
论文网址:Graph Meets LLMs: Towards Large Graph Models | OpenReview
论文代码:GitHub - THUMNLab/awesome-large-graph-model: Papers about large graph models.
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.3. Desired Characteristics of Large Graph Models
2.4. Graph Representation Basis
2.4.1. Graph Domains and Transferability
2.4.2. Aligning with Natural Languages
2.7.6. Urban Computing and Transportation
1. 心得
(1)怎么讲呢...总感觉对于已经有稍稍了解的人来说这篇文章略显小科普,不过如果有寻找模型需求的人可以从这里面找。主要是他们陈述的问题都是多年来大家也都知道的
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①Despite breakthrough achievements in the field of large-scale modeling, it still falls short of the development of visual and natural language
2.2. Introduction
①Four key desired characteristics of graph LLM: graph models with a) scaling laws, b) graph foundation model, c) in-context graph understanding and processing abilities, and d) versatile graph reasoning capabilities
②They analyse 3 aspects, a) graph representation, b) graph data, c) graph model
2.3. Desired Characteristics of Large Graph Models
①4 features of graph LLM:

(1)Graph models with scaling laws
①Scaling laws: empirically, when model size ↑, dataset size ↑, the training costs ↑ → the performance of LLM ↑
(2)Graph foundation model
①Different from LLM in vision, graph strongly differs
(3)In-context graph understanding and processing abilities
①In-context understanding helps generations
(4)Versatile graph reasoning capabilities
①LLMs shoud understand the structure, nodes, edges etc. of graphs
2.4. Graph Representation Basis
2.4.1. Graph Domains and Transferability
①Given the strong heterogeneity of graphs, researchers have begun to search for more advanced and abstract universal graph representations
2.4.2. Aligning with Natural Languages
①Strategy one: align graph and text, similar to computer vision
②Strategy two: transform graph to nature language (big challenge due to topological structure of graph)
③Strategy three: find common hidden space for graph and language
2.5. Graph Data
①Two situations of graph data: large number of small size graph (eg. molecule) or single/few number of big size graph (eg. social networks or citation graphs)
②Important principles: expand domain, type, statistics, task and modality diversity of graph LLMs
2.6. Graph Models
2.6.1. Backbone Architecture
①Different from CNN model, GNN performance decreases when model expands
②Compared GNN and Graph Transformer
2.6.2. Pre-training
①Advantages of graph pre-training: a) Encoding structural information, b) Easing data sparsity and label scarcity, c) Expanding applicability domains, d) Enhancing robustness and generalization
2.6.3. Post-processing
①Representative post-processing methods: prompting, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, reinforcement learning with human feedbacks, and model compression
②Listing techniques based on these methods
2.6.4. LLMs as Graph Models
①Transform graph data to nature language and regard it as common NLP problem
②Key features: model architectures, modeling Graph structure for LLMs, and graph data:
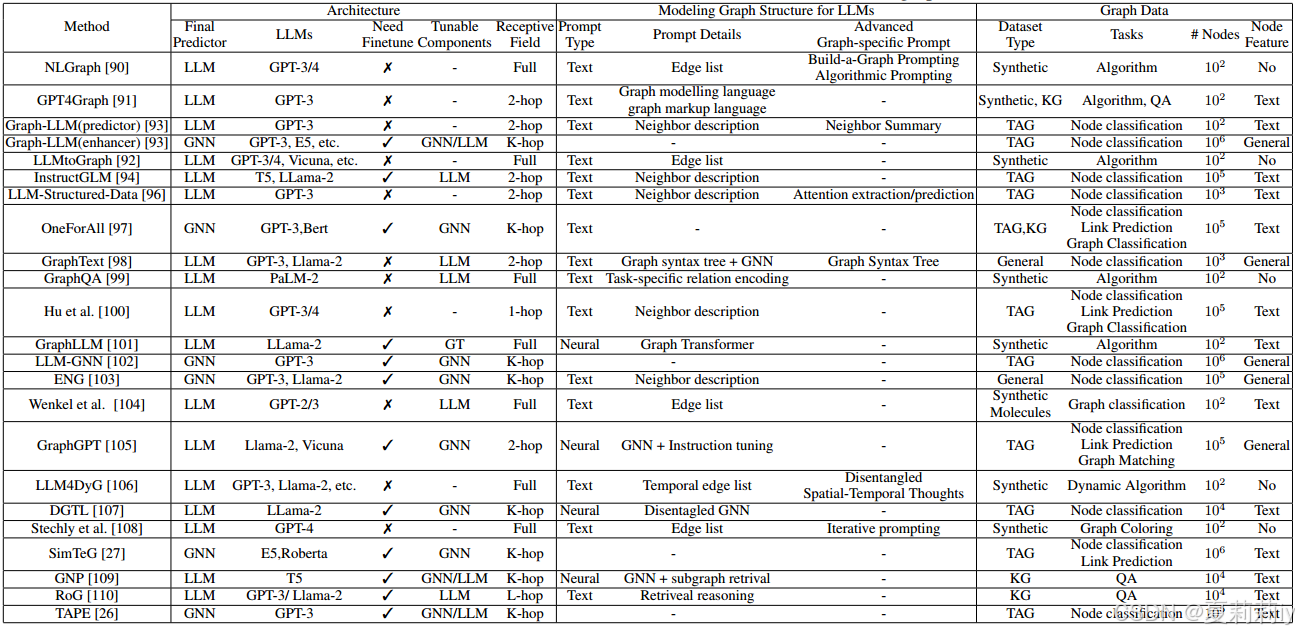
2.6.5. Summary
①No clear framework effectively integrates all techniques in graph LLM
2.7. Applications
①以下在介绍图的主要应用领域,比较偏科普了,我就不细说了,都是很常见的东西
2.7.1. Recommendation System
2.7.2. Knowledge Graph
2.7.3. Molecules
2.7.4. Finance
2.7.5. Code and Program
2.7.6. Urban Computing and Transportation
2.7.7. Beyond
2.8. Conclusion
~
4. Reference
Zhu, W. et al. (2023) 'Graph Meets LLMs: Towards Large Graph Models', NeurIPS 2023 GLFrontiers Workshop Poster. doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2308.14522

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








