一、acc、recall、F1、混淆矩阵、分类综合报告
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_26917383/article/details/75199996?locationNum=3&fps=1
1、准确率
第一种方式:accuracy_score
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
y_pred = [0, 2, 1, 3,9,9,8,5,8]
y_true = [0, 1, 2, 3,2,6,3,5,9]
accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
Out[127]: 0.33333333333333331
accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred, normalize=False)
Out[128]: 3
第二种方式:metrics
宏平均比微平均更合理,但也不是说微平均一无是处,具体使用哪种评测机制,还是要取决于数据集中样本分布
宏平均(Macro-averaging),是先对每一个类统计指标值,然后在对所有类求算术平均值。
微平均(Micro-averaging),是对数据集中的每一个实例不分类别进行统计建立全局混淆矩阵,然后计算相应指标。(来源:谈谈评价指标中的宏平均和微平均)
from sklearn import metrics
metrics.precision_score(y_true, y_pred, average='micro')
Out[130]: 0.33333333333333331
metrics.precision_score(y_true, y_pred, average='macro')
Out[131]: 0.375
metrics.precision_score(y_true, y_pred, labels=[0, 1, 2, 3], average='macro')
Out[133]: 0.5
其中average参数有五种:(None, ‘micro’, ‘macro’, ‘weighted’, ‘samples’)
.
2、召回率
metrics.recall_score(y_true, y_pred, average='micro')
Out[134]: 0.33333333333333331
metrics.recall_score(y_true, y_pred, average='macro')
Out[135]: 0.3125
.
3、F1
metrics.f1_score(y_true, y_pred, average='weighted')
Out[136]: 0.37037037037037035
.
4、混淆矩阵
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
Out[137]:
array([[1, 0, 0, ..., 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, ..., 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, ..., 0, 0, 1],
...,
[0, 0, 0, ..., 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, ..., 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, ..., 0, 1, 0]])
横为true label 竖为predict

.
5、 分类报告
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
y_true = [0, 1, 2, 2, 0]
y_pred = [0, 0, 2, 2, 0]
target_names = ['class 0', 'class 1', 'class 2']
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=target_names))
其中的结果:
precision recall f1-score support
class 0 0.67 1.00 0.80 2
class 1 0.00 0.00 0.00 1
class 2 1.00 1.00 1.00 2
avg / total 0.67 0.80 0.72 5
包含:precision/recall/fi-score/均值/分类个数
.
6、 kappa score
kappa score是一个介于(-1, 1)之间的数. score>0.8意味着好的分类;0或更低意味着不好(实际是随机标签)
from sklearn.metrics import cohen_kappa_score
y_true = [2, 0, 2, 2, 0, 1]
y_pred = [0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 2]
cohen_kappa_score(y_true, y_pred)
.
二、ROC
1、计算ROC值
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
y_true = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
y_scores = np.array([0.1, 0.4, 0.35, 0.8])
roc_auc_score(y_true, y_scores)
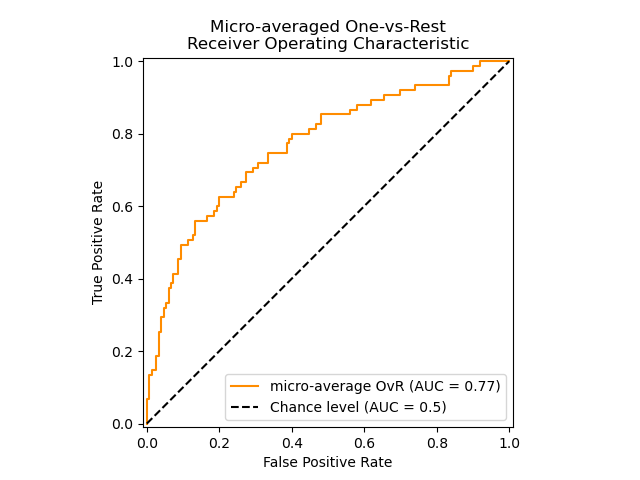
2、ROC曲线
y = np.array([1, 1, 2, 2])
scores = np.array([0.1, 0.4, 0.35, 0.8])
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y, scores, pos_label=2)
来看一个官网例子,贴部分代码,全部的code见:Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from itertools import cycle
from sklearn import svm, datasets
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import label_binarize
from sklearn.multiclass import OneVsRestClassifier
from scipy import interp
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
all_fpr = np.unique(np.concatenate([fpr[i] for i in range(n_classes)]))
mean_tpr = np.zeros_like(all_fpr)
for i in range(n_classes):
mean_tpr += interp(all_fpr, fpr[i], tpr[i])
mean_tpr /= n_classes
fpr["macro"] = all_fpr
tpr["macro"] = mean_tpr
roc_auc["macro"] = auc(fpr["macro"], tpr["macro"])
plt.figure()
plt.plot(fpr["micro"], tpr["micro"],
label='micro-average ROC curve (area = {0:0.2f})'
''.format(roc_auc["micro"]),
color='deeppink', linestyle=':', linewidth=4)
plt.plot(fpr["macro"], tpr["macro"],
label='macro-average ROC curve (area = {0:0.2f})'
''.format(roc_auc["macro"]),
color='navy', linestyle=':', linewidth=4)
colors = cycle(['aqua', 'darkorange', 'cornflowerblue'])
for i, color in zip(range(n_classes), colors):
plt.plot(fpr[i], tpr[i], color=color, lw=lw,
label='ROC curve of class {0} (area = {1:0.2f})'
''.format(i, roc_auc[i]))
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], 'k--', lw=lw)
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('Some extension of Receiver operating characteristic to multi-class')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
.
三、距离
.
1、海明距离
from sklearn.metrics import hamming_loss
y_pred = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y_true = [2, 2, 3, 4]
hamming_loss(y_true, y_pred)
0.25
.
2、Jaccard距离
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import jaccard_similarity_score
y_pred = [0, 2, 1, 3,4]
y_true = [0, 1, 2, 3,4]
jaccard_similarity_score(y_true, y_pred)
0.5
jaccard_similarity_score(y_true, y_pred, normalize=False)
2
.
四、回归
1、 可释方差值(Explained variance score)
from sklearn.metrics import explained_variance_score
y_true = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
y_pred = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
explained_variance_score(y_true, y_pred)
.
2、 平均绝对误差(Mean absolute error)
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
y_true = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
y_pred = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
mean_absolute_error(y_true, y_pred)
.
3、 均方误差(Mean squared error)
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
y_true = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
y_pred = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred)
.
from sklearn.metrics import median_absolute_error
y_true = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
y_pred = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
median_absolute_error(y_true, y_pred)
.
5、 R方值,确定系数
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
y_true = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
y_pred = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
r2_score(y_true, y_pred)
.
参考文献:
sklearn中的模型评估


























 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








