前言
前不久,公司有一项业务需要给出下一周的的预测(这是公司业务,这里不细说)。于是,我接触到了机器学习领域的知识,我觉得机器学习真是一个很奇妙的领域,它是一门交叉的学科,对各个业务领域冲击性很大。可以说,在任何领域都有运用机器学习的相关知识。
我并没有很完善的数学理论基础,但我会用我自己的理解来讲述所涉及到的算法,我想这样也是有好处的,那就是将复杂难懂的公式转换成了更接地气更让人明白的方式展现给大家。接下来的内容,如果有错,请大家多多指教。
正文
分类器就是以历史数据的“特征向量-结果”集合为依据,在给定特征向量时预测对应的具体类别。
Example:你天天看都接触人,当你再看到一个人时,你能分辨出它是男是女。
朴素贝叶斯分类器是基于贝叶斯定理实现的一种高效、容易理解、容易实现的分类器,朴素贝叶斯分类器适用于标称型数据分类,即使数据规模不够大时也能有效分类。
贝叶斯定理:
,P(A|B)表示在B发生时A发生的概率
此时,我们就能明白朴素贝叶斯分类器的基本思想是什么样子的了。
就是当给定特征出现时,求类别出现的概率,比较出现不同类别的概率,找到最大概率,最大概率对应的类别就是我们预测的类别
Example:
有两个特征A={a1,a2,a3},B={b1,b2,b3},类别C={yes,no}
给定一个特征集合(a2,b1),求此特征集合数据什么类别?
针对训练样本,进行计算:
根据贝叶斯定理计算:
P(C=yes|(a2,b1))=P((a2,b1)|C=yes)*P(C=yes)/P((a2,b1))
P(C=no|(a2,b1))=P((a2,b1)|C=no)*P(C=no)/P((a2,b1))
比较P(C=yes|(a2,b1))和P(C=no|(a2,b1))大小,谁大就是谁
我们来看一下P((a2,b1)|C=yes),由于两个特征是相对独立的,所以可以这样计算:
P((a2,b1)|C=yes)=P(a2|C=yes)*P(b1|C=yes)
P(a2|C=yes)=(C=yes时出现a2的次数)/(C=yes出现的次数)
当单一特征出现的概率=0,那么整个结果的概率就是0,这样就会造成单一特征,影响整体结果(这个影响太大了),为了避免单一特征主导影响整体情况,当频次等于0的时候,把分子分母都加1,表示此特征出现的概率特别特别的小
这里可以做一步优化,在进行比较时,由于分母P((a2,b1))的值是相等的,所以可以去掉P((a2,b1)),减少计算量
代码实现
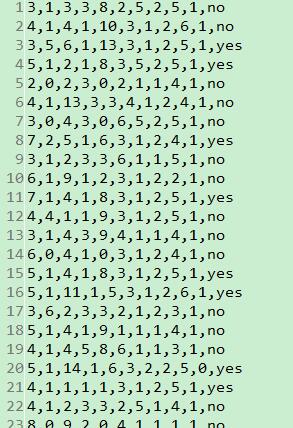
训练样本中特征向量共有10个元素(也就是每条数据10个特征),类别有两个yes or no,共100条数据
这里,我们可以把他当成银行贷款,根据贷款人的十个特征(年龄、月收入、存款、是否已婚、是否有房等等),判断贷款人是否是低风险用户的例子
保存样本中记录的特征,类别类
/** * @ClassName RecordWithFeaturesString * @Description 特征值为字符串类型的记录 * @author "liumingxin" * @Date 2017年6月20日 下午1:57:28 * @version 1.0.0 */ public class RecordWithFeaturesString { private List<String> features;//特征集合 private Object category;//类别 public List<String> getFeatures() { return features; } public void setFeatures(List<String> features) { this.features = features; } public Object getCategory() { return category; } public void setCategory(Object category) { this.category = category; } }具体实现,这里不多少了,代码里注释写的很清楚
代码我已经放在了github上了https://github.com/moonLazy/MoonML.gitpackage moon.ml.naivebayesian; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileReader; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import moon.ml.record.RecordWithFeaturesString; /** * @ClassName NaiveBayesian * @Description 朴素贝叶斯分类器 * 对于给出的待分类特征向量,求出此特征时出现各个类别的概率, * 最大概率的类别就认为是哪一类别 * @author "liumingxin" * @Date 2017年6月23日 上午11:07:16 * @version 1.0.0 */ public class NaiveBayesian { /** * 读取测试文档 */ private static List<RecordWithFeaturesString> readTest(String fileIn) { List<RecordWithFeaturesString> outList = new ArrayList<RecordWithFeaturesString>(); try { File file = new File(fileIn); FileReader reader = new FileReader(file); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(reader); String line = null; while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) { RecordWithFeaturesString record = new RecordWithFeaturesString(); List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); String[] mArray = line.split(","); for (Integer i = 0; i < mArray.length - 1; i++) { list.add(mArray[i]); } record.setFeatures(list); record.setCategory(mArray[mArray.length - 1]); outList.add(record); } in.close(); reader.close(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("读取出错"); e.printStackTrace(); } return outList; } /** * @Title: getCategoryRecordsMapper * @Description: 得到类型-记录映射 * @param trainList * @return * @return Map<String,List<RecordWithFeaturesString>> */ private static Map<Object, List<RecordWithFeaturesString>> getCategoryRecordsMapper( List<RecordWithFeaturesString> trainList) { Map<Object, List<RecordWithFeaturesString>> categoryRecordsMapper = new HashMap<Object, List<RecordWithFeaturesString>>(); for (RecordWithFeaturesString record : trainList) { Object category = record.getCategory(); List<RecordWithFeaturesString> list = categoryRecordsMapper.get(category); if (list == null) { list = new ArrayList<RecordWithFeaturesString>(); } list.add(record); categoryRecordsMapper.put(category, list); } return categoryRecordsMapper; } /** * @Title: calFeatureIProbability * @Description: 计算第I个特征在集合中的概率,用于计算P(特征1|结果1) * @param records * @param testList * @param i * @return * @return double */ private static double calFeatureIProbability(List<RecordWithFeaturesString> records, List<String> testList, int i) { int fiCount = 0; int totalSize = records.size(); // 在类别C出现时第I个特征出现的概率 double featureIProbability = 1d; for (RecordWithFeaturesString record : records) { List<String> features = record.getFeatures(); if (features.size() == testList.size()) { String test = testList.get(i); String feature = features.get(i); if (test.equals(feature)) { fiCount++; } } } //P(特征1,特征2,特征3|结果1) = P(特征1|结果1)*P(特征2|结果1)*P(特征3|结果1) //当单一特征出现的概率=0,那么整个结果的概率就是0,这样就会造成单一特征,影响整体结果(这个影响太大了), //为了避免单一特征主导影响整体情况,当频次等于0的时候,把分子分母都加1,表示此特征出现的概率特别特别的小 if(fiCount == 0){ fiCount++; totalSize++; } featureIProbability = (double) fiCount / totalSize; return featureIProbability; } /** * @Title: getResult * @Description: 得到结果 * @param trainList * 训练集合 * @param testList * 测试数据 * @return Object */ public static Object getResult(List<RecordWithFeaturesString> trainList, List<String> testList) { int totalTrainList = trainList.size(); // 类型-记录映射 Map<Object, List<RecordWithFeaturesString>> categoryRecordsMapper = getCategoryRecordsMapper(trainList); // 类型-概率映射,也就是最终结果 Map<Object, Double> categoryProbabilityMapper = new HashMap<Object, Double>(); // 计算类别概率 for (Object category : categoryRecordsMapper.keySet()) { List<RecordWithFeaturesString> records = categoryRecordsMapper.get(category); // 类别概率 double categoryProbability = (double) records.size() / totalTrainList; // 在类别C出现时第I个特征出现的概率 double featureIProbability = 1d; // P(特征1,特征2,特征3|结果1) = P(特征1|结果1)*P(特征2|结果1)*P(特征3|结果1),假设特征123相互独立 for (int i = 0; i < testList.size(); i++) { featureIProbability = featureIProbability * calFeatureIProbability(records, testList, i); } // P(结果1|特征1,特征2,特征3) = // P(特征1,特征2,特征3|结果1)*P(结果1),因为P(特征1,特征2,特征3)相等,所以省略 featureIProbability = featureIProbability * categoryProbability; categoryProbabilityMapper.put(category, featureIProbability); } Object maxCategory = null; double maxProbability = 0d; for (Object category : categoryProbabilityMapper.keySet()) { double probability = categoryProbabilityMapper.get(category); if (probability > maxProbability) { maxProbability = probability; maxCategory = category; } } return maxCategory; } public static void main(String[] args) { //给定十个特征,求出数据哪一类别 String test1 = "6,1,9,1,2,3,1,2,2,1"; String[] testArr = test1.split(","); List<String> testList = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String str : testArr) { testList.add(str); } String trainTxt = "data/naivebayesian/naivebayesian1.txt"; // 读取训练数据 List<RecordWithFeaturesString> trainList = readTest(trainTxt); Object result = getResult(trainList, testList); System.out.println(result); } }






















 1047
1047

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








