C++ 入门笔记
- Functions in C++
- C++ header Files
- 如何在VStudio的环境下Debug C++ (看memory值)
- 12.C++中的条件和分支(IF语句) CONDITIONS and BRANCHES in C++ (if statements)
- 13. BEST Visual Studio Setup for C++ Projects!
- 14 loops in C++ (for loops , while loops)
- 15. Control Flow in C++ (continue, break, return)
- 16 pointers in C++(指针)
- 17 references in c++ (C++中的引用)
- 18 classes in C++
- 19 classes VS structs in C++
- 20 how to write a C++ class
- 21 Static in C++
- 22.static for classes and structs in c++
- 23 local static in C++(本地静态)(err)
- 24 ENUMS in C++ 枚举
- 25 constructors in C++
- 26 Destructors in C++
- 27 inheritance in C++
- 28 Virtual Functions in C++ 中的接口 纯虚函数
- 29 interfaces in C++中的接口
- 30 C++中的数组
- 32 C++中的字符串
- 33 C++ 字符串字面量
- 34 C++ 中的const
- 35 C++ 中的mutable关键字
- 36 C++ 构造函数初始化列表
- 37 C++ 的三元操作符 (a? b:C)
- 38 创建并,初始化C++对象
下面主要是我学习C++的一个笔记,记录学习中遇到的一些重点事项。
下面是视频的连接
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ay4y1i7Z6/?p=10&spm_id_from=333.1007.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=e6e8f67c0845f6b64075a5c82b90f71d
Functions in C++
主要介绍了函数/方法,在C++ 中的声明等信息。返回值,以及定义等
C++ header Files
主要讲解了C++ 头文件的一些注意事项
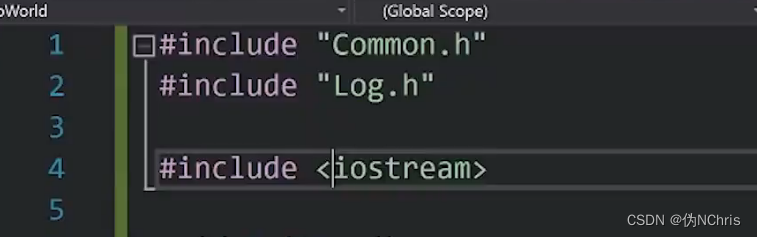
- 如图 1~2 行所示的,使用双引号的,一般表示是自己写的头文件
- 如图4行所写的,一般表示系统带的头文件
如图增加了一个条件,有没有定义LOG.H 文件,如果定义了则是不进行下面的 声明?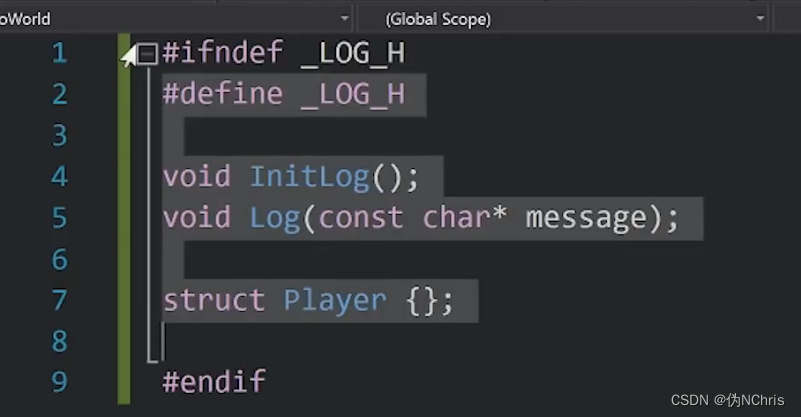
如何在VStudio的环境下Debug C++ (看memory值)
1.断点:在debug的时候使得代码停止,需要放在有代码的行上
2. 调试模式和发布模式在断点上会有一些差异
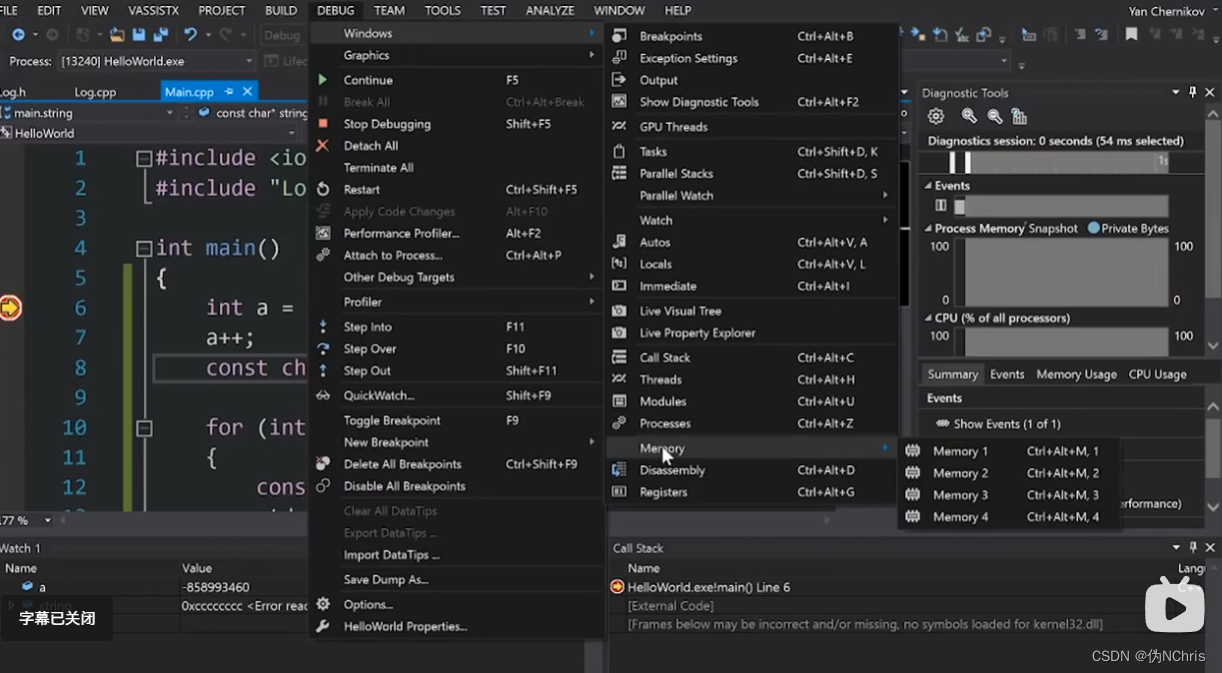
3. 调出界面查看数值,debug后会有一个Autos的界面,其中可以在name上输入值。然后查看
4. 查看memory地址下的值,打开窗口后输入address即可。
12.C++中的条件和分支(IF语句) CONDITIONS and BRANCHES in C++ (if statements)
汇编的角度查看if循环中执行的代码
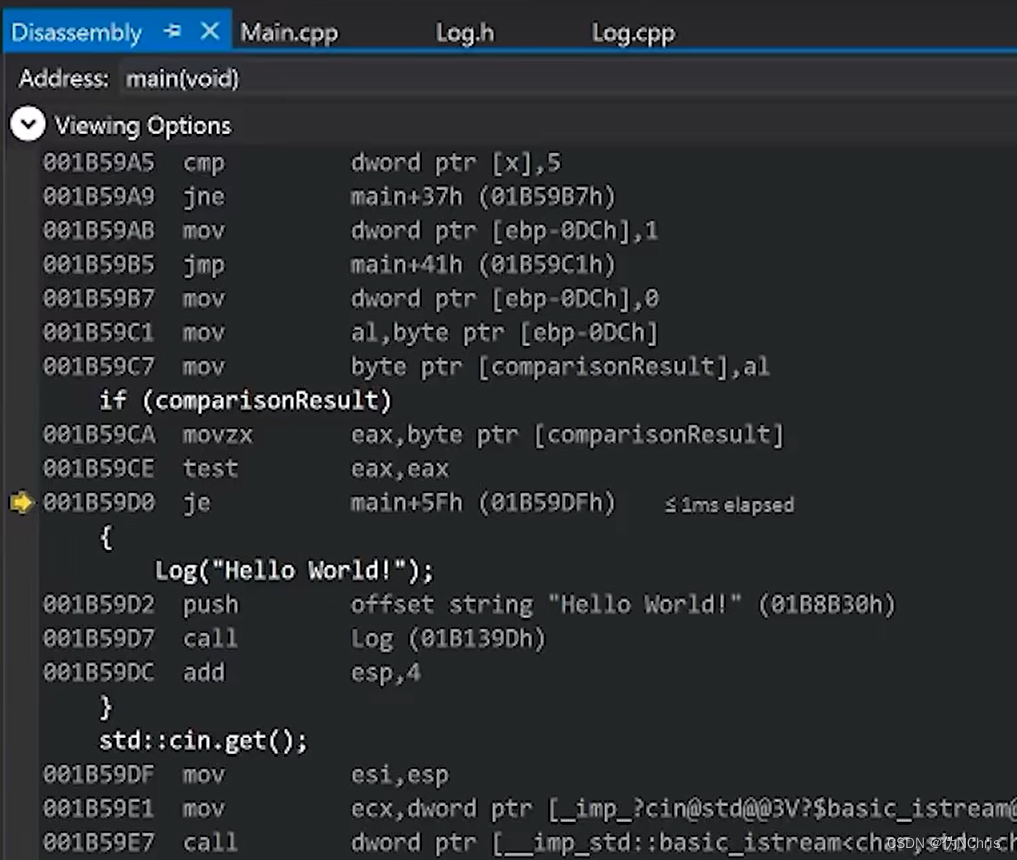
查看汇编 需要在DEBUG 模式中?
13. BEST Visual Studio Setup for C++ Projects!
主要讲解了如何初始化一个工程,将工程中的文件去分开到不同的文件夹中去。项目显示可以以文件格式来显示,也可以通过文件的路径来显示。
主要就是修改了如下图上的文件位置
14 loops in C++ (for loops , while loops)
代码多次执行的问题,讨论,不通过多次复制代码来执行,通过循环来执行。
for循环的基础格式
int main()
{
for(int i = 0; i < 5;i++)
{
log("hello word");
}
std::cin.get();
}
如下代码也可以实现5次的循环输出 hello word
int main()
{
int i = 0;
bool condition = false;
for(; condition ;)
{
log("hello word");
i++;
if(!(i < 5))
condition = flase;
}
std::cin.get();
}
bool condition = false;
while(condition )
{
log("hello word!");
}
do{
}while(condition );
15. Control Flow in C++ (continue, break, return)
continue:跳出单次循环,如果for执行5次,第三次循环触发continue,则第三次不执行,其他4次都执行
break:跳出大循环,如果第三次触发break,则45都不执行,直接出循环
return: 直接跳到大括号处,跳出子程序?
16 pointers in C++(指针)
笔者注:一直都说指针是C/C++的核心操作,也是非常容易引起混乱的操作,也许它也是比较容易的方式去理解其中精髓
查看memory的数据,如下操作可以查看数据
debug>>windows>>memory
如下代码将var的值,传递到了ptr上,memory的值可以看到,就是var的值
int main()
{
int var = 8;
void* ptr = &var;
std::cin.get();
}
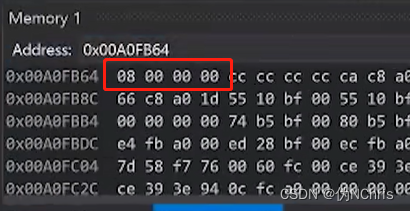
如下所示*ptr = 10,则是对ptr这个地址进行赋值,这样值就从8改到了10
int main()
{
int var = 8;
void* ptr = &var;
*ptr = 10;
std::cin.get();
}
给指针分配一个固定的大小
int main()
{
char* buffer = new char[8];
memset(buffer,0,8);
char** ptr = &buffer;//使得指针指向指针???
delete[] buffer;// 删除buffer的数据
std::cin.get();
}
可以看到这个数字的位置,被声明了
17 references in c++ (C++中的引用)
下面是引用的一个实例
最后输出的是6,a的值有被增加
void Increment(int* value)
{
(*value)++;
}
int main()
{
int a = 5;
Increment(&a);
log(a);
std::cin.get();
}
这个代码和上面的代码运行输出的结果是一样的,可以详细参考其中的差异
void Increment(int& value)
{
value++;
}
int main()
{
int a = 5;
Increment(a);
log(a);
std::cin.get();
}
指针和引用的另外一种用法
int main()
{
int a = 5;
int b = 8;
int* ref = &a;//关联上a的地址
*ref = 2;//给ref赋值2
int* ref = &b;//关联上b的地址
*ref = 1;//给ref赋值1
log(a);//out put 2
log(b);// out put 1
std::cin.get();
}
18 classes in C++
下面展示了class的方式去声明代码
#define LOG(X) std::cout << X << std::endl
class Player
{
public://允许下面声明的信息,被外部使用
int x,y;
int speed;
};
void Move(Player& player ,int xa ,int ya)
{
player.x += xa* player.speed;
player.y += ya* player.speed;
}
int main()
{
Player player;// a new objects
Move(player,1,-1);
std::cin.get();
}
下面就是把,move 放到class里面去写,推荐使用这样的方式去写,会简化代码
#define LOG(X) std::cout << X << std::endl
class Player
{
public://允许下面声明的信息,被外部使用
int x,y;
int speed;
void Move(int xa ,int ya)
{
x += xa * speed;
y += ya * speed;
}
};
int main()
{
Player player;// a new objects
player,Move(1,-1);
std::cin.get();
}
19 classes VS structs in C++
笔者看了两遍也没看明白人家要说啥~~~~尴了个尬
20 how to write a C++ class
通过下面的代码,展示了main函数中去调用class下的函数的方式
class中可以申明变量,常量,函数等信息,可以通过这样的方式实现数据的传递。
class log
{
public:
const int LogLevelError = 0;
const int LogLevelwarning = 1;
const int LogLevelInfo = 2;
private:
int m_Loglevel = LogLevelInfo ;
public:
void SetLevel(int level)
{
m_Loglevel = level;
}
void Error(const char* message)
{
if(m_Loglevel >= LogLevelError )
std::cout << "[Error]: " << message << std::endl
}
void Warn(const char* message)
{
if(m_Loglevel >= LogLevelwarning )
std::cout << "[WARNING]: " << message << std::endl
}
void Info(const char* message)
{
if(m_Loglevel >= LogLevelInfo )
std::cout << "[Info]: " << message << std::endl
}
}
int main()
{
Log log;
log.StLevel(log.LogLevelwarning );//通过这个实现了不同级别的输出,后面代码也可通过这样的方式实现不同级别的输出信息
log.Warn("Hellow! ");
log.Error("Hellow! ");
log.Info("Hellow! ");
std::cin.get();
}
21 Static in C++
Static 一般表示静态链接,声明的函数,或者字符串不再产生变化
如下展示了外部链接和内部链接的情况
static.cpp
int s_Variable = 5;
main.c
extern int s_Variable;
int main ()
{
std::count << s_Variable <<std::endl;
std::cin.get();
}
static.cpp改成如下的申明
static int s_Variable = 5;
所以static 变量可以全局使用??
22.static for classes and structs in c++
static 更改之后只有一个实例,所以实际的值以最后一个为准
所以下面的代码输出的值则是
5,8
5,8
#include <iostream>
#include"log.h"
struct Entity
{
static int x, y;
void Print()
{
std::cout << x << ", " << y << std::endl;
}
};
int Entity::x;
int Entity::y;
int main()
{
Entity e;
e.x = 2;
e.y = 3;
Entity e1;
e1.x = 5;
e1.y = 8;
e.Print();
e1.Print();
std::cin.get();
}
因为静态变量对于私有的来说是无意义的,所以在实际的使用中可以更换成如下的方式去书写,可以将它看成是一个公共的空间去处理
#include <iostream>
struct Entity
{
static int x, y;
static void Print()
{
std::cout << x << ", " << y << std::endl;
}
};
int Entity::x;
int Entity::y;
int main()
{
Entity::x = 2;
Entity::y = 3;
Entity::x = 5;
Entity::y = 8;
Entity::Print();
Entity::Print();
std::cin.get();
}
静态与非静态之间的访问关系,只能单向去使用,静态不能访问非静态的函数
也可以使用如下的方式去使用
static void Print(Entity a)
{
std::cout << a.x << ", " << a.y << std::endl;
}
23 local static in C++(本地静态)(err)
?_ ?
讲了一些笔者看不懂的东西,下一课吧
24 ENUMS in C++ 枚举
如下面所示,枚举的格式是“char”,
枚举的数值则是从第一个开始,后边的逐个增大
所以 A = 5,则 B= 6,C = 7
ABC的代码值,会随顺序增大
#include <iostream>
enum Example : char
{
A = 5,B,C
};
int main()
{
Example value = B;
if (value == 1)
{
// Do something here
}
std::cin.get();
}
下面展示了枚举在一个稍微完整一些的项目中的使用
还是使用了之前的 分级打印log的方式,在分级标志位上增加了枚举的使用,使得只要定义第一个值,后面的值就自动出现了
#include <iostream>
class Log
{
public:
enum Level
{
LevelError = 0, LevelWaring, LevelInfo //从小到大变化 0 ,1,2
};
private:
Level m_LogLevel = LevelInfo;
public:
void SetLevel(Level level)
{
m_LogLevel = level;
}
void Error(const char* message)
{
if (m_LogLevel >= LevelError)
std::cout << "[ERROR]: " << message << std::endl;
}
void Warn(const char* message)
{
if (m_LogLevel >= LevelWaring)
std::cout << "[Warn]: " << message << std::endl;
}
void Info(const char* message)
{
if (m_LogLevel >= LevelInfo)
std::cout << "[Info]: " << message << std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Log log;
log.SetLevel(Log::LevelError);
log.Warn("hello!");
log.Error("hello!");
log.Info("Hello!");
std::cin.get();
}
25 constructors in C++
下面主要是展示了没有传入变量的情况下,代码的结构
#include <iostream>
class Entity
{
public:
Entity();
~Entity();
float X, Y;
void Init()
{
X = 0.0f;
Y = 0.0f;
}
void Print()
{
std::cout << X << "," << Y << std::endl;
}
private:
};
//初始化class的时候,也会运行其中的程序
Entity::Entity()
{
X = 0.0f;
Y = 0.0f;
}
Entity::~Entity()
{
}
int main()
{
Entity e;
std::cout <<e.X << std::endl;
e.Print();
std::cin.get();
}
下面则是传入了一个浮点的参数
#include <iostream>
class Entity
{
public:
float X, Y;
Entity()
{
}
Entity( float x, float y)
{
X = x;
Y = y;
}
void Init()
{
X = 0.0f;
Y = 0.0f;
}
void Print()
{
std::cout << X << "," << Y << std::endl;
}
private:
};
int main()
{
Entity e(10.0f,5.0f);
std::cout <<e.X << std::endl;
e.Print();
std::cin.get();
}
26 Destructors in C++
#include <iostream>
class Entity
{
public:
float X, Y;
Entity()
{
X = 0.0f;
Y = 0.0f;
std::cout << " Created Entity!" << std::endl;
}
~Entity()
{
std::cout << " Destroyed Entity!" << std::endl;
}
void Init()
{
X = 0.0f;
Y = 0.0f;
}
void Print()
{
std::cout << X << "," << Y << std::endl;
}
private:
};
void Fucntion()
{
Entity e;
e.Print();
}
int main()
{
Fucntion();
std::cin.get();
}
27 inheritance in C++
继承代码
#include <iostream>
class Entity
{
public:
float X, Y;
void Move(float xa, float ya)
{
X += xa;
Y += ya;
}
};
class Player :public Entity
{
public:
const char* Name;
void PrintName()
{
std::cout << Name << std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
std::cout << sizeof(Player) << std::endl;
Player player;
player.Move(5,5);
player.X = 2;
player.Name = "Hello ";
player.PrintName();
std::cin.get();
}
28 Virtual Functions in C++ 中的接口 纯虚函数
下面是演示的代码,在增加和不增加virtual 的时候有输出信息的差异,也可以看做传递函数,在这代码中产生了差异
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Entity
{
public:
virtual std::string GetName() { return "Entity"; }//virtual 修正覆盖??
};
class Player :public Entity
{
private:
std::string m_Name;
public:
Player(const std::string& name)
:m_Name(name) {}
std::string GetName() override { return m_Name; }//override 和上面的virtual呼应
};
int main()
{
Entity* e = new Entity();
std::cout << e->GetName() << std::endl; //输出Entity
Player* p = new Player("Cherno");//将值传到player中
std::cout << p->GetName() << std::endl;//输出 Cherno
Entity* entity = p;
std::cout << entity->GetName() << std::endl;//输出Entity
std::cin.get();
}
29 interfaces in C++中的接口
展示了Class 如何相互链接?继承等关系,具体代码还需要一些时间去领悟相关信息
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Printable
{
public:
virtual std::string GetClassName() = 0;
};
class Entity :public Printable
{
public:
virtual std::string GetName() { return "Entity"; }//virtual 修正覆盖??
std::string GetClassName() override { return "Entity"; }
};
class Player :public Entity
{
private:
std::string m_Name;
public:
Player(const std::string& name)
:m_Name(name) {}
std::string GetName() override { return m_Name; }//override 和上面的virtual呼应
std::string GetClassName() override { return "Player"; }
};
void PrintName(Entity* entity)
{
std::cout << entity->GetName() << std::endl;
}
void Print(Printable* obj)
{
std::cout << obj->GetClassName() << std::endl;
}
class A:public Printable
{
public:
std::string GetClassName() override { return "A"; }
private:
};
int main()
{
Entity* e = new Entity();
PrintName(e);
Player* p = new Player("Cherno");//将值传到player中
PrintName(e);
Print(e);
Print(p);
Print(new A());
std::cin.get();
}
30 C++中的数组
32 C++中的字符串
33 C++ 字符串字面量
34 C++ 中的const
const 代表了不可以被改变的量,如下图,a的值就是不能被改变
如下中的给a赋值2 ,则会被报编译错误
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
const int a = 5;
a = 2;
std::cin.get();
}
int main()
{
const int MAX_AGE = 90;
const int* a = new int;//表示不得修改指针所指的内容
int const* a = new int;//两句意义相同
*a = 2//这条会报错
a = (int*)&MAX_AGE;
std::cout << *a << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
}
int main()
{
const int MAX_AGE = 90;
int* const a = new int;//表示不得修改指针所指的位置
*a = 2
a = (int*)&MAX_AGE;//这条会报错
std::cout << *a << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
}
下面这一段则是演示了,const 在下面函数中的用法
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Entity
{
private :
int m_X, m_Y;
public:
int GetX() const //代表这个累不会被改
{
return m_X;
}
};
void PrintEntity(const Entity& e)
{
std::cout << e.GetX() << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
const int MAX_AGE = 90;
int* const a = new int;//表示不得修改指针所指的位置
*a = 2;
std::cout << *a << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
}
35 C++ 中的mutable关键字
mutable 定义允许在const 中更改的变量
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Entity
{
private:
std::string m_Name;
mutable int m_DebugCount = 0; //定义可以 被更改的函数
public:
const std::string& GetName() const
{
m_DebugCount++;
return m_Name;
}
};
int main()
{
const Entity e;
e.GetName();
}
36 C++ 构造函数初始化列表
在calss类中,可以有多个不同的初始化函数,从而传递不同的参数进去?
基础用法,如下所示,传递参数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Entity
{
private:
std::string m_Name;
public:
Entity()
{
m_Name = "Unknown";
}
Entity(const std::string& name)
{
m_Name = name;
}
const std::string& GetName() const
{
return m_Name;
}
};
int main()
{
Entity e0;
std::cout << e0.GetName() << std::endl;
Entity e1("Hellow !");
std::cout << e1.GetName() << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
}
如下代码产生了两次的Entity
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Example
{
public:
Example()
{
std::cout << "Created Entity !" << std::endl;
}
Example(int x)
{
std::cout << "Created Entity with " << x << "!" << std::endl;
}
};
class Entity
{
private:
std::string m_Name;
Example m_Example; //第一次产生Entity
public:
Entity()
{
m_Name = std::string("Unknown");
m_Example = Example(8);//第二次产生Entity
}
Entity(const std::string& name)
:m_Name(name)
{
}
const std::string& GetName() const
{
return m_Name;
}
};
int main()
{
Entity e0;
std::cin.get();
}
如下代码则是产生了一次的Entity ,需要对比两个部分的差异,得出结论
class Entity
{
private:
std::string m_Name;
Example m_Example; //第一次产生Entity
public:
Entity()
:m_Example(Example(8))
{
m_Name = std::string("Unknown");
}
Entity(const std::string& name)
:m_Name(name)
{
}
const std::string& GetName() const
{
return m_Name;
}
};
或者也可以这样写
class Entity
{
private:
std::string m_Name;
Example m_Example; //第一次产生Entity
public:
Entity()
:m_Example(8)
{
m_Name = std::string("Unknown");
}
Entity(const std::string& name)
:m_Name(name)
{
}
const std::string& GetName() const
{
return m_Name;
}
};
37 C++ 的三元操作符 (a? b:C)
下面就是整个操作的 展示
a? b:C
如果a为真,执行b,否则执行C
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
static int s_Level = 1;
static int s_Speed = 2;
int main()
{
if (s_Level > 5)
s_Speed = 10;
else
s_Speed = 5;
s_Speed = s_Level > 5 ? 10 : 5;
s_Speed = s_Level > 5 ? s_Level > 10 ? 15 : 10 : 5;//减少了if的使用?不推荐嵌套使用
std::cout << s_Speed << std::endl;
std::string rank = s_Level > 10 ? "Master" : "Beginner";
std::string otherRank;
if (s_Level > 10)
otherRank = "Master";
else
{
otherRank = "Bigger";
}
std::cin.get();
}
























 733
733











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








