The superformula is a generalization of the superellipse and was first proposed by Johan Gielis.
Gielis suggested that the formula can be used to describe many complex shapes and curves that are found in nature.
In polar coordinates, with  the radius and
the radius and 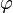 the angle, the superformula is:
the angle, the superformula is:
The formula appeared in a work by Gielis. It was obtained by generalizing the superellipse, named and popularized by Piet Hein, a Danish mathematician.
Extension to higher dimensions[edit]
It is possible to extend the formula to 3, 4, or n dimensions, by means of the spherical product of superformulas. For example, the 3D parametric surface is obtained by multiplying two superformulas r1and r2. The coordinates are defined by the relations:
where  varies between -π/2 and π/2 (latitude) and θ between -π and π (longitude).
varies between -π/2 and π/2 (latitude) and θ between -π and π (longitude).
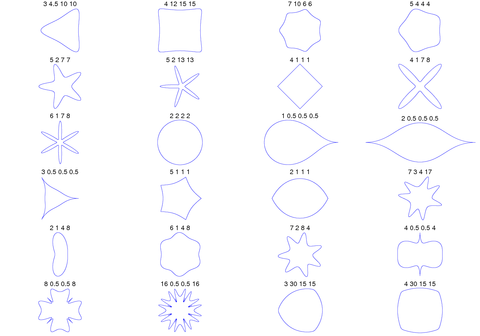
Plots[edit]
A GNU Octave program for generating these figures:
function sf2d(n,a) u=[0:.001:2*pi]; raux=abs(1/a(1).*abs(cos(n(1)*u/4))).^n(3)+abs(1/a(2).*abs(sin(n(1)*u/4))).^n(4); r=abs(raux).^(-1/n(2)); x=r.*cos(u); y=r.*sin(u); plot(x,y); end
3d Superformula: a=b=1; m, n1, n2 and n3 are shown in the pictures.
A GNU Octave program for generating these figures:
function sf3d(n, a) u=[-pi:.05:pi]; v=[-pi/2:.05:pi/2]; nu=length(u); nv=length(v); for i=1:nu for j=1:nv raux1=abs(1/a(1)*abs(cos(n(1).*u(i)/4))).^n(3)+abs(1/a(2)*abs(sin(n(1)*u(i)/4))).^n(4); r1=abs(raux1).^(-1/n(2)); raux2=abs(1/a(1)*abs(cos(n(1)*v(j)/4))).^n(3)+abs(1/a(2)*abs(sin(n(1)*v(j)/4))).^n(4); r2=abs(raux2).^(-1/n(2)); x(i,j)=r1*cos(u(i))*r2*cos(v(j)); y(i,j)=r1*sin(u(i))*r2*cos(v(j)); z(i,j)=r2*sin(v(j)); endfor; endfor; mesh(x,y,z); endfunction;
int segments = 800;
float scale = 20.0;
float a = 1.0;
float b = 0.80;
float m = 15.0;
float n1 = -8.0;
float n2 = 12.0;
float n3 = 10.0;
float tau = 6.28318530718;
float step = tau / segments;
float phi = 0.0;
for (float o=0.0; o<0.5; o+=0.01) {
for (int i=0; i<segments; i++) {
float mp4 = (m * phi) / 4.0;
float term_a = pow(abs((cos(mp4) / a)), n2);
float term_b = pow(abs((sin(mp4) / b)), n3);
float r = pow((term_a + term_b), -(1 / n1));
addpoint( geoself(), set(cos(phi)*scale*r, sin(phi)*scale*r, 0) );
phi += step;
}
a += o;
b += o/25;
}
References[edit]
- Gielis, Johan (2003), "A generic geometric transformation that unifies a wide range of natural and abstract shapes", American Journal of Botany 90 (3): 333–338, doi:10.3732/ajb.90.3.333, ISSN 0002-9122
External links[edit]
- Website with information about the superformula and Johan Gielis
- Some Experiments on Fitting of Gielis Curves by Simulated Annealing and Particle Swarm Methods of Global Optimization
- Least Squares Fitting of Chacón-Gielis Curves By the Particle Swarm Method of Optimization
- Superformula 2D Plotter & SVG Generator
- Interactive example using JSXGraph
- 3D Superdupershape Explorer using Processing
- Interactive 3D Superformula plotter using Processing (with code)
- SuperShaper: An OpenSource, OpenCL accelerated, interactive 3D SuperShape generator with shader based visualisation (OpenGL3)
- Simpel, WebGL based SuperShape implementation
- The Gielis Supershape Formula, Provides an interactive Java applet for exploring the variety of different shapes, natural or mathematical, that can be formed with the formula.









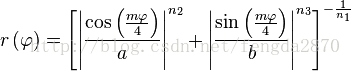


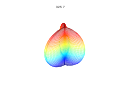
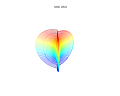
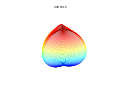
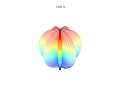
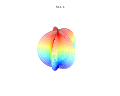
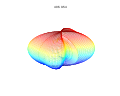
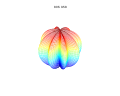
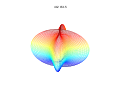













 1087
1087











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








