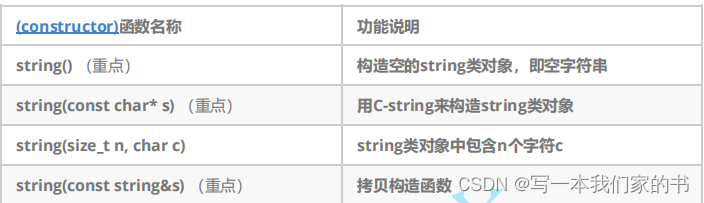
string类
1. string
是表示字符串的字符串类
2.
该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作
string
的常规操作。
3. string
在底层实际是:
basic_string
模板类的别名,
typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator>
string;
4.
不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。
在使用string类时,必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
string类常用接口
1. size()
与
length()
方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入
size()
的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一
致,一般情况下基本都是用
size()
。
2. clear()
只是将
string
中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小。
3. resize(size_t n)
与
resize(size_t n, char c)
都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到
n
个,不同的是当字
符个数增多时:
resize(n)
用
0
来填充多出的元素空间,
resize(size_t n, char c)
用字符
c
来填充多出的
元素空间。注意:
resize
在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大
小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变。
4. reserve(size_t res_arg=0)
:为
string
预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当
reserve
的参数小于
string
的底层空间总大小时,
reserver
不会改变容量大小。
5.
在
string
尾部追加字符时,
s.push_back(c) / s.append(1, c) / s += 'c'
三种的实现方式差不多,一般
情况下
string
类的
+=
操作用的比较多,
+=
操作不仅可以连接单个字符,还可以连接字符串。
6.
对
string
操作时,如果能够大概预估到放多少字符,可以先通过
reserve
把空间预留好。
vector和字符串配合使用:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class String
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const String& s);
public:
String(const char* str)
{
this->m_data = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(this->m_data, str);
}
String(const String& s)
{
this->m_data = new char[strlen(s.m_data) + 1];
strcpy(this->m_data, s.m_data);
}
String& operator=(const String& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
delete[] this->m_data;
this->m_data = new char[strlen(s.m_data) + 1];
strcpy(this->m_data, s.m_data);
}
return *this;
}
~String()
{
delete[] this->m_data;
this->m_data = nullptr;
}
private:
char* m_data;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const String& s)
{
cout << s.m_data;
return cout;
}
void test1()
{
vector<char> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
v.push_back('a' + i);
}
for (auto& e : v)
{
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test02()
{
const char* str[] = { "abc","xyz","lmn" };
//vector<char*> v(str,str+3);
vector<const char*>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
v.push_back(str[i]);
}
for (auto& e : v)
{
cout << e << endl;
}
}
void test03()
{
String str[] = { "abc","xyz","lmn" };
vector<String>v;
v.push_back(str[0]);
v.push_back(str[1]);
v.push_back(str[2]);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << endl;
}
}
void main()
{
test02();
system("pause");
}string类的接口测试:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
//C语言没有真正的字符串
char str[] = "abc";
const char* pstr = "abc";
//C++
string s;
cout << "s="<<s << endl;
string s1(pstr);
cout << "s1=" << s1 << endl;
string s2("xyz");
cout << "s2=" << s2 << endl;
string s3(3, 'f');
cout << "s3=" << s3 << endl;
string s4 = s3;
cout << "s4=" << s4 << endl;
}
void test02()
{
string s3(3, 'f');
cout << "s3.size()=" << s3.size() << endl;//3 有效长度
cout << "s3.length()=" << s3.length() << endl;//3 功能和实现在底层与size相同
cout << "s3.capacity()=" << s3.capacity() << endl;
s3.append("ajghoajgoqjgnoqjngoqn");
cout << "s3.capacity()=" << s3.capacity() << endl;//底层空间会扩容
s3.clear();
cout << "s3=" << s3 << endl;
cout << "s3.size()=" << s3.size() << endl;//0 有效长度
cout << "s3.capacity()=" << s3.capacity() << endl;//空间不会缩
}
void test03()
{
string s1("abc");
s1.reserve(100);//预留空间
cout << "s3=" << s1 << endl;
cout << "s3.size()=" << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s3.length()=" << s1.length() << endl;
cout << "s3.capacity()=" << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.resize(10);//以a填充?
cout << "s3=" << s1 << endl;
cout << "s3.size()=" << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s3.length()=" << s1.length() << endl;
cout << "s3.capacity()=" << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.resize(20, 's');//大小默认用a填充,容量以\0填充
cout << "s3=" << s1 << endl;
cout << "s3.size()=" << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s3.length()=" << s1.length() << endl;
cout << "s3.capacity()=" << s1.capacity() << endl;
}
void test04()//利用reserve提高插入数据的效率,避免增容带来的开销
{
}
void test05()
{
string s("abcxyz"); //C语言的字符串可以直接输出
cout << "s=" << s << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
{
cout << s[i];
}
cout << endl;
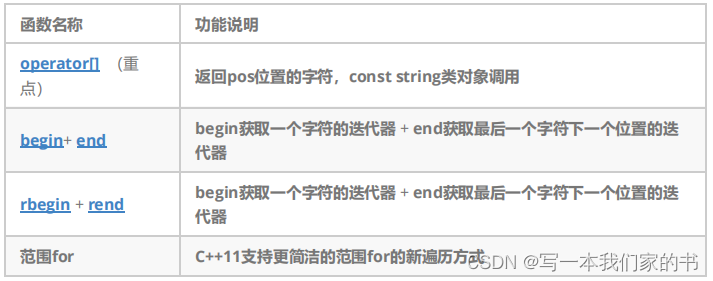
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;
const string s1 = "ajfoqojgoqhgkqnfq9";
string::const_iterator cit = s1.cbegin();//注意是cbegin不是begin
while (cit != s1.cend())
{
cout << *cit;
++cit;
}
cout << endl;
string::const_reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
while (rit != s1.rend())
{
cout << *rit;
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test06()
{
string s("abc");
s.push_back('s');//尾插只能插字符
cout << s << endl;
s.append("fgh");
cout << s << endl;
}
void test07()
{
string s1 = "abc";
string s2 = "xyz";
string s3 = s1 + s2;
cout << "s1=" << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2=" << s2 << endl;
cout << "s3=" << s3 << endl;
s1 += s2;
cout << "s1=" << s1 << endl;
}
void test08()
{
//转换成c风格字符串,即字符指针
string s1 = "abc";
cout<<strlen(s1.c_str())<<endl;
string s2;
s2.resize(10);
cout << "s2=" << s2 << endl;
cout << "s2.zize=" << s2.size() << endl;//打印10,以\0填充
cout << "s2.size=" << strlen(s2.c_str()) << endl;//打印0 识别\0之前的部分
}
void test09()
{
string s("abcxyz");
//int pos = s.find('x');//从头找
//int pos =s.find('x',4);//从指定位置开始找
//int pos = s.find("cxy",3);
int pos = s.find("cxy", 2,4);//分别为查找目标,查找位置,查找目标中的几个字符
cout << "pos=" << pos << endl;
if (pos == string::npos)
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
else
cout << "找到了,pos=" << pos << endl;
}
void test10()
{
string s("abcxyz");
string ret=s.substr(3,2);//从某个位置截取n个字符串将其返回
cout << "ret=" << ret << endl;
cout << "s=" << s << endl;
}
void test11()
{
//正则表达式
string file("string.cpp");
string email = "xxxxx@qq.com";
size_t pos = file.rfind('.');
string suffix(file.substr(pos, file.size() - pos));
cout << suffix << endl;
}
void test12()
{
string s("string.cpp");
s += 'c';//可+=字符和字符串
s += "java";
}
void test13()
{
string s1 = "abc";
string s2 = "xyz";
string s3 = s1 + s2;
//cout << "s3=" << s3 << endl;
string str;
//cin >> str;//有空格会剪短
getline(cin, str,' ');
cout << "str=" << str << endl;
}
void test14()
{
string s1 = "abc";
string s2 = "abc";
string s3 = s1 + s2;
if (s1 > s2)
{
cout << "s1>s2" << endl;
}
else if(s1<s2)
{
cout << "s1<s2" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "s1==s1" << endl;
}
}
void main()
{
test14();
system("pause");
}
巧用临时对象,实现string类的构造、拷贝构造和赋值操作。
注意当采用系统默认提供的拷贝构造和赋值操作时,会造成浅拷贝的问题,所以要明确给出拷贝构造和赋值运算符重载函数。
这里主要是避免浅拷贝,实现深拷贝,同时利用了临时对象生命周期为函数体内部,函数执行完毕临时对象会自动调用析构函数进行数据的释放,不需要手动delete。
其实浅拷贝和深拷贝各有其优缺点,通过引用计数实现的写时拷贝能够够将二者的优点结合(读时为浅拷贝,写时为深拷贝)。
引用计数:用来记录资源使用者的个数。在构造时,将资源的计数给成
1
,每增加一个对象使用该资源,就给
计数增加
1
,当某个对象被销毁时,先给该计数减
1
,然后再检查是否需要释放资源,如果计数为
1
,说明该
对象时资源的最后一个使用者,将该资源释放;否则就不能释放,因为还有其他对象在使用该资源。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace test
{
class string
{
public:
/*string()
:_str(new char[1])
{*_str = '\0';}
*/
//string(const char* str = "\0") 错误示范
//string(const char* str = nullptr) 错误示范
//现代写法
string(const string& s):_str(nullptr)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(_str, tmp._str);
}
//现代写法
string& operator=( string& s)//异常安全
{
if (this != &s)
{
string tmp(s);//拷贝构造
//string tmp(s._str);//有参构造
swap(_str, s._str);
}
return *this;
}
/*string& operator=(string& s)//异常安全
{
if (this != &s)
{
char* newstr = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
strcpy(newstr, s._str);
delete[] this->_str;
this->_str = newstr;
}
return *this;
}*/
//传统写法
/* string& operator=(const string& s)//异常不安全的代码,申请新空间之前先释放了旧空间,申请有可能不成功
{
if (this != &s)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
return *this;
}*/
//传统写法
//string(const string& s) :_str(new char[strlen(s._str) + 1])//初始化列表方式
//{
// strcpy(_str, s._str);
//}
string(const char* str = "")
{
// 构造string类对象时,如果传递nullptr指针,认为程序非法,此处断言下
if (nullptr == str)
{
assert(false);
return;
}
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
~string()
{
if (_str)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
}
// 测试
void Teststring()
{
test::string s1("abc");
test::string s2(s1);//浅拷贝
test::string s3("xyz");
s3 = s1;//浅赋值
}
void main()
{
Teststring();
system("pause");
}string类模拟实现:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
//字符串的模拟实现
namespace hym
{
class string
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const string& s);
public:
static size_t npos;
typedef char* iterator;
string() :_str(nullptr), _size(0), _capacity(0) {}
string(const char* str)
{
_size = strlen(str);
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
string(const string& s):_str(nullptr),_size(0),_capacity(0)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(*this,tmp);
}
string& operator=(const string& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
string tmp(s);//
swap(*this, tmp);
}
return *this;
}
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
size_t capacity()const
{
return _capacity;
}
bool empty()const
{
return _size == 0;
}
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
void push_back(char c)
{
if (_size + 1 > _capacity)
{
int n = _capacity == 0 ? 1 : _capacity * 2;
reserve(n);
}
_str[_size++] = c;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void append(const char* str)
{
size_t sz = strlen(str);
if (_size + sz > _capacity)
{
reserve(sz + _size);
}
strcat(_str, str);
_size += sz;
}
string& operator+=(const char c)
{
push_back(c);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const string& s)
{
append(s._str);
return *this;
}
char& operator[](int i)
{
assert(i >= 0 && i < _size);
return _str[i];
}
const char& operator[](int i)const
{
assert(i >= 0 && i < _size);
return _str[i];
}
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
void reserve(int n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* new_str = new char[n + 1];
memset(new_str, 0, n + 1);
if (_str != nullptr)
{
memcpy(new_str, _str, _capacity + 1);
}
_capacity = n;
delete[] _str;
_str = new_str;
}
}
void resize(int new_sz, char ch = '\0')
{
if (new_sz > _capacity);
{
reserve(new_sz);
for (int i = _size; i < new_sz; ++i)
{
_str[i] = ch;
}
}
_size = new_sz;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
bool operator<(const string& s)
{
return (strcmp(_str, s._str) < 0);
}
bool operator<=(const string& s)
{
return !(operator>(s));
}
bool operator>(const string& s)
{
return (strcmp(_str, s._str) > 0);
}
bool operator>=(const string& s)
{
return !(operator<(s));
}
bool operator==(const string& s)
{
return (strcmp(_str, s._str) == 0);
}
bool operator!=(const string& s)
{
return !(operator==(s));
}
static void swap(string& s1,string& s2)
{
std::swap(s1._str, s2._str);
std::swap(s1._size, s2._size);
std::swap(s1._capacity, s2._capacity);
}
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const
{
for (int i = pos; i < _size; ++i)
{
if (_str[i] == c)
return i;
}
return npos;
}
size_t rfind(char c, size_t pos = npos) const
{
int newpos = (pos == npos ? _size - 1 : pos);
for (int i = newpos - 1; i > 0; --i)
{
if (_str[i] == c)
return i;
}
return npos;
}
size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const
{
int i = pos;//_str
int j = 0;//s
while (i < _size && j < strlen(s))
{
if (_str[i] == s[j])
{
++i;
++j;
}
else
{
j = 0;
i = i - j + 1;
}
}
if (j > strlen(s))
return i - strlen(s);
return npos;
}
/*size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const
{
char* t = _str + pos;
const char* ps = s;
while (*ps != '\0'&&*t !='\0')
{
if (*ps != *t)
{
ps = s;
}
else
{
ps++;
}
t++;
}
if (*ps == '\0')
return t - _str - strlen(s);
return npos;
}*/
string& insert(size_t pos, char c)
{
if (_size + 1 > _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity*2);
}
for (int i = _size; i > pos; --i)
{
_str[i] = _str[i - 1];
}
_str[pos] = c;
_size++;
return *this;
}
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
int len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len> _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity +len);
}
for (int i = _size; i >=pos; --i)
{
_str[i+len] = _str[i];
}
int j = 0;
for (int i = pos; j < len; ++i,++j)
{
_str[i] = str[j];
}
_size+=len;
return *this;
}
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len)
{
char* tmp = new char[_size - len + 1];
memset(tmp, 0, _size - len + 1);
strncpy(tmp, _str, pos);
strncat(tmp, _str + pos + len, _size - pos - len + 1);
strcpy(_str, tmp);
_size -= len;
delete[] tmp;
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
_size = 0;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};
size_t string::npos= (size_t)-1;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const string& s)
{
cout << s._str;
return cout;
}
bool operator!=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return (strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str()));
}
}
void test01()
{
hym::string s;
hym::string s1("hello");
cout << "s1= " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s1.size" << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s1.capccity" << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.reserve(100);
cout << "s1= " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s1.size" << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s1.capccity" << s1.capacity() << endl;
}
void test02()
{
/*hym::string s1("hello");
s1.push_back('c');*/
hym::string s1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
s1.push_back('a' + i);
}
cout << "s1= " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s1.size=" << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s1.capccity=" << s1.capacity() << endl;
}
void test03()
{
hym::string s1("xyz");
//s1.append("abc");
hym::string s2("abc");
s1 += 'a';
s1 += "ABC";
s1 += s2;
cout << "s1=" << s1 << endl;
}
void test04()
{
hym::string s1("xyz");
cout << strlen(s1.c_str()) << endl;
}
void test05()
{
hym::string s1("xyz");
for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i];
}
cout << endl;
s1[2] = 'X';
cout << s1[2] << endl;
}
void test06()
{
hym::string s1("abcXYZabc");
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;
hym::string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it++;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test07()
{
hym::string s1("abcdef");
s1.resize(9,'@');
cout << "s1= " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s1.size=" << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s1.capccity=" << s1.capacity() << endl;
}
void test08()
{
hym::string s1("xyzabc");
hym::string s2("xyzabc");
if (s1 == s2)
{
cout << "YES" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
}
void test09()
{
hym::string s1("xyzabc");
hym::string s2(s1);
hym::string s3 = s1;
cout << "s3= " << s3 << endl;
cout << "s3.size=" << s3.size() << endl;
cout << "s3.capccity=" << s3.capacity() << endl;
}
void test10()
{
hym::string s1("xyzabc");
//cout << s1.find('a') << endl;
if (s1.find('z') == hym::string::npos)
cout << "NO" << endl;
else
cout << " YES" << endl;
}
void test11()
{
hym::string s("abcxyzyc");
cout << s.rfind('y',5) << endl;
}
void test12()
{
hym::string s("abcdefaxyz");
cout<<s.find("axy")<<endl;
}
void test13()
{
hym::string s("abcdefgh");
int pos = s.find('f');
//s.insert(pos, '&');
//s.insert(5, "lll");
s.erase(3, 3);
cout << s << endl;
}
void test14()
{
hym::string s("abcde");
s.clear();
cout << "s.size=" << s.size() << endl;
cout << s << endl;
if (s.empty())
{
cout << "empty" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "not empty" << endl;
}
}
void test15()
{
hym::string s1("abc");
hym::string s2("adc");
if (s1 == s2)
cout << "s1==s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1!=s2" << endl;
if (s1 > s2)
cout << "s1>s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1<=s2" << endl;
if (s1 < s2)
cout << "s1<s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1>=s2" << endl;
}
void main()
{
test15();
system("pause");
}




















 348
348











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








