Deep Reinforcemen learning - 2. 基于tensorflow的DDPG实现
基于我上一篇博客的算法介绍, 使用tensorflow的代码实现,仿真环境使用gym torcs
为了快速训练出结果,我没有使用driver view图像作为输入,而是使用low dimension传感器数据作为输入,
总共29个数据,包括:
- 赛车速度: speedX, speedY, speedZ.
- 赛车在跑道中的位置
- 19个range finder的探测数据:车身与跑道边缘的距离
- 发动机转速
- 车轮速度
输出action有三个维度:
- steer: 方向, 取值范围 [-1,1]
- accel: 油门,取值范围 [0,1]
- brake: 刹车,取值范围 [0,1]
训练1M steps的视频链接:ddpg视频
完整代码的github链接:https://github.com/kennethyu2017/ddpg
下面分模块讲解:
代码框架
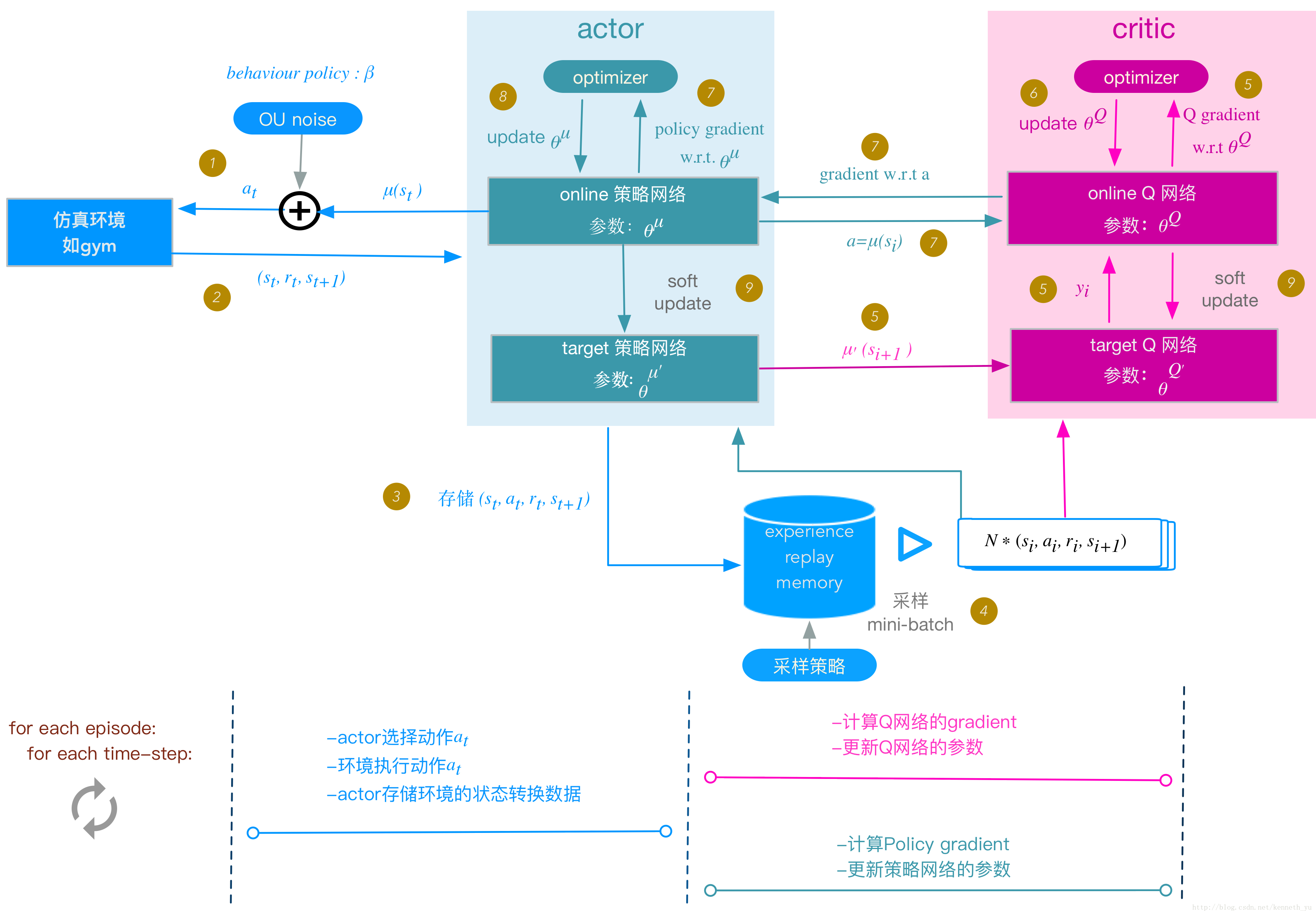
再回顾一下ddpg算法的流程图:
actor
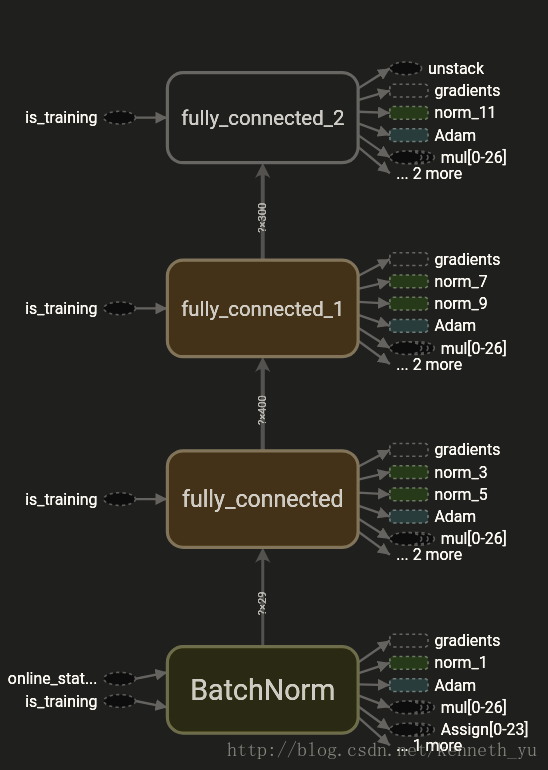
actor包含online policy和 target policy 两张神经网络, 其结构是一样的,由于使用low dimension 的数据输入,我没有使用卷积层,
policy网络架构如下 ,取自tensorboard生成的 computation graph:
包括:
- BatchNorm: input batch norm layer
- fully_connected,fully_connected_1: 2个hidden layers
- fully_connected_2: output layer
为了限定policy网络的输出action范围,使用tanh对steer,sigmoid对accelerate和brake,作为bound函数,进行范围限定:
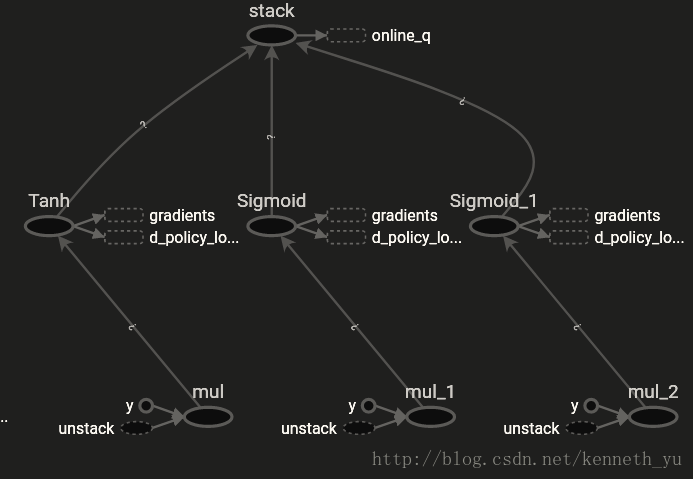
Actor class的主要代码如下:
为了在调试时可以灵活的修改模型架构,policy 网络的模型架构、配置、参数,全部通过在实例化Actor时指定,包括: 对输入数据做归一化的batch norm层、全连接fully-connected层、输出层、
输出bound 函数等。
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.layers import fully_connected,batch_norm
from common.common import soft_update_online_to_target, copy_online_to_target
DDPG_CFG = tf.app.flags.FLAGS # alias
class Actor(object):
def __init__(self, action_dim,
online_state_inputs, target_state_inputs,input_normalizer, input_norm_params,
n_fc_units, fc_activations, fc_initializers,
fc_normalizers, fc_norm_params, fc_regularizers,
output_layer_initializer, output_layer_regularizer,
output_normalizers, output_norm_params,output_bound_fns,
learning_rate, is_training):
self.a_dim = action_dim
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
...
使用Adam作为gradient descent的算法:
self.optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=self.learning_rate) # use beta1, beta2 default.创建online policy网络:
self._online_action_outputs = self.create_policy_net(scope=DDPG_CFG.online_policy_net_var_scope,
state_inputs=self.online_state_inputs,
trainable=True)
self.online_policy_net_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES,
scope=DDPG_CFG.online_policy_net_var_scope)
self.online_policy_net_vars_by_name = {var.name.strip(DDPG_CFG.online_policy_net_var_scope):var
for var in self.online_policy_net_vars}创建target policy 网络,由于我们采用soft update的方法更新target 网络的参数,所以在创建target网络时指定其参数trainable为False。
self._target_action_outputs = self.create_policy_net(scope=DDPG_CFG.target_policy_net_var_scope,
state_inputs=self.target_state_inputs,
trainable=False)
self.target_policy_net_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES,
scope=DDPG_CFG.target_policy_net_var_scope)
self.target_policy_net_vars_by_name = {var.name.strip(DDPG_CFG.target_policy_net_var_scope):var
for var in self.target_policy_net_vars}
策略网络的创建函数 create_policy_net ,根据网络架构参数创建各个layer:
def create_policy_net(self, state_inputs, scope, trainable):
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
#input norm layer
prev_layer = self.input_normalizer(state_inputs, **self.input_norm_params)
##fc layers
for n_unit, activation, initializer, normalizer, norm_param, regularizer in zip(
self.n_fc_units, self.fc_activations, self.fc_initializers,
self.fc_normalizers,self.fc_norm_params, self.fc_regularizers):
prev_layer = fully_connected(prev_layer, num_outputs=n_unit, activation_fn=activation,
weights_initializer=initializer,
weights_regularizer=regularizer,
normalizer_fn=normalizer,
normalizer_params=norm_param,
biases_initializer=None, #skip bias when use norm.
trainable=trainable)
##output layer
output_layer = fully_connected(prev_layer, num_outputs=self.a_dim, activation_fn=None,
weights_initializer=self.output_layer_initializer,
weights_regularizer=self.output_layer_regularizer,
normalizer_fn=self.output_normalizers,
normalizer_params=self.output_norm_params,
biases_initializer=None, # to skip bias
trainable=trainable)
## bound and scale each action dim
action_unpacked = tf.unstack(output_layer, axis=1)
action_bounded = []
for i in range(self.a_dim):
action_bounded.append(self.output_bound_fns[i](action_unpacked[i]))
action_outputs = tf.stack(action_bounded, axis=1)
return action_outputs
policy网络的输出tensor,即action:
# of online net
@property
def online_action_outputs_tensor(self):
return self._online_action_outputs
# of target net
@property
def target_action_outputs_tensor(self):
return self._target_action_outputs
定义计算online policy gradient的函数,由于我们只训练online 网络, 所以不用计算target网络的gradient :
def compute_online_policy_net_gradients(self, policy_loss):
grads_and_vars = self.optimizer.compute_gradients(
policy_loss,var_list=self.online_policy_net_vars)
grads = [g for (g, _) in grads_and_vars if g is not None]
compute_op = tf.group(*grads)
return (grads_and_vars, compute_op)定义函数,通过Adam optimize将计算好的gradient用于更新online policy网络的参数:
def apply_online_policy_net_gradients(self, grads_and_vars):
vars_with_grad = [v for g, v in grads_and_vars if g is not None]
if not vars_with_grad:
raise ValueError(
"$$ ddpg $$ policy net $$ No gradients provided for any variable, check your graph for ops"
" that do not support gradients,variables %s." %
([str(v) for _, v in grads_and_vars]))
return self.optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars)
从功能上来讲,上面这两步可以直接合并为使用 optimizer.minimize()函数,我是为了在调试过程中观察gradient的变化情况,所以拆开来实现,
这样可以在调试时取得gradient的tensor,观察其是否收敛。
定义函数,将online policy网络的参数在初始化时copy到target policy 网络,以及在训练时soft update到 target policy网络,
函数返回的是具体操作的op:
def soft_update_online_to_target(self):
return soft_update_online_to_target(self.online_q_net_vars_by_name,
self.target_q_net_vars_by_name)
def copy_online_to_target(self):
return copy_online_to_target(self.online_q_net_vars_by_name,
self.target_q_net_vars_by_name)
critic
critic包含online q和 target q 两张神经网络, 其结构也是一样的,q网络结构如下,取自tensorboard生成的computation graph:








 本文详细介绍了如何基于TensorFlow实现DDPG(Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient)算法,用于解决连续动作空间的强化学习问题。在仿真环境中,使用gym torcs,通过低维度传感器数据而非图像输入进行训练。文章涵盖了代码框架、actor和critic网络结构、replay buffer、训练和评估策略、噪声设计以及训练结果分析。作者提供了训练视频链接和完整代码的GitHub仓库地址。
本文详细介绍了如何基于TensorFlow实现DDPG(Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient)算法,用于解决连续动作空间的强化学习问题。在仿真环境中,使用gym torcs,通过低维度传感器数据而非图像输入进行训练。文章涵盖了代码框架、actor和critic网络结构、replay buffer、训练和评估策略、噪声设计以及训练结果分析。作者提供了训练视频链接和完整代码的GitHub仓库地址。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 14万+
14万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








