游戏说明
一个用pixi.js编写的h5塔防游戏,可以用electron打包为exe,支持移动端,也可以用webview控件打包为app在移动端使用
环境说明
cnpm@6.2.0
npm@6.14.13
node@12.22.7
npminstall@3.28.0
yarn@1.22.10
npm config list
electron_mirror = "https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/electron/"
home = "https://www.npmjs.org"
registry = "https://registry.npmmirror.com/" 四叉树的应用:
对于复杂的运算,循环次数多的应用我们可以使用四叉树来减少运算。
四叉树对象的封装:
/**
* 四叉树
*/
export class Quadtree {
/**
* 拆分的最大数量
*/
maxObjects:number
/**
* 拆分递归等级
*/
maxLevels:number
/**
* 当前等级
*/
level:number
/**
* 视图大小
*/
bounds:RECT
/**
* 区域拥有的对象
*/
objects:RECT[]
/**
* 子四叉树
*/
nodes:Quadtree[]
/**
* 构造函数
* @param bounds 视图大小
* @param maxObjects 拆分的最大数量
* @param maxLevels 拆分等级
* @param level 当前等级
*/
constructor(bounds:RECT, maxObjects:number, maxLevels:number, level:number) {
this.maxObjects = maxObjects || 10
this.maxLevels = maxLevels || 4
this.level = level || 0
this.bounds = bounds
this.objects = []
this.nodes = []
}
/**
* 分割
*/
split() {
const nextLevel = this.level + 1
const subWidth = this.bounds.width / 2
const subHeight = this.bounds.height / 2
const x = this.bounds.x
const y = this.bounds.y
// top right node
this.nodes[0] = new Quadtree({
x: x + subWidth,
y: y,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, this.maxObjects, this.maxLevels, nextLevel)
// top left node
this.nodes[1] = new Quadtree({
x: x,
y: y,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, this.maxObjects, this.maxLevels, nextLevel)
// bottom left node
this.nodes[2] = new Quadtree({
x: x,
y: y + subHeight,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, this.maxObjects, this.maxLevels, nextLevel)
// bottom right node
this.nodes[3] = new Quadtree({
x: x + subWidth,
y: y + subHeight,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, this.maxObjects, this.maxLevels, nextLevel)
}
/**
* 获取矩形所在的范围
* @param pRect
* @returns 返回范围索引
*/
getIndex(pRect:RECT) {
const indexes = []
const verticalMidpoint = this.bounds.x + (this.bounds.width / 2)
const horizontalMidpoint = this.bounds.y + (this.bounds.height / 2)
const startIsNorth = pRect.y < horizontalMidpoint
const startIsWest = pRect.x < verticalMidpoint
const endIsEast = pRect.x + pRect.width > verticalMidpoint
const endIsSouth = pRect.y + pRect.height > horizontalMidpoint
// top-right quad
if (startIsNorth && endIsEast) {
indexes.push(0)
}
// top-left quad
if (startIsWest && startIsNorth) {
indexes.push(1)
}
// bottom-left quad
if (startIsWest && endIsSouth) {
indexes.push(2)
}
// bottom-right quad
if (endIsEast && endIsSouth) {
indexes.push(3)
}
return indexes
}
/**
* 插入矩形
* @param pRect 要插入的矩形
* @returns
*/
insert(pRect:RECT) {
let i = 0
let indexes
// 如果拆分了就取子集node插入
if (this.nodes.length) {
indexes = this.getIndex(pRect)
for (i = 0; i < indexes.length; i++) {
this.nodes[indexes[i]].insert(pRect)
}
return
}
// 储存矩形对象
this.objects.push(pRect)
// 拆分逻辑判断
if (this.objects.length > this.maxObjects && this.level < this.maxLevels) {
// 拆分状态判断
if (!this.nodes.length) {
this.split()
}
// 拆分了重置对象
for (i = 0; i < this.objects.length; i++) {
indexes = this.getIndex(this.objects[i])
for (let k = 0; k < indexes.length; k++) {
this.nodes[indexes[k]].insert(this.objects[i])
}
}
// 拆分了清除储存的对象
this.objects = []
}
}
/**
* 获取矩形周围的对象
* @param pRect
* @returns 返回四分算法的矩形数据
*/
retrieve(pRect:RECT) {
const indexes = this.getIndex(pRect)
let returnObjects = this.objects
// 如果拆分了就用拆分的子集
if (this.nodes.length) {
for (let i = 0; i < indexes.length; i++) {
returnObjects = returnObjects.concat(this.nodes[indexes[i]].retrieve(pRect))
}
}
// 移除重复项
returnObjects = returnObjects.filter(function(item, index) {
return returnObjects.indexOf(item) >= index
})
return returnObjects
}
/**
* 获取圆范围的矩形对象
* @param p 圆心点
* @param r 圆半径
* @returns 返回与圆相碰撞的矩形对象
*/
retrieveArc(p:POINT, r:number) {
const rect = {
x: p.x - r,
y: p.y - r,
width: r * 2,
height: r * 2
}
const arr = this.retrieve(rect)
const returnArr = []
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
const itemRect = arr[i]
const b = userUtils.collsion.boxCircle(itemRect.x, itemRect.y, itemRect.width, itemRect.height, p.x, p.y, r)
if (b) {
returnArr.push(itemRect)
}
}
return returnArr
}
/**
* 清楚缓存
*/
clear() {
this.objects = []
for (let i = 0; i < this.nodes.length; i++) {
if (this.nodes.length) {
this.nodes[i].clear()
}
}
this.nodes = []
}
}
在游戏中的使用
四叉树对象是在场景对象(scene/index.ts)中的quadtree属性上
在每一帧中我们都要更新一下四叉树对象 将场景中的所有对象都更新到四叉树中。这样我们就可以分区域的寻找区域的对象。
如果不适用四叉树:我们寻找一个区域里面的对象需要循环所有的对象然后判断是否在区域中。
使用了四叉树:我们就可以根据四叉树的规律先从大的区域找然后一层一层的找到区域里面的对象 这样可以减少循环复杂度。
相当于原本需要循环很多的次的遍历全部对象,变成了循环一次,遍历部分对象
比如我们需要选择一个矩形变量里面的单位。这时候就可以使用四叉树,然后我们获取到了矩形区域里面的对象 我们可以通过圆形与矩形的碰撞判断从而实现获取圆形范围里面的单位。
这样我们就可以做到当敌人接近攻击范围就可以自动开火。
这是我们要做的目标: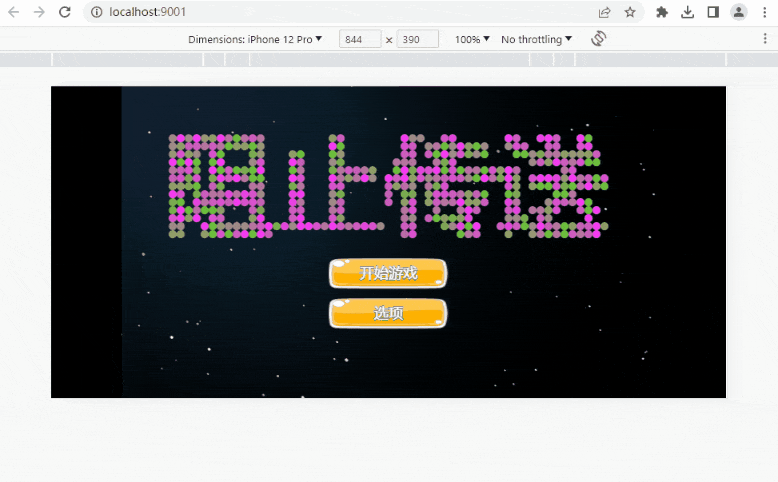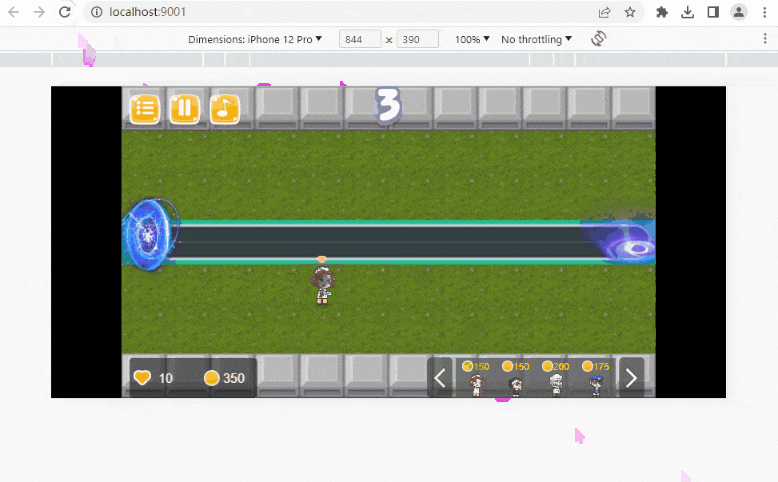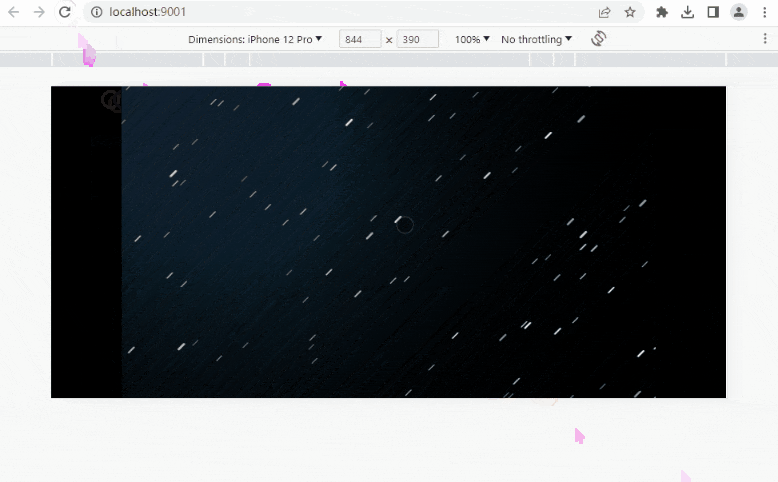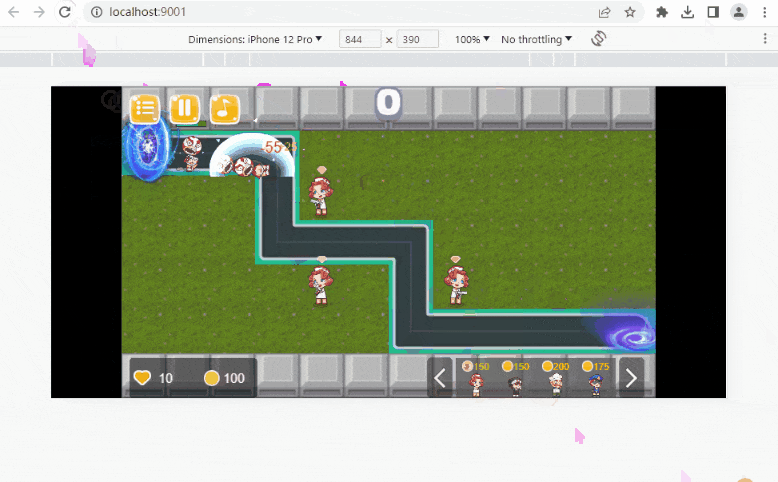
项目开源地址:
https://github.com/yinhui1129754/towerDefense
游戏开发交流群:
859055710
























 587
587

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








