1.oc的方法:
// 方法(行为):方法名、参数、返回值(声明、实现)
// 只要是OC对象的方法,必须以减号 -开头
// OC方法中任何数据类型都必须用小括号()扩住
// OC方法中的小括号():括住数据类型
- (void)run;
2.方法的实现(说清楚方法里面有什么代码)
- (void)run
{
NSLog(@"车子跑起来了");
}
3.给对象的属性赋值
// 给p所指向对象的wheels属性赋值
p->wheels = 4;
p->speed = 250;
传说中oc的消息机制
//给p所指向对象发送一条run消息
[p run];
5.对象在调用方法,所以如下代码中对象可以直接调用方法
所以可以直接写age,weight.
- (void)walk
{
NSLog(@"%d岁、%f公斤的人走了一段路", age, weight);
}
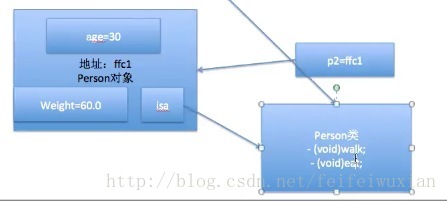
6. 在使用类创建对象之前,会将类加载进内存对像里面有个isa成员变量(指针)
7.变量声明的时候
//int wheels = 4; 不允许在这里初始化
//static int wheels; 不能随便将成员变量当做C语言中的变量来使用
二、类的合理设计
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
typedef enum {
SexMan,
SexWoman
} Sex;
typedef struct {
int year;
int month;
int day;
} Date;
typedef enum {
ColorBlack,
ColorRed,
ColorGreen
} Color;
@interface Dog : NSObject
{
@public
double weight; // 体重
Color curColor; // 毛色
}
- (void)eat;
- (void)run;
@end
@implementation Dog
- (void)eat
{
// 每吃一次,体重就加1
weight += 1;
//weight = weight + 1;
NSLog(@"狗吃完这次后的体重是%f", weight);
}
- (void)run
{
weight -= 1;
NSLog(@"狗跑完这次后的体重是%f", weight);
}
@end
/*
学生
成员变量:性别、生日、体重、最喜欢的颜色、狗(体重、毛色,吃、跑)
方法:吃、跑步、遛狗(让狗跑)、喂狗(让狗吃)
*/
@interface Student : NSObject
{
@public
Sex sex; // 性别
Date birthday; // 生日
double weight; // 体重(kg)
Color favColor; // 最喜欢的颜色
char *name;
// 重点:狗
Dog *dog;
}
- (void)eat;
- (void)run;
- (void)print;
- (void)liuDog;
- (void)weiDog;
@end
@implementation Student
- (void)liuDog
{
// 让狗跑起来(调用狗的run方法)
[dog run];
}
- (void)weiDog
{
// 让狗吃东西(调用狗的eat方法)
[dog eat];
}
- (void)print
{
NSLog(@"性别=%d, 喜欢的颜色=%d, 姓名=%s, 生日=%d-%d-%d", sex, favColor, name, birthday.year, birthday.month, birthday.day);
}
- (void)eat
{
// 每吃一次,体重就加1
weight += 1;
//weight = weight + 1;
NSLog(@"学生吃完这次后的体重是%f", weight);
}
- (void)run
{
weight -= 1;
NSLog(@"学生跑完这次后的体重是%f", weight);
}
@end
int main()
{
Student *s = [Student new];
Dog *d = [Dog new];
d->curColor = ColorGreen;
d->weight = 20;
s->dog = d;
[s liuDog];
[s weiDog];
return 0;
}
void test()
{
Student *s = [Student new];
s->weight = 50;
// 性别
s->sex = SexMan;
// 生日
Date d = {2011, 9, 10};
s->birthday = d;
s->name = "Jack";
/*
s->birthday.year = 2011;
s->birthday.month = 9;
s->birthday.day = 10;
*/
// 喜欢的颜色
s->favColor = ColorBlack;
/*
[s eat];
[s eat];
[s run];
[s run];
*/
[s print];
}
8、类中枚举类型定义的规范
常量一定要包含枚举类型的名称,
也可以加上kSexMan, k代表常量
Sex前要有空格
typedef enum {
SexMan,
SexWoman
} Sex;
typedef struct {
int year;
int month;
int day;
} Date;
Student *s = [Student s]
//下面这种是错误的
//s->birthday = {2011, 9, 10}
第一种方法
s->birthday .year = 2011;
s->birthday.month = 9;
s->birthday.day = 11;
第二种方法
Date d= {2011, 9 , 10}; //只有在定义结构体变量的同时才能直接赋值
s->birthday = d;
三、类的参数
oc 方法中,一个参数对应一个冒号
1. 带一个参数的方法
设计一个计算平方的方法
// 方法声明
- (double)square:(double)number;
//方法实现
- (double)square:(double)number
{
return number * number;
}
2. 带多个参数的方法
多个参数之间要有空格,
:号前面要有描述
设计一个计算和的方法
// 方法声明
- (double)sumOfNum1:(double)num1 andNum2:(double)num2;
//方法实现
- (double)sumOfNum1:(double)num1 andNum2:(double)num2
{
return num1 + num2;
}
3.方法名是包括后面的部分
l 冒号也是方法名的一部分
l 同一个类中不允许两个对象方法同名
4.调用方法传递参数
JiSuanQi *jsq = [JiSuanQi new];
int a = [jsq sumWithNum1:20 andNum2:5];
5.如果参数是对象
- (int)compareSpeedWithOther:(Car *)other;
调用的时候
[c1 compareSpeedWithOther:c2]
6.匿名对像
//不要写类似匿名对象这样的代码
//只要求能说出输出结果
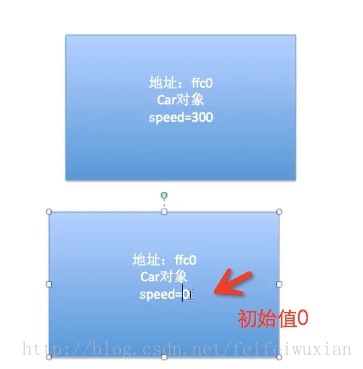
[Car new]->speed =300;
[[Car new] run];//输出是0,
这里面300是之前的对象,共创建了两个对象
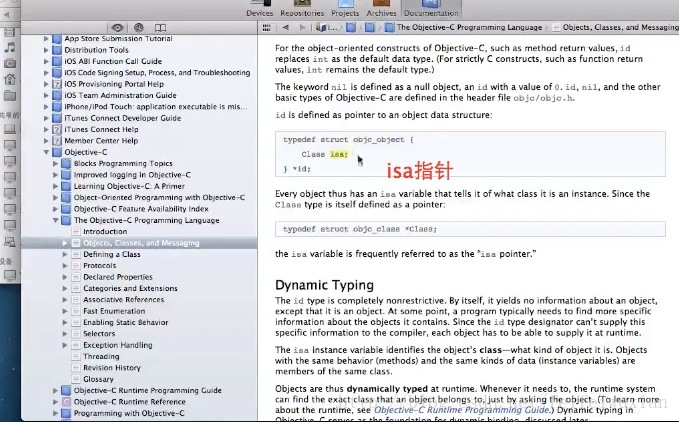
四、学习查文档






















 678
678

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








