UVM 1.2
-
UVN类库

-
工厂机制?
UVM工厂存在的意义就是为了更方便的替换验证环境中的实例或者已经注册的类型,工厂的注册机制给配置带来了灵活性。 -
工厂注册:
component::type_id::create("c2",null); -
工厂覆盖:有两种方法
1、set_inst_override(uvm_object_wrapper override_type,string inst_path)
2、set_type_override(uvm_object_wrapper override_type)
initial begine
comp1::type_id::set_type_override(comp2::get_type());
c1 = new("c1");
c2 = comp1::type_id::create("c2",null);
c1.hello("c1");
c2.hhell("c2");
end
注意事项:
1、类型替换必须发生在例化之前
2、在声明成c2的时候,句柄类型为comp1,若是没发生替换则c2 handle仍是comp1.若是发生了替换则comp1的handle会指向comp2类型的对象,这要求保证comp2是comp1的子类。
3、c2调用hello()的时候,通过多态特性直接调用了comp2的hello()。注意基类中的方法考虑是否加上虚函数关键字。
-
核心基类:
1、copy() //复制数据
2、clone() //创建对象并且复制数据
3、compare()
4、print()
5、pack\unpack() -
域的自动化
uvm_field_int(val,UVM_ALL_ON)//类似的
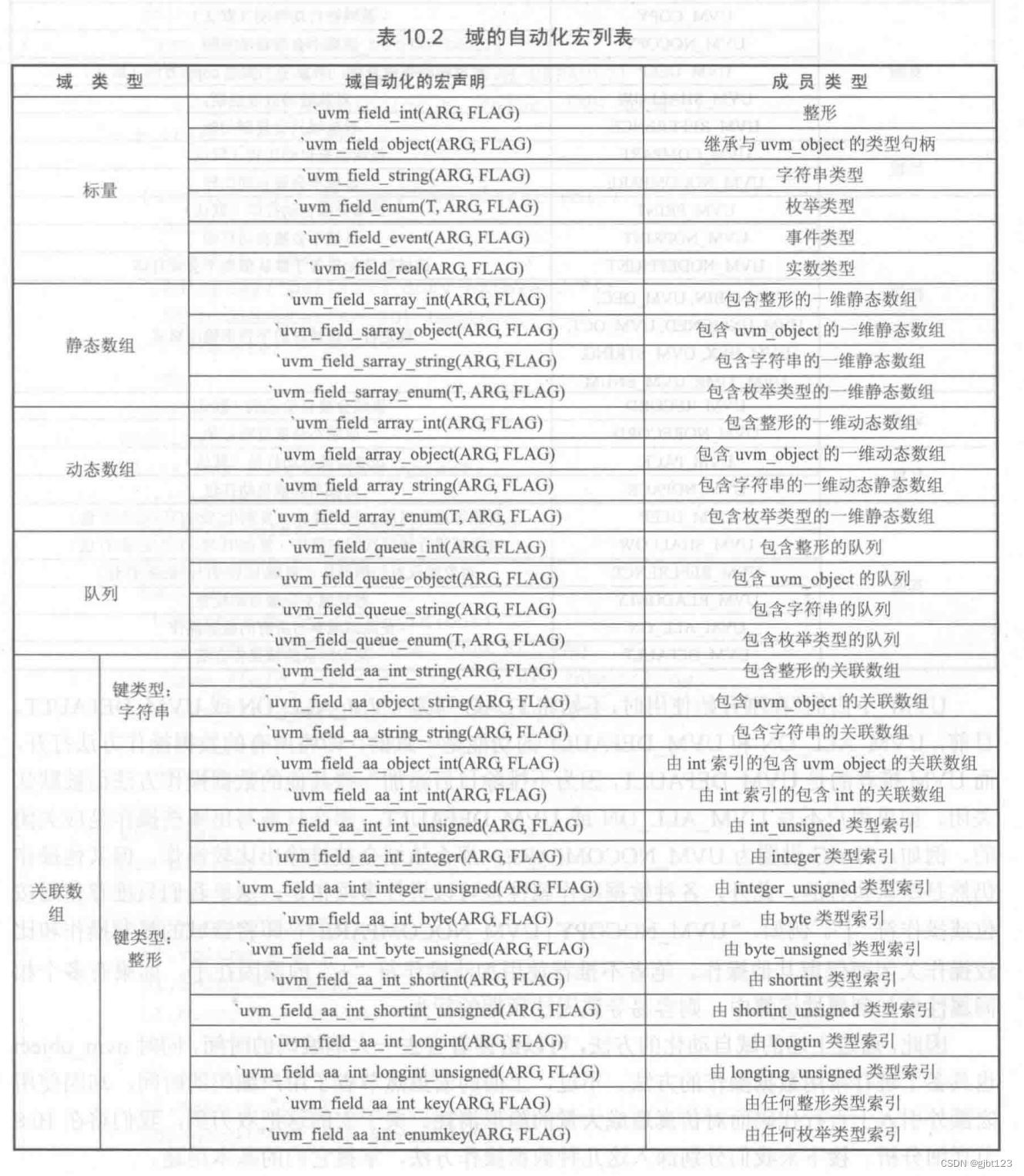
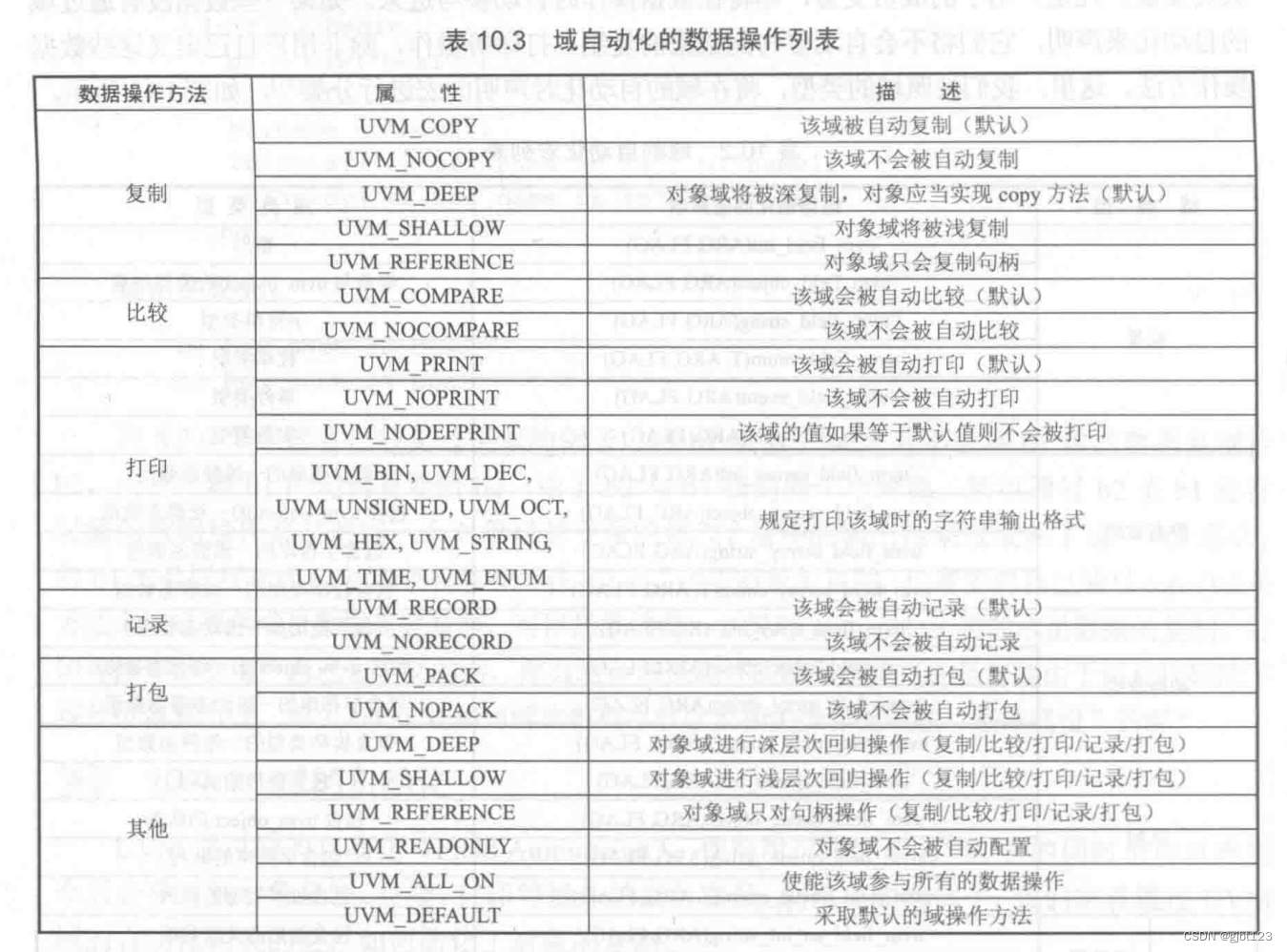
1、UVM_ALL_ON跟UVM_DEFAULT的功能是一致的,推荐使用UVM_DEFAULT。
2、可以使用位或操作符:UVM_NOCOPY|UVM_NOCPMPARE -
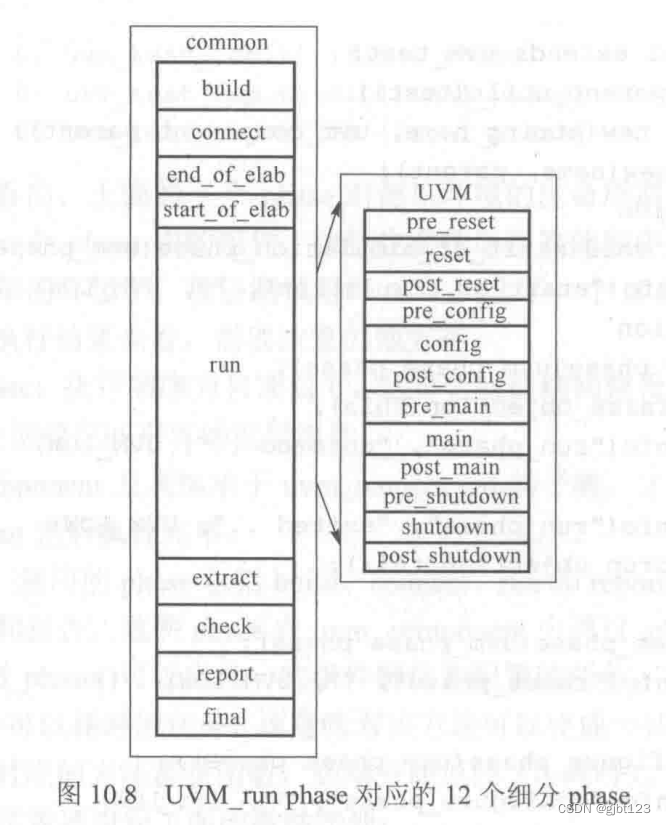
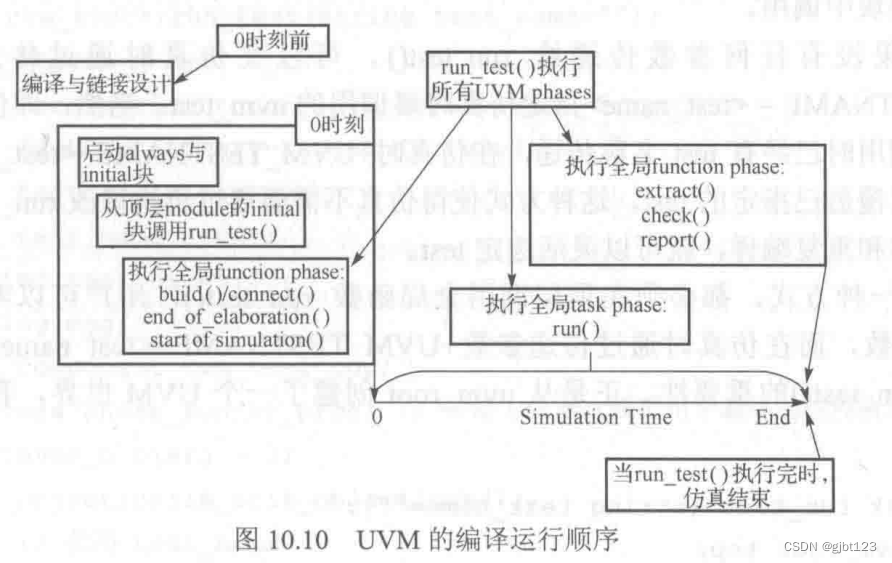
phase机制:解决了层次化例化顺序的问题。

-
objection机制:挂起防退出
在run_phase中一开始就要挂起,#1ps都会完犊子。
class test1 extends uvm_test;
...
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
// #1ps; //万万不可
phase.raise_objection(this);
'uvm_info("run_phase","entered ..",UVM_LOW)
#1us;
'uvm_info("run_phase","exited ..",UVM_LOW)
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
-
config机制:interface传递、环境变量设置、object传递
-
interface传递
class comp1 extends uvm_component;
virtual intf1 vif;
uvm_config_db#(viryual intf1)::get(this,“”,“vif”,vif)
class test1 extends uvm_test;
comp1 c1;
intf1 intf();
uvm_config_db#(viryual intf1)::set(uvm_root::get(),“uvm_test_top.c1”,“vif”,intf) -
环境变量设置
int vall = 1;
string str1 = “null”;
uvm_config_db#(int)::get(this,“”,“vall”,vall);
uvm_config_db#(sring)::get(this,“”,“str1”,str1);
comp1 c1;
uvm_config_db#(int)::set(this,“c1”,“vall”,100);
uvm_config_db#(sring)::set(this,“c1”,“str1”,“comp1”); -
object传递
class config1 extends uvm_object;
config1 cfg;
uvm_object tmp;
uvm_config_db#(uvm_object)::get(this,“”,“cfg”,tmp);
comp1 c1,c2;
config cfg1,cfg2;
uvm_config_db#(uvm_object)::set(this,“c1”,“cfg”,cfg1); -
在使用config机制的过程中,应注意的点有:
(1)set()和get()应成对出现;
(2)传递的参数类型必须保持一致;
(3)get()方法和set()方法的路径应能够匹配;
(4)应先在上层做set(),然后再在下层用get()。上层的set()要发生在create()之前。 -
UVM结构
-
组件家族
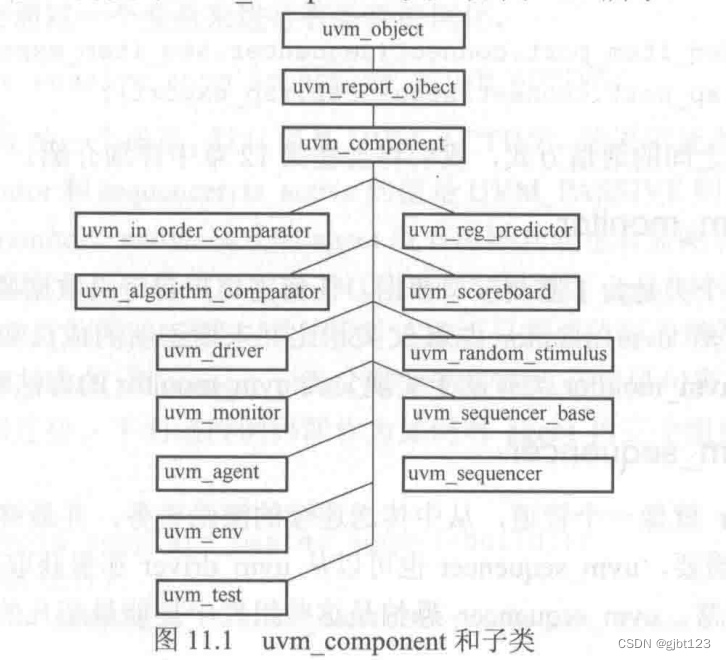
-
UVM通信—TLM
待补充…






















 1170
1170











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








