(一)程序来自如下链接:
程序实现2D histogram_filter。
(二)参考文档:
(1)自动驾驶定位算法(九)-直方图滤波定位-腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云
(2)histgoram_filter_localization_main.rst
(三)车辆运动轨迹
不考虑车辆位置概率的运动模式以及观察模式,仅根据运动方程得到的车辆运动轨迹,如下图示:

图1:车辆运动轨迹
程序中注释:
#grid_map = histogram_filter_localization(grid_map, u, z, yaw)
#draw_heat_map(grid_map.data, mx, my)
(四)根据车辆位置概率大小来预测车辆轨迹
根据histogram_filter_localization_main.rst描述,如何根据车辆位置的概率大小来预测车辆位置:

取车辆位置概率最大处作为车辆的预测轨迹,如下图示:
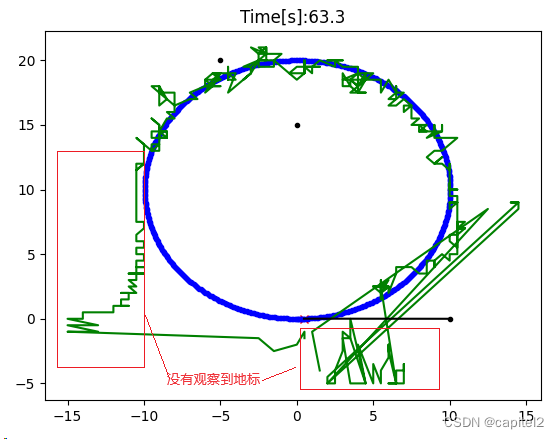
图2:车辆预测轨迹
从图2可以看出,刚开始车辆没有观察到地标的时候,其预测的位置轨迹与其实际的运行轨迹相差很大,说明车辆定位失败;而当车辆通过传感器观察到地标后,其预测位置逐渐与运行位置相接近,说明车辆定位成功。
(五)修改的程序代码
def main():
print(__file__ + " start!!")
# RF_ID positions [x, y]
RF_ID = np.array([[10.0, 0.0],
[10.0, 10.0],
[0.0, 15.0],
[-5.0, 20.0]])
time = 0.0
xTrue = np.zeros((4, 1))
px = []
py = []
px_est = []
py_est = []
px.append(xTrue[0, 0])
py.append(xTrue[1, 0])
#px_est.append(xTrue[0, 0])
#py_est.append(xTrue[1, 0])
grid_map = init_grid_map(XY_RESOLUTION, MIN_X, MIN_Y, MAX_X, MAX_Y)
mx, my = calc_grid_index(grid_map) # for grid map visualization
while SIM_TIME >= time:
time += DT
print(f"{time=:.1f}")
u = calc_control_input()
yaw = xTrue[2, 0] # Orientation is known
xTrue, z, ud = observation(xTrue, u, RF_ID)
px.append(xTrue[0, 0])
py.append(xTrue[1, 0])
grid_map = histogram_filter_localization(grid_map, u, z, yaw)
r, c = np.where(grid_map.data == np.max(grid_map.data))
px_est.append(r[0] * 0.5 - 15)
py_est.append(c[0] * 0.5 - 5)
if show_animation:
plt.cla()
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect(
'key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
#draw_heat_map(grid_map.data, mx, my)
plt.plot(xTrue[0, :], xTrue[1, :], "xr")
plt.plot(RF_ID[:, 0], RF_ID[:, 1], ".k")
plt.plot(px, py, ".b")
plt.plot(px_est, py_est, linestyle = '-', color = 'g')
for i in range(z.shape[0]):
plt.plot([xTrue[0, 0], z[i, 1]],
[xTrue[1, 0], z[i, 2]],
"-k")
plt.title("Time[s]:" + str(time)[0: 4])
plt.pause(0.1)
print("Done")





















 217
217











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








