目录
1.理论基础
1.1A星寻路是用来解决什么问题的
A星寻路是用来计算玩家行进最短路径的
1.2A星寻路的基本原理
不停的找周围的点,通过找出寻路消耗最小的点作为新的起点再循环的找,直到找到终点。
寻路消耗公式
f(寻路消耗)=g(离起点距离)+h(离终点距离);
开启列表和关闭列表
每次寻找的时候把周围不是阻挡的点且不在开启列表或者关闭列表的点放在开启列表中,每次开启列表中寻路消耗最低的点放入关闭列表中,判断该点是否是终点,如果是则寻路结束,反之则继续寻路
死路
如果开启列表为空的时候,则判定为死路。
2.代码实现
2.1每个格子的信息
创建格子类
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
/// <summary>
/// 格子类型
/// </summary>
public enum NodeType
{
walk,//可以走
stop,//不能走
}
public class AStarNode
{
//格子对象坐标
public int x;
public int y;
//寻路消耗
public float f;
//离起点的距离
public float g;
//离终点的距离
public float h;
//父对象
public AStarNode father;
public NodeType type;
public AStarNode (int x,int y,NodeType type)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.type = type;
}
}
2.2A星寻路管理器
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class AStarManager
{
private static AStarManager instance;
public static AStarManager Instance
{
get
{
if (instance == null)
instance = new AStarManager();
return instance;
}
}
//地图的宽高
int mapW;
int mapH;
//地图相关所有的格子对象容器
public AStarNode[,] nodes;
//开启列表和关闭列表
private List<AStarNode> openList=new List<AStarNode>();
private List<AStarNode> closeList=new List<AStarNode>() ;
//初始化地图信息
public void InitMapInfo(int w,int h)
{
this.mapH = h;
this.mapW = w;
nodes = new AStarNode[w, h];
for(int i=0;i<w;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<h;j++)
{
//随机阻挡只是为了测试,真正的项目中阻挡信息应该是从地图的配置文件中读出来的
AStarNode node = new AStarNode(i, j, Random.Range(0, 100) < 20 ? NodeType.stop: NodeType.walk);
nodes[i, j] = node;
}
}
}
public List<AStarNode> FindPath(Vector2 startPos,Vector2 endPos)
{
//实际项目中,传入的点往往是世界坐标系的位置,可能是小数,需要转化成整数也就是转化成每个格子的坐标,这里默认传入的数据为整数
//首先判断传入的两个点是否合法
//1.判断是否在地图内
if (startPos.x < 0 || startPos.x >= mapW || startPos.y < 0 || startPos.y >= mapH || endPos.x < 0 || endPos.x >= mapW || endPos.y < 0 || endPos.y >= mapH)
{
Debug.Log("开始或者结束点在地图外");
return null;
}
//2.判断是否是阻挡
AStarNode startNode = nodes[(int)startPos.x,(int)startPos.y];
AStarNode endNode = nodes[(int)endPos.x, (int)endPos.y];
if (startNode.type == NodeType.stop || endNode.type == NodeType.stop)
{
Debug.Log("开始或者结束点是阻挡");
return null;
}
openList.Clear();
closeList.Clear();
startNode.father = null;
startNode.h = 0;
startNode.g = 0;
startNode.f = 0;
closeList.Add(startNode);
while(true)
{
//寻找四周的点
//左上
FindNearlyNodetoOpenList(startNode.x - 1, startNode.y + 1, 1.4f, startNode, endNode);
//上
FindNearlyNodetoOpenList(startNode.x, startNode.y + 1, 1f, startNode, endNode);
//右上
FindNearlyNodetoOpenList(startNode.x + 1, startNode.y + 1, 1.4f, startNode, endNode);
//左
FindNearlyNodetoOpenList(startNode.x - 1, startNode.y, 1f, startNode, endNode);
//右
FindNearlyNodetoOpenList(startNode.x + 1, startNode.y, 1f, startNode, endNode);
//左下
FindNearlyNodetoOpenList(startNode.x - 1, startNode.y - 1, 1.4f, startNode, endNode);
//下
FindNearlyNodetoOpenList(startNode.x, startNode.y - 1, 1f, startNode, endNode);
//右下
FindNearlyNodetoOpenList(startNode.x + 1, startNode.y - 1, 1.4f, startNode, endNode);
//死路判断
if (openList.Count==0)
{
return null;
}
openList.Sort(SortOpenList);
startNode = openList[0];
closeList.Add(openList[0]);
openList.RemoveAt(0);
if(startNode==endNode)
{
List<AStarNode> path = new List<AStarNode>();
path.Add(endNode);
while(endNode.father!=null)
{
path.Add(endNode.father);
endNode = endNode.father;
}
path.Reverse();
return path;
}
}
}
//将最近的点放进开始列表并计算寻路消耗
private void FindNearlyNodetoOpenList(int x,int y,float g,AStarNode father,AStarNode end)
{
//边界判断
if (x < 0 || x > mapW || y < 0 || y > mapH)
return;
AStarNode node = nodes[x, y];
//判断是否是阻挡
if (node == null || node.type == NodeType.stop || closeList.Contains(node) || openList.Contains(node))
return;
node.father = father;
node.g = father.g + g;
node.h = Mathf.Abs(end.x - x) + Mathf.Abs(end.y - y);
node.f = node.g + node.h;
openList.Add(node);
}
//开始列表排序
private int SortOpenList(AStarNode a, AStarNode b)
{
if (a.f > b.f)
return 1;
else if (a.f == b.f)
return 1;
else
return -1;
}
}
2.3测试代码
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class TestAStar : MonoBehaviour
{
//左上角第一个立方体的位置
public int beginX=-3;
public int beginY=5;
//之后每一个立方体的偏移位置
public int offsetX=2;
public int offsetY=2;
//地图的宽高
public int mapH=5;
public int mapW=5;
public Material red;
public Material yello;
public Material green;
public Material normal;
private Dictionary<string, GameObject> cubes = new Dictionary<string, GameObject>();
//开始点,给它一个坐标为负的点
public Vector2 beginPos = Vector2.right * -1;
private List<AStarNode> list = new List<AStarNode>();
private void Start()
{
AStarManager.Instance.InitMapInfo(mapW, mapH);
for (int i= 0; i < mapW;++i)
{
for(int j=0;j<mapH;++j)
{
GameObject obj = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube);
obj.transform.position = new Vector3(beginX + i * offsetX, beginY +j* offsetY, 0);
//名字
obj.name = i + "_" + j;
cubes.Add(obj.name, obj);
AStarNode node = AStarManager.Instance.nodes[i, j];
if(node.type==NodeType.stop)
{
obj.GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material = red;
}
}
}
}
private void Update()
{
if(Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0))
{
RaycastHit inFo;
Ray ray = Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition);
if(Physics.Raycast(ray,out inFo,1000))
{
if(beginPos==Vector2.right*-1)
{
if (list != null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
cubes[list[i].x + "_" + list[i].y].GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material = normal;
}
}
string[] strs = inFo.collider.gameObject.name.Split('_');
beginPos = new Vector2(int.Parse(strs[0]), int.Parse(strs[1]));
inFo.collider.gameObject.GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material = yello;
}
else
{
string[] strs = inFo.collider.gameObject.name.Split('_');
Vector2 endPos = new Vector2(int.Parse(strs[0]), int.Parse(strs[1]));
// inFo.collider.gameObject.GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material = yello;
list = AStarManager.Instance.FindPath(beginPos, endPos);
if(list!=null)
{
for(int i=0;i<list.Count;i++)
{
cubes[list[i].x + "_" + list[i].y].GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material = green;
}
}
cubes[(int)beginPos.x + "_" +(int) beginPos.y].GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material = normal;
beginPos = Vector2.right * -1;
}
}
}
}
}
3.实例演示
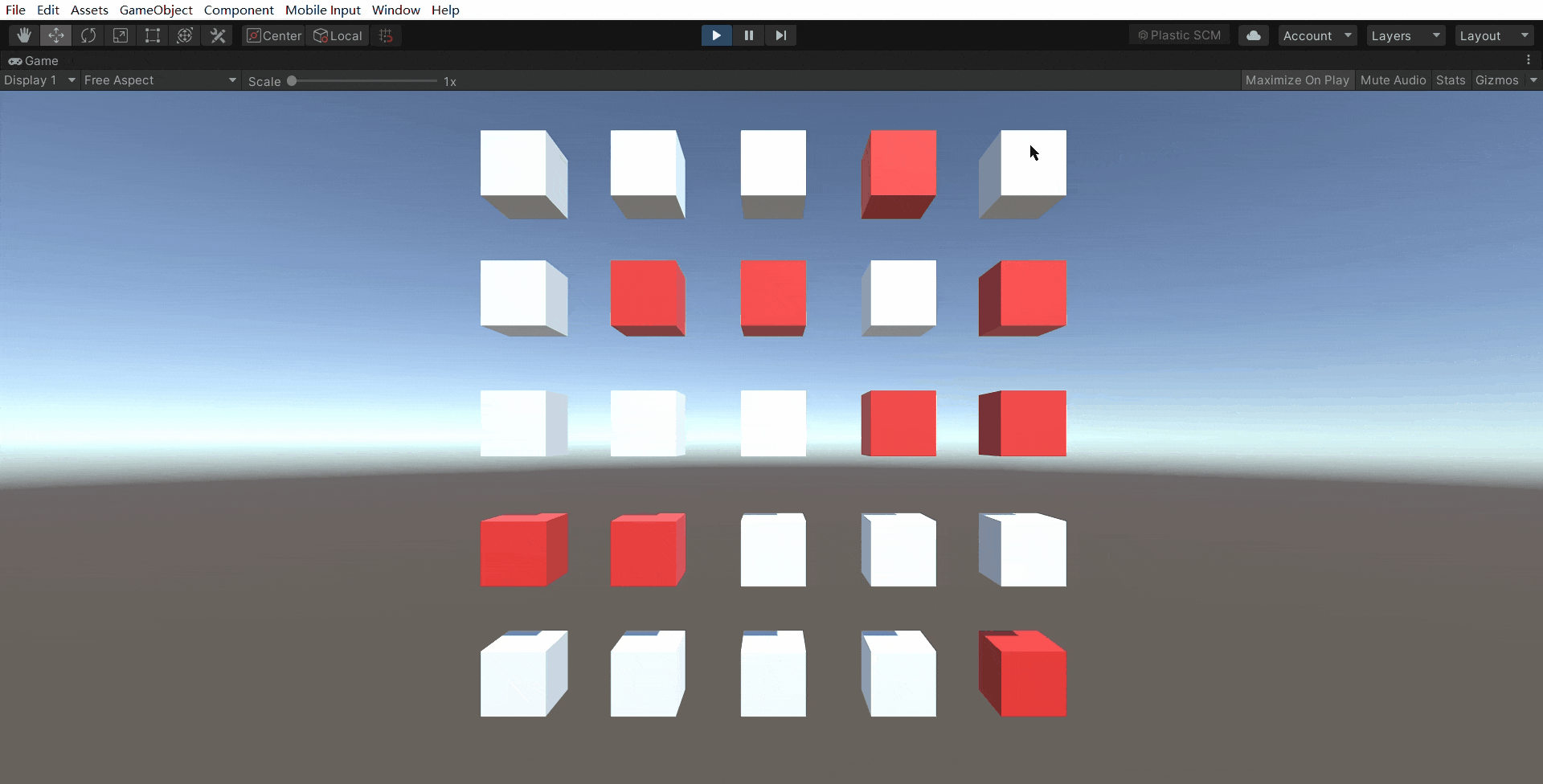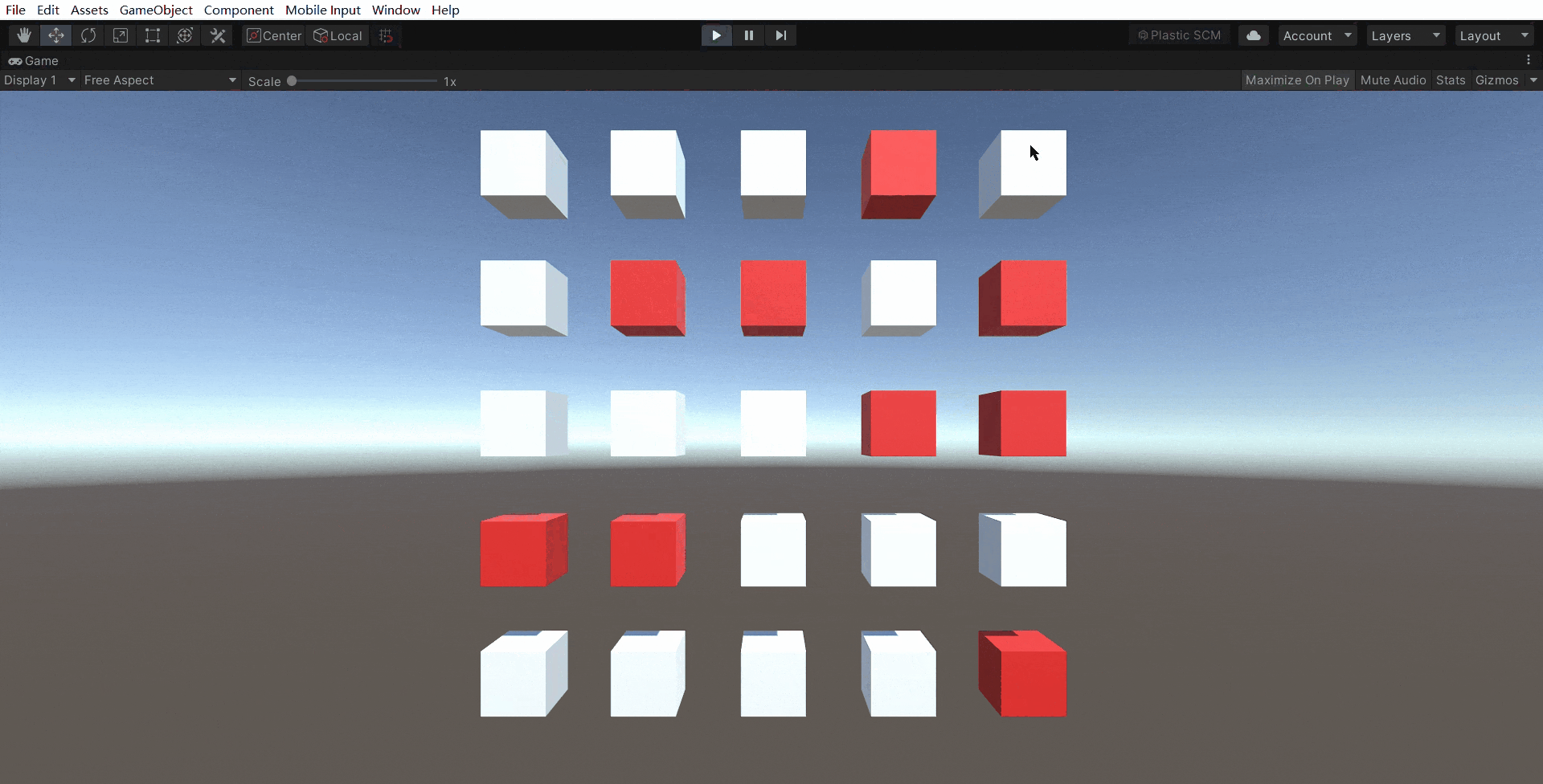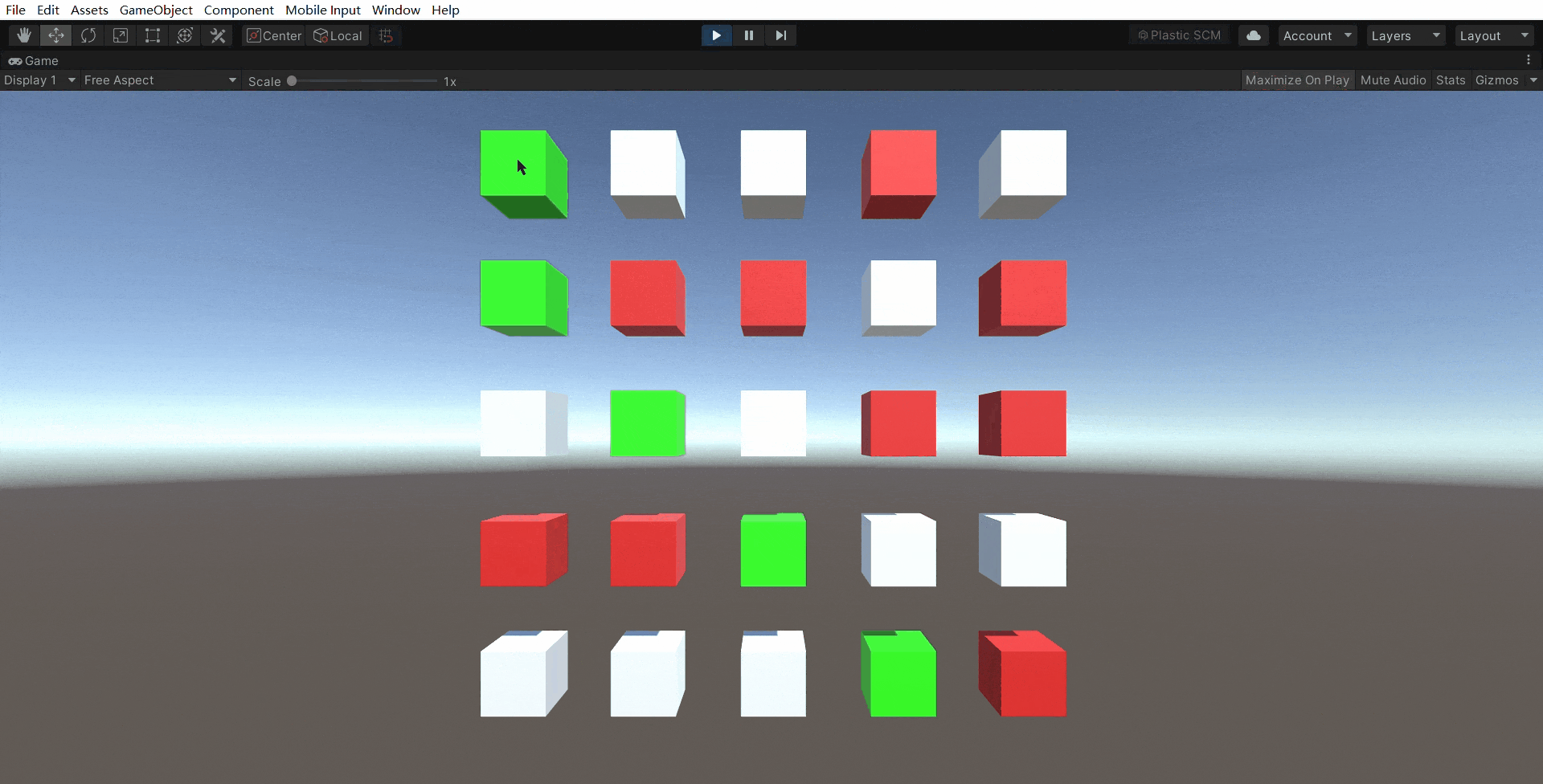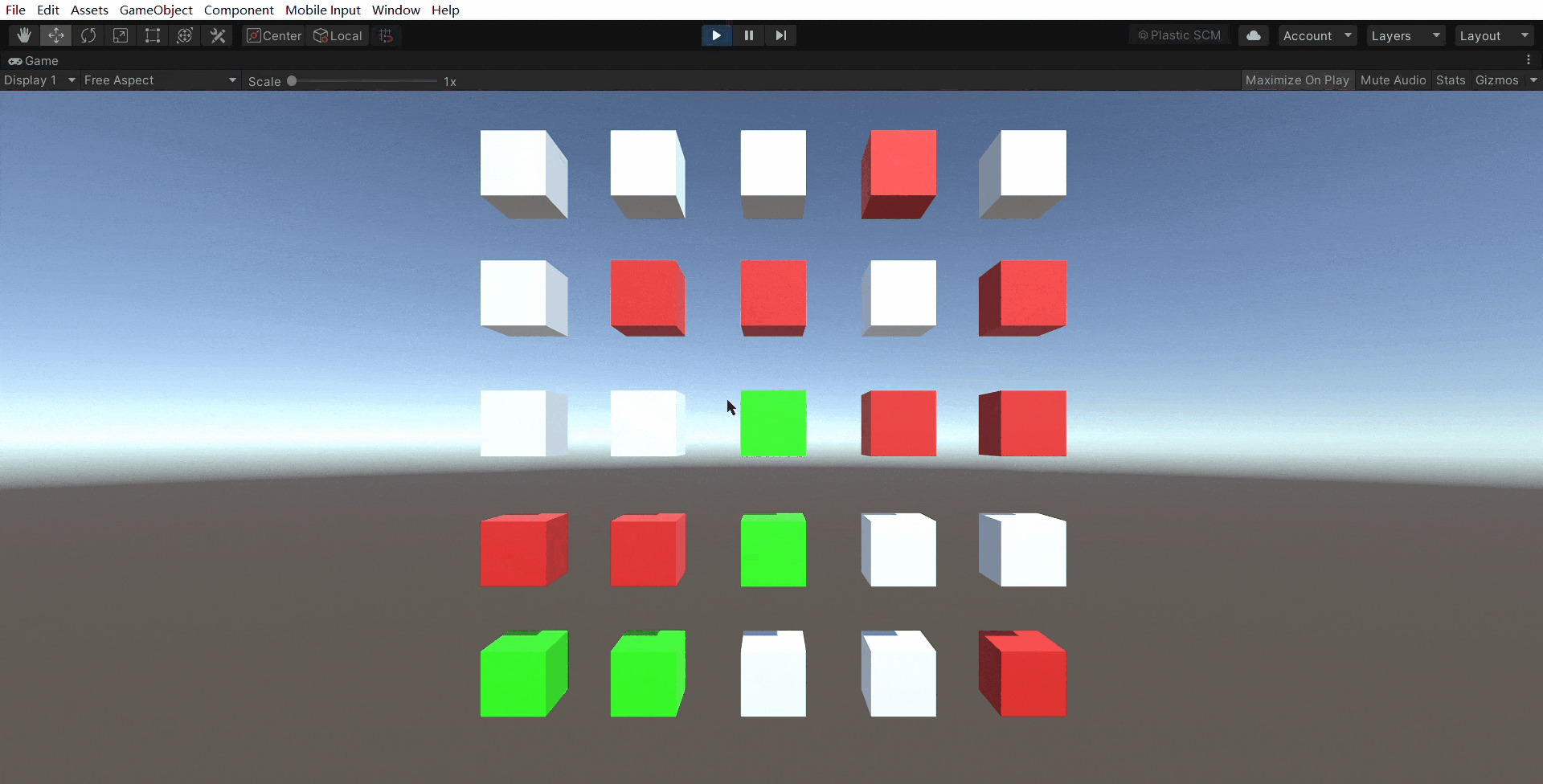






















 1530
1530

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








