论文主要内容与创新点总结
主要内容
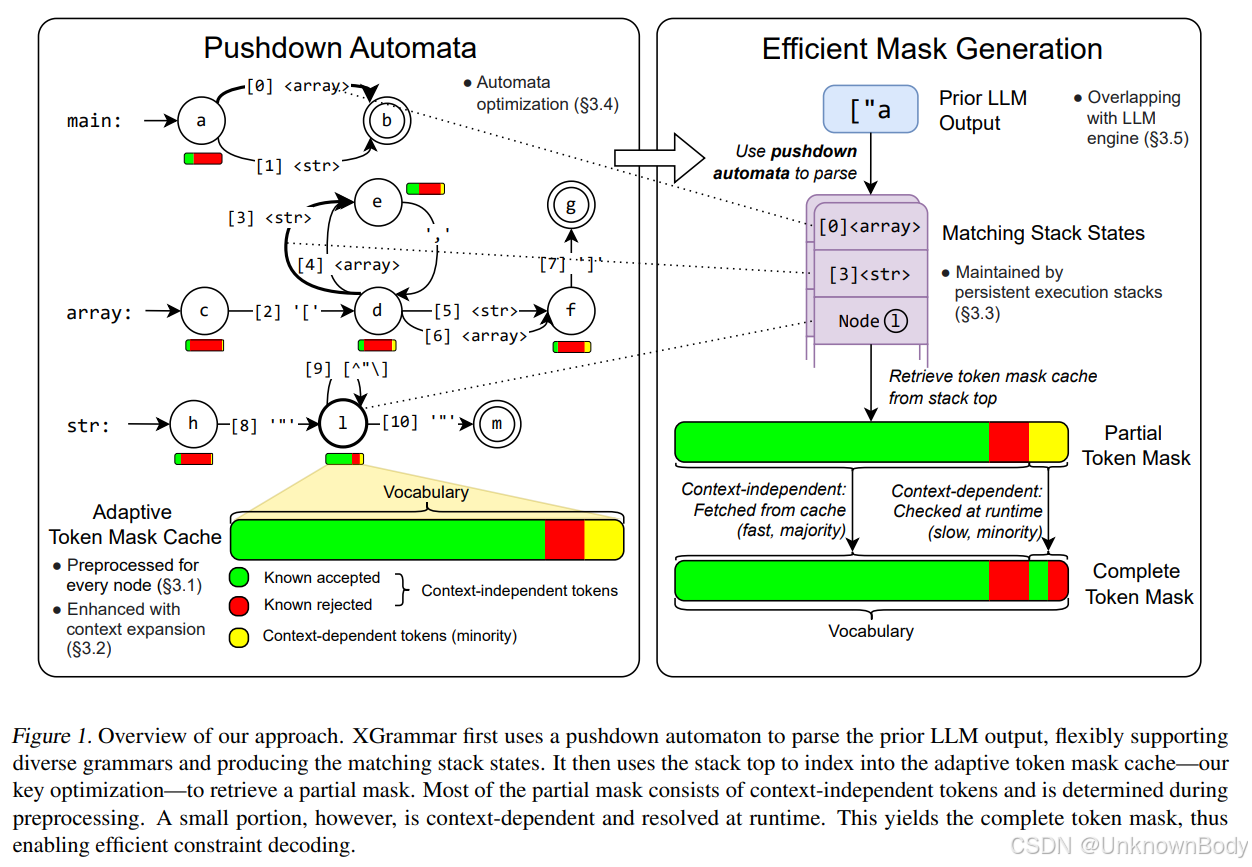
本文提出了XGrammar,一个针对大语言模型(LLM)的灵活高效结构化生成引擎,旨在解决上下文无关文法(CFG)在约束解码中效率低下的问题。XGrammar通过以下方式优化结构化生成:
- 词汇分类与缓存:将词汇分为上下文无关token(可预检查)和上下文相关token(运行时解释),构建自适应令牌掩码缓存,减少运行时检查开销。
- 上下文扩展:通过预计算规则的扩展后缀,过滤无效的上下文相关令牌,进一步减少运行时处理量。
- 持久化栈机制:设计高效的持久化执行栈,支持状态分支和回滚,加速上下文相关令牌的检查。
- 与LLM推理引擎协同设计:将文法计算与GPU执行重叠,实现端到端服务中的近零开销结构化生成。
实验结果表明,XGrammar相比现有方案实现了最高100倍的加速,在Llama-3.1模型上结合LLM推理引擎可实现结构化生成的近零开销。
创新点
- 自适应令牌掩码缓存:通过分类上下文无关和相关令牌,预计算











 订阅专栏 解锁全文
订阅专栏 解锁全文


















 3193
3193

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










