udacity Markov定位程序,实现观察模式定位,并最终实现完整定位。python版本,根据网上的C++程序改写,方便大家参考。
参考代码:
(1)https://github.com/informramiz?page=5&tab=repositories
这个工程项目里有代码以及数据。感谢作者的无私分享。
参考文章:
(1)自动驾驶定位算法(九)-直方图滤波定位-腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云
这篇文章对于理解Bayes滤波很有帮助。
参考公式:

一、观察模式
本程序实现Markov定位中的观察模式。
二、车辆观察方式
车辆的传感器实现观察。车辆在实现移动到新的位置后,观察周边环境。
如下图示:
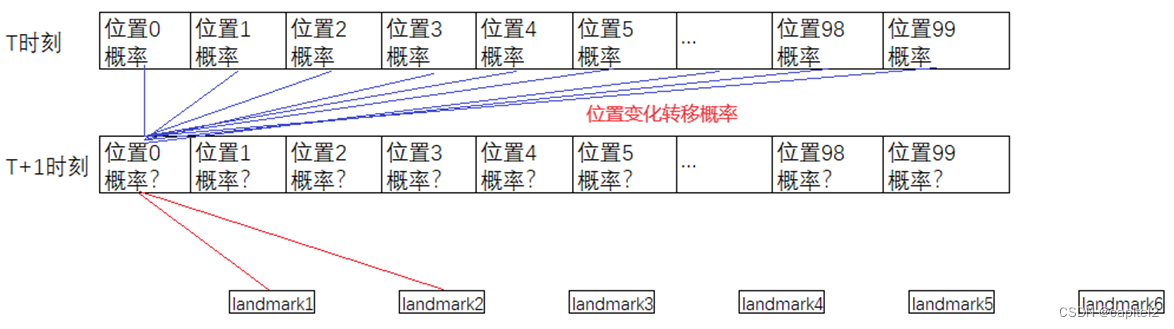
图1:观察模式
如上图示,车辆在某位置可以观察到landmark1,landmark2;也可以不进行观察。
三、数据说明
(1)地图数据
map_1d = [[1,9],[2,15],[3,25],[4,31],[5,59],[6,77]]
(2)移动控制数据
controls_data = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
车辆一次移动1米。
(3)观察数据
observations_data = [[1, 4.5], [2, -1], [3, -1], [4, -1], [5, -1], [6, -1], [7, 28], [8, 27], [9, 26], [10, 25], [11, -1], [12, -1], [13, -1], [14, -1]] observations_data2 = [[1, 4.5], [1, 13.5], [2, -1], [3, -1], [4, -1], [5, -1], [6, -1], [7, 28], [8, 27], [9, 26], [10, 25], [11, -1], [12, -1], [13, -1], [14, -1]] observations_data3 = [[1, 4.5], [1, 13.5], [2, -1], [3, -1], [4, -1], [5, -1], [6, -1], [7, 28], [8, 27], [9, 26], [10, 25], [11, -1], [12, -1], [13, -1], [14, 21]] observations_data4 = [[1, 4.5], [1, 13.5], [2, -1], [3, -1], [4, -1], [5, -1], [6, -1], [7, 28], [8, 27], [9, 26], [10, 25], [11, -1], [12, -1], [13, -1], [14, 21],[14,30]]
observations_data,说明1,7,8,9,10时刻观察到路标,且每次只观察到1个路标。
observations_data2,说明1,7,8,9,10时刻观察到路标,1时刻观察到了2个路标;
observations_data3,说明1,7,8,9,10,14时刻观察到路标,1时刻观察到2个路标;
observations_data4,说明1,7,8,9,10,14时刻观察到路标,1,14时刻观察到2个路标。
四、Markov定位程序--包含移动模式+观察模式
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class MeasurementPackage:
def __init__(self,delta_x_f,obs):
self.delta_x_f = delta_x_f
self.observation_s_ = obs
b_initialized = 0
map_1d = [[1,9],[2,15],[3,25],[4,31],[5,59],[6,77]] #index,xf
controls_data = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
observations_data = [[1, 4.5], [2, -1], [3, -1], [4, -1], [5, -1], [6, -1], [7, 28], [8, 27], [9, 26], [10, 25], [11, -1], [12, -1], [13, -1], [14, -1]]
observations_data2 = [[1, 4.5], [1, 13.5], [2, -1], [3, -1], [4, -1], [5, -1], [6, -1], [7, 28], [8, 27],
[9, 26], [10, 25], [11, -1], [12, -1], [13, -1], [14, -1]]
observations_data3 = [[1, 4.5], [1, 13.5], [2, -1], [3, -1], [4, -1], [5, -1], [6, -1], [7, 28], [8, 27],
[9, 26], [10, 25], [11, -1], [12, -1], [13, -1], [14, 21]]
observations_data4 = [[1, 4.5], [1, 13.5], [2, -1], [3, -1], [4, -1], [5, -1], [6, -1], [7, 28], [8, 27],
[9, 26], [10, 25], [11, -1], [12, -1], [13, -1], [14, 21],[14,30]]
bel_x_init = np.zeros(100)
bel_x = np.zeros(100)
M_PI = 3.1415926
ONE_OVER_SQRT_2PI = 1 / np.sqrt(2 * M_PI)
control_std = 1.0
observation_std = 1.0
distance_max = 100
measurement_elem = MeasurementPackage([], [])
measurement_pack_list = []
def square(x):
return x * x
def normpdf(x, mu, std):
return (ONE_OVER_SQRT_2PI / std) * np.exp(-0.5 * square((x - mu) / std))
def process_measurement(MeasurementPackage):
global b_initialized
global bel_x_init
global bel_x
if(b_initialized == 0):
b_initialized = 1
for l in range(len(map_1d)):
landmark_temp = map_1d[l]
if(landmark_temp[1] > 0 and landmark_temp[1] < len(bel_x_init)):
position_x = landmark_temp[1]
bel_x_init[position_x] = 1.0
bel_x_init[position_x - 1] = 1.0
bel_x_init[position_x + 1] = 1.0
#normalize bel_x_init
sum = np.sum(bel_x_init)
bel_x_init = bel_x_init / sum
delta_x_f = MeasurementPackage.delta_x_f
observations = MeasurementPackage.observation_s_
for i in range(len(bel_x)):
pos_i = float(i)
posterior_motion = 0.0
for j in range(len(bel_x)):
pos_j = float(j)
distance_ij = pos_i - pos_j
transition_prob = normpdf(distance_ij, delta_x_f, control_std)
posterior_motion = posterior_motion + transition_prob * bel_x_init[j]
pseudo_ranges = []
for l in range(len(map_1d)):
map_elem = map_1d[l]
range_l = map_elem[1] - pos_i
if(range_l > 0.):
pseudo_ranges.append(range_l)
pseudo_ranges.sort()
posterior_obs = 1.0
for z in range(len(observations)):
if(len(pseudo_ranges) > 0):
pseudo_range_min = pseudo_ranges[0]
pseudo_ranges.remove(pseudo_ranges[0])
else:
pseudo_range_min = distance_max
posterior_obs *= normpdf(observations[z], pseudo_range_min, observation_std)
bel_x[i] = posterior_obs * posterior_motion
# normalize bel_x
sum = np.sum(bel_x)
bel_x = bel_x / sum
bel_x_init = bel_x.copy()
def display_map(grid, bar_width=1):
if(len(grid) > 0):
x_labels = range(len(grid))
plt.bar(x_labels, height=grid, width=bar_width-0.2, color='b')
plt.xlabel('Grid Cell')
plt.ylabel('Probability')
plt.ylim(0, 1) # range of 0-1 for probability values
plt.title('Probability of the robot being at each cell in the grid')
plt.xticks(np.arange(min(x_labels), max(x_labels)+1, 3))
plt.show()
else:
print('Grid is empty')
def read_measurement_data():
obs_index = 0
match_len = 0
for i in range(len(controls_data)):
delta_x_f = controls_data[i]
obs_index = i + match_len
observation = observations_data[obs_index]
distance_f = observation[1]
if(distance_f < 0):
measurement_elem = MeasurementPackage(delta_x_f, [])
measurement_pack_list.append(measurement_elem)
continue
obs_vector = []
obs_vector.append(distance_f)
bSearch = 1
bFind = 0
j = obs_index
idx1 = observation[0]
while(bSearch):
if((j + 1) == len(observations_data)):
break
else:
observation = observations_data[j+1]
idx2 = observation[0]
if(idx1 == idx2):
bFind = 1
distance_f = observation[1]
obs_vector.append(distance_f)
j = j + 1
match_len = match_len + 1
else:
bSearch = 0
measurement_elem = MeasurementPackage(delta_x_f, obs_vector)
measurement_pack_list.append(measurement_elem)
if __name__ == '__main__':
read_measurement_data()
for t in range(len(measurement_pack_list)):
process_measurement(measurement_pack_list[t])
display_map(bel_x)
五、结果展示
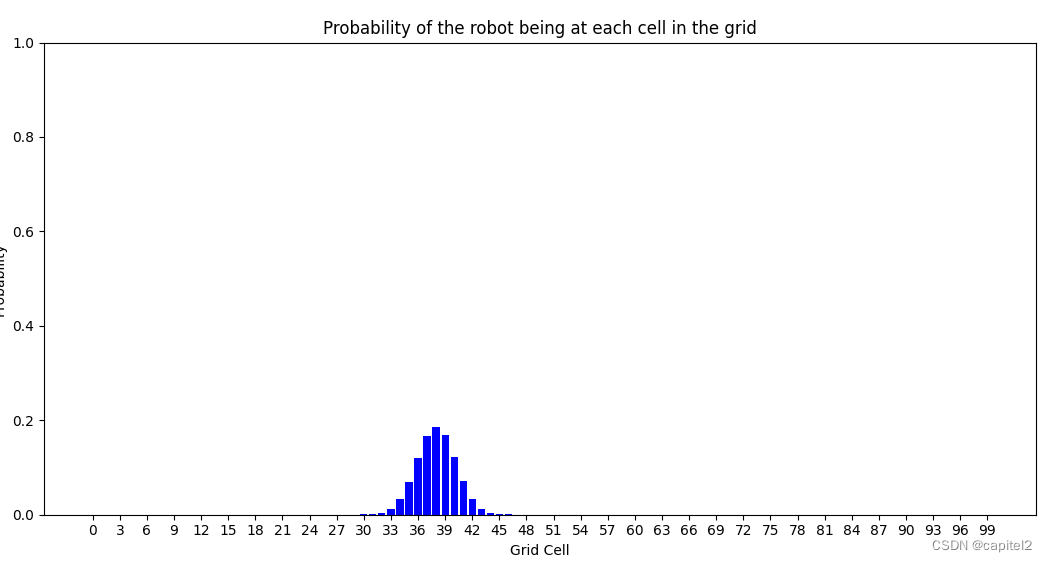
由图可见,通过观察模式,能够实现车辆的定位。





















 321
321











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








