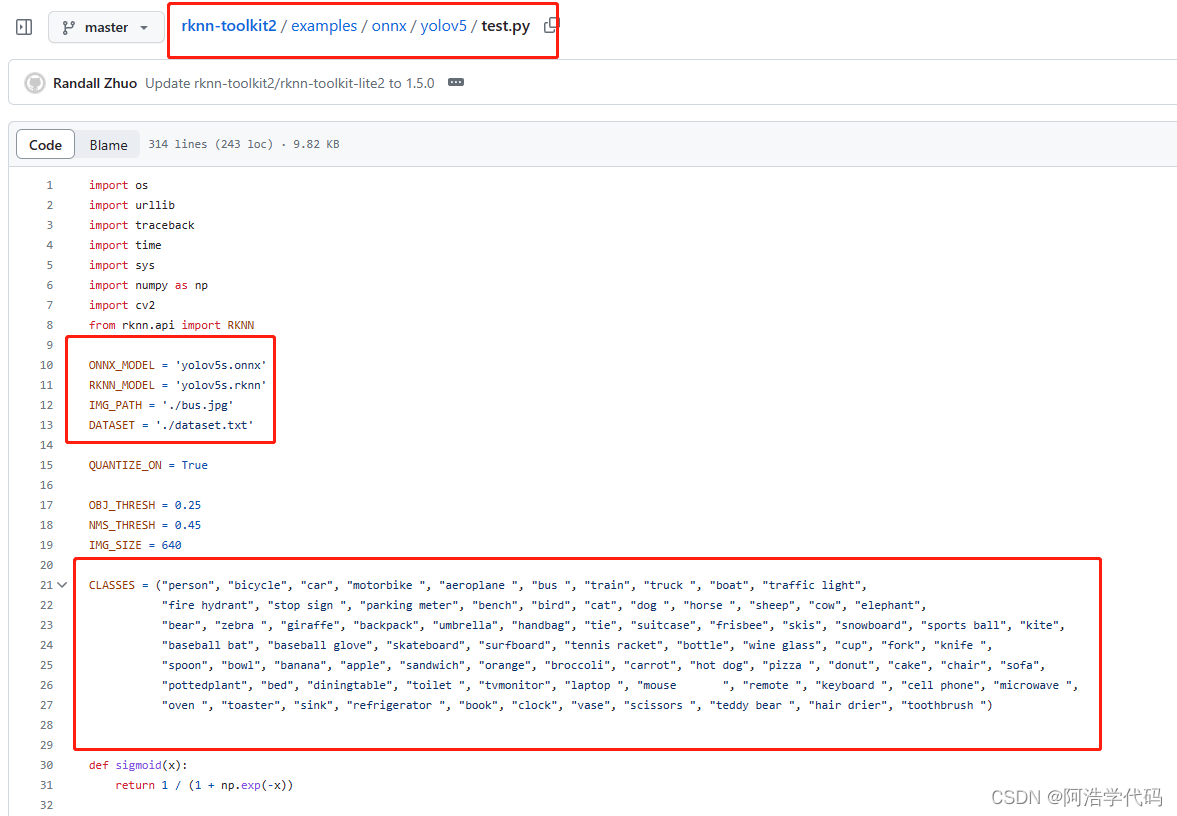
修改完之后在终端输入(目录转到yolov5中)
python test.py
顺利运行完之后就可以看到rknn模型了
四.在板子上使用rknpu2工具调用rknn模型,实现NPU推理加速
在3588的主目录上获取官方demo
git clone https://github.com/rockchip-linux/rknpu2.git进入yolov5目录
cd /home/ptay/rknpu2-master/examples/rknn_yolov5_demo修改include文件中的头文件postprocess.h
#define OBJ_CLASS_NUM 3 #这里的数字修改为数据集的类的个数修改model目录下的coco_80_labels_list.txt文件, 改为自己的类并保存
xxxxxxxxx将转换后的rknn文件放在model/RK3588目录下
编译,运行shell
bash ./build-linux_RK3588.sh成功后生成install目录
cd install/rknn_yolov5_demo_linux在model目录下放入需要推理的图片
运行
./rknn_yolov5_demo ./model/RK3588/last.rknn ./model/0625_xx_005.jpg注:后面的图片用的全路径,因为当前的相对路径识别不到(主要是看图片所在的位置)
在rknn_yolov5_demo_linux获取到结果
如果有什么问题大家可以在评论区一起交流探讨学习!!1






















 2178
2178











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










