random process: we know what outcomes could happen, but we don’t know which particular outcome will happen
two ways to interpret probability
- frequentist interpretation
- bayesian interpretation
law of large numbers
disjoint events(mutually exclusive) cannot happen at the same time.
p
non-disjoint events
for disjoint events A and B,
union of disjoint events
P(A or B)=P(A)+P(B)
union of non-disjoint events
P(J or red) = P(J)+P(red)-P(J and red)
general addition rule:
P(A or B) = P(A) +P(B)-P(A and B)
sample space
a collection of all possible outcomes of a trial
a probability distribution lists all possible outcomes in the sample space and the probabilities with which they occur
rules of probabilities distribution
- the events listed must be disjoint(mutually exclusive)
- each 0–1
- sum to 1 to represent the entire sample space
complementary events:
two disjoint event which sum up to 1.
disjoint -> complementary
two precesses are independent if knowing the outcome of one provides no useful information about the outcome of the other.
knowing B tells nothings about A
P(A|B) = P(A) where A and B are independent.
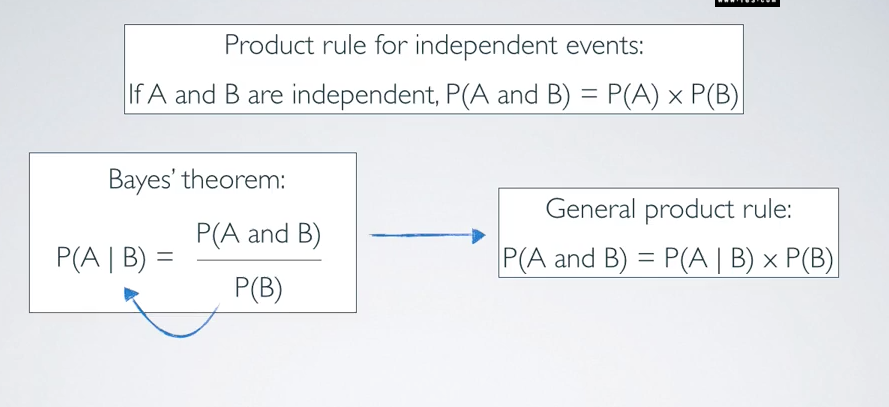
product rule for independent events:
P(A and B) = P(A)*P(B)
when choose sample, random select means the samples are independent
marginal probability
joint probability
conditional p
calculate condition p based on the bayed’s theorem:
bayes inference
bayes inference
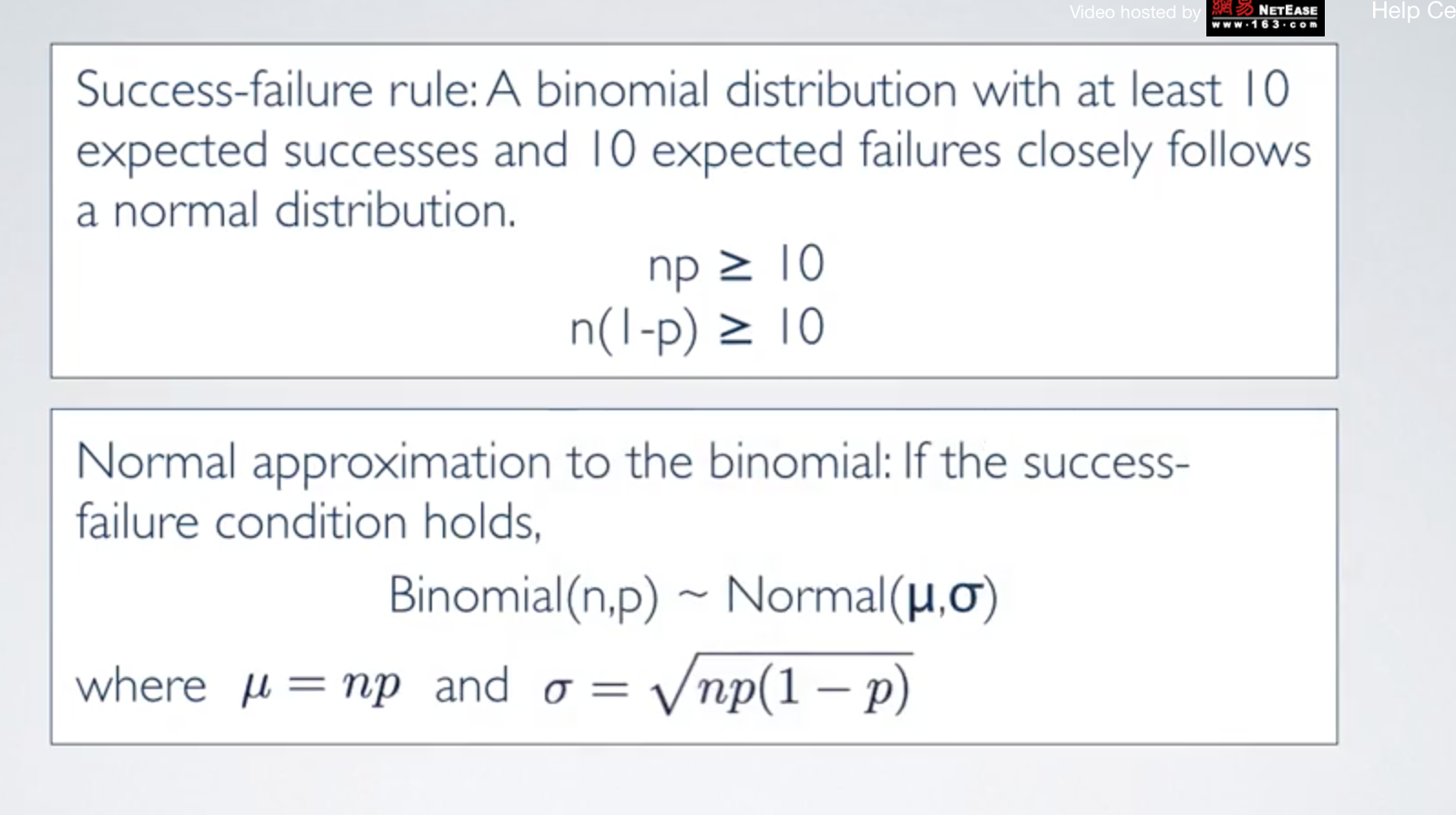
二项分布的标准差
二项分布与正泰分布的转换

























 47
47

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








