目录
一.逻辑回归
logistic回归是一种广义线性回归(generalized linear model),因此与多重线性回归分析有很多相同之处。它们的模型形式基本上相同,都具有 w‘x+b,其中w和b是待求参数,其区别在于他们的因变量不同,多重线性回归直接将w‘x+b作为因变量,即y =w‘x+b,而logistic回归则通过函数L将w‘x+b对应一个隐状态p,p =L(w‘x+b),然后根据p 与1-p的大小决定因变量的值。如果L是logistic函数,就是logistic回归,如果L是多项式函数就是多项式回归。
logistic回归的因变量可以是二分类的,也可以是多分类的,但是二分类的更为常用,也更加容易解释,多类可以使用softmax方法进行处理
参考逻辑回归概念
逻辑回归:解决分类问题
将样本特征和样本发生地概率联系起来,概率是一个数。

sigmoid函数


用θ替换t。找到参数θ,使用函数或者样本x对应的y。
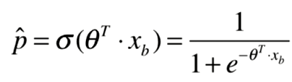
二.逻辑函数的损失函数

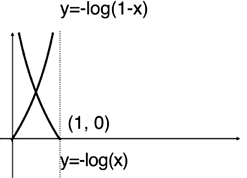
y实际是1,如果p是0,预测分类0,误差最大
y实际是0,如果p是1,预测分类1,误差最大
![]()
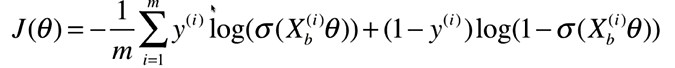
求解只能使用梯度下降法
![]() =
=![]()
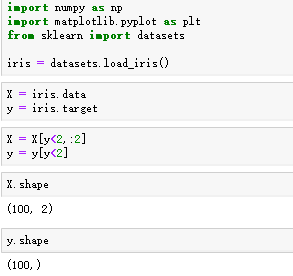
三.实现逻辑回归
对J函数,梯度dJ函数,predict等做修改
import numpy as np
from .metrics import accuracy_score
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化Logistic Regression模型"""
self.coef_ = None
self.intercept_ = None
self._theta = None
def _sigmoid(self, t):
return 1. / (1. + np.exp(-t))
def fit(self, X_train, y_train, eta=0.01, n_iters=1e4):
"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法训练Logistic Regression模型"""
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
def J(theta, X_b, y):
y_hat = self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(theta))
try:
return - np.sum(y*np.log(y_hat) + (1-y)*np.log(1-y_hat)) / len(y)
except:
return float('inf')
def dJ(theta, X_b, y):
return X_b.T.dot(self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(theta)) - y) / len(y)
def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8):
theta = initial_theta
cur_iter = 0
while cur_iter < n_iters:
gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
if (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):
break
cur_iter += 1
return theta
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
self._theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, eta, n_iters)
self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]
self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]
return self
def predict_proba(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果概率向量"""
assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict), 1)), X_predict])
return self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(self._theta))
def predict(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""
assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
proba = self.predict_proba(X_predict)
return np.array(proba >= 0.5, dtype='int')
def score(self, X_test, y_test):
"""根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度"""
y_predict = self.predict(X_test)
return accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
def __repr__(self):
return "LogisticRegression()"
jupter中实现























 2982
2982











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








