(一)发行版:Ubuntu16.04.7
(二)记录:
(1)为什么介绍exec函数族
在父进程fork()创建子进程中,子进程会拷贝父进程的代码,但是有时候不想要子进程拷贝父进程的代码,则需要引入exec函数族。
(2)exec函数原型
在Linux中并没有exec函数,而是有6个以exec开头的函数族,下面列举了exec函数族的6个函数成员的函数原型:
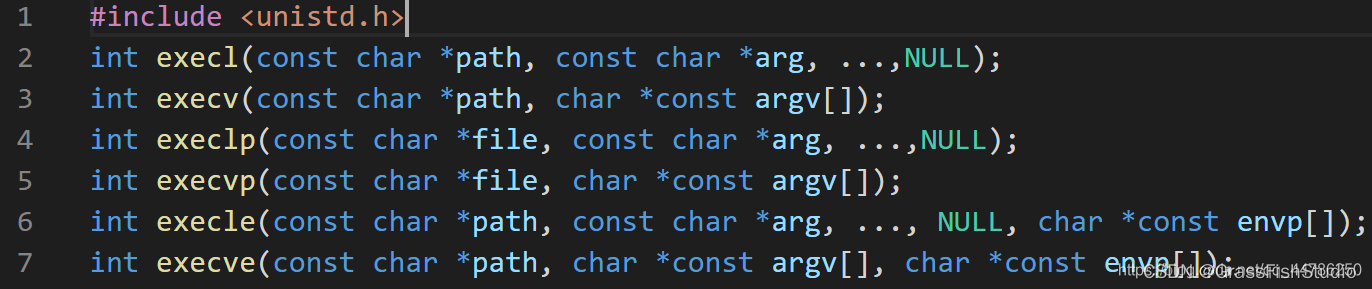
(3)exec函数族能够更换程序的原因
“换核不换壳”,exec不换创建新进程,但是会换进程里面的执行代码。
(4)调用exec函数族的情况
a.当进程认为自己不能再为系统和用户做出任何贡献时,就可以调用任何exec函数让自己重生。
b.如果一个进程想执行另一个程序,那么他就可以调用fork函数新建一个进程,然后调用一个exec函数使子进程重生。
(5)使用execl换核
a.创建一个c文件,编译生成可执行文件(即图中hello 会打印hello world.)
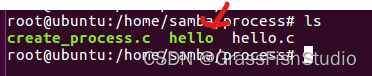
b.在上篇文章代码基础上增加
//子进程
if(pid==0)
{
execl("/home/samba/process/hello","hello",NULL);
exit(1);
// printf("This is a child process,child_pid: %d\nparent_pid: %d\n",getpid(),getppid());
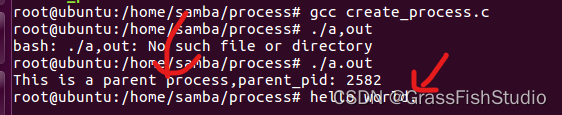
}在子进程中增加execl函数换核,第一个参数为可执行文件的绝对路径,第二个参数可执行文件的名字。
c.编译运行
(6)换核换自有的命令
//子进程
if(pid==0)
{
// execl("/home/samba/process/hello","hello",NULL);
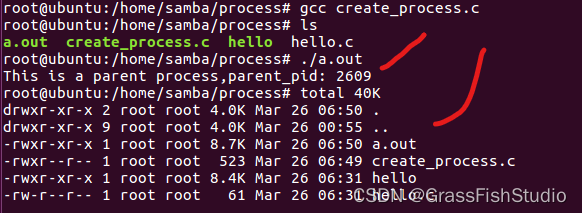
execl("/bin/ls","ls","-al",NULL);
exit(1);
// printf("This is a child process,child_pid: %d\nparent_pid: %d\n",getpid(),getppid());
}-al为传给ls的命令
(三)命令:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
pid=fork();
if(pid<0){
printf("fork is error.\n");
return -1;
}
//父进程
if(pid>0)
printf("This is a parent process,parent_pid: %d\n",getpid());
//子进程
if(pid==0)
{
// execl("/home/samba/process/hello","hello",NULL);
execl("/bin/ls","ls","-alh",NULL);
exit(1);
// printf("This is a child process,child_pid: %d\nparent_pid: %d\n",getpid(),getppid());
}
return 0;
}





















 1874
1874











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








