Takt Time can be defined as the maximum time per unit allowed to produce a product in order to meet demand. In automobile manufacturing, for example, cars are assembled on a line, and are moved on to the next station after a certain time - the takt time. Therefore, the time needed to complete work on each station has to be less than the takt time in order for the product to be completed within the allotted time.
Definition:
Takt time can be first determined with the formula:
Where
T = Takt time, e.g. [minutes of work / unit produced]
Ta = Net time available to work, e.g. [minutes of work / day]
Td = Time demand (customer demand), e.g. [units required / day]
Example:
If there is a total of 8 hours (or 480 minutes) in a shift (gross time) less 30 minutes lunch, 30 minutes for breaks (2 × 15 mins), 10 minutes for a team briefing and 10 minutes for basic maintenance checks, then the net Available Time to Work = 480 - 30 - 30 - 10 - 10 = 400 minutes. If customer demand was, say, 400 units a day and one shift was being run, then the line would be required to spend a maximum of one minute to make a part in order to be able to keep up with Customer Demand.
JIT is Just In Time production method is also called the Toyota Production System. To meet JIT objectives, the process relies on signals or Kanban (看板 Kanban?) between different points in the process, which tell production when to make the next part. Kanban are usually 'tickets' but can be simple visual signals, such as the presence or absence of a part on a shelf. Implemented correctly, JIT can improve a manufacturing organization's return on investment, quality, and efficiency.
JIT implementation design:
1) F Design Flow Process
- F Redesign/relayout for flow
- L Reduce lot sizes
- O Link operations
- W Balance workstation capacity
- M Preventive maintenance
- S Reduce Setup Times
2) Q Total quality control
- C worker compliance
- I Automatic inspection
- M quality measures
- M fail-safe methods
- W Worker participation
3) S Stabilize Schedule
- S Level Schedule
- W establish freeze windows
- UC Underutilize Capacity
4) K Kanban Pull System
- D Demand pull
- B Backflush
- L Reduce lot sizes
5) V Work with vendors
- L Reduce lead time
- D Frequent deliveries
- U Project usage requirements
- Q Quality Expectations
6) I Further reduce inventory in other areas
S Stores
- T Transit
- C Implement Carroussel to reduce motion waste
- C Implement Conveyor belts to reduce motion waste
7) P Improve Product Design
- P Standard Production Configuration
- P Standardize and reduce the number of parts
- P Process design with product design
- Q Quality Expectations
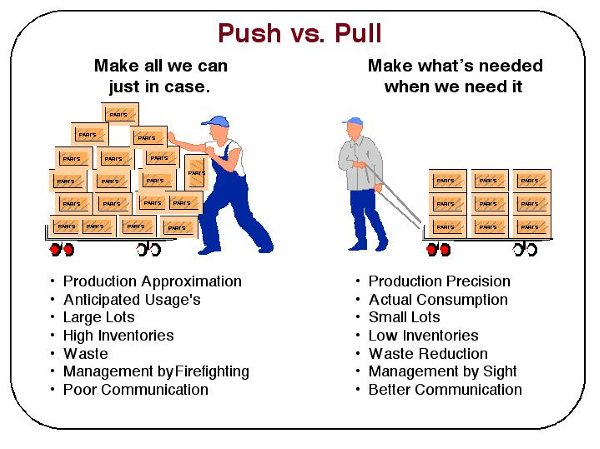
Push system vs Pull system
I use two pictures to demonstrate what are the push and the pull system and their difference.
























 577
577

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








