🍺 要求:
-1. 自己搭建VGG-16网络框架
-2. 调用官方的VGG-16网络框架
-3. 如何查看模型的参数量以及相关指标
🍻 拔高(可选):
-1. 验证集准确率达到100%
-2. 使用PPT画出VGG-16算法框架图(发论文需要这项技能)
🔎 探索(难度有点大)
-1. 在不影响准确率的前提下轻量化模型
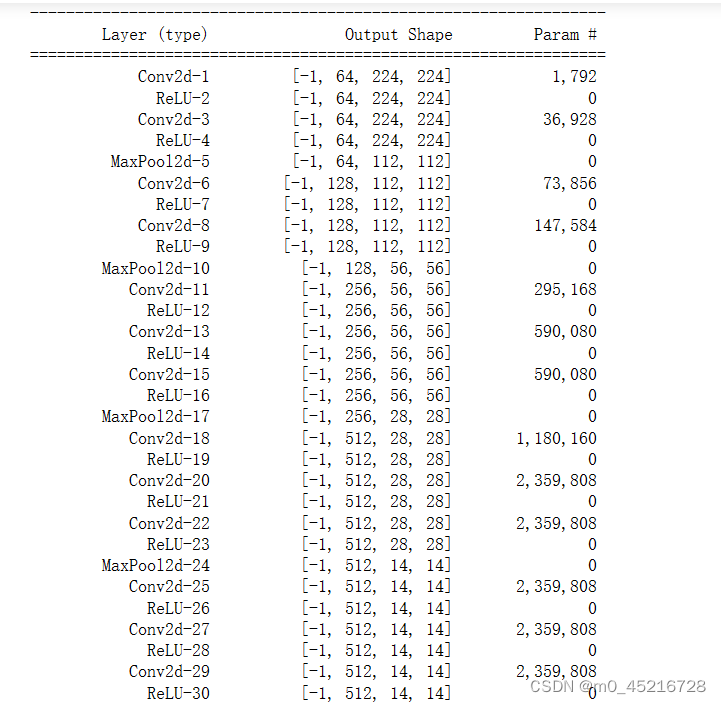
目前VGG16的Total params是134,276,932
我的环境
语言环境:python3.7
编译器:Jupyter notebook
深度学习环境:Pytorch
一、前期准备
1.1 设置GPU
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms,datasets
import os,warnings,PIL,pathlib
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
1.2 导入数据¶
import os,PIL,random,pathlib
data_dir = './7-data'
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
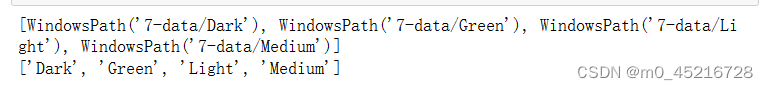
print(data_paths)
# 获取类的名字
className = [str(path).split('\\')[1] for path in data_paths]
data_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224,224]),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
total_data = datasets.ImageFolder('./7-data/', transform=data_transforms)
total_data

1.3 划分数据
train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
# 批量
batch_size = 32
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle = True, num_workers = 1)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle = True, num_workers = 1)
二、动手搭建VGG-16
13个卷积层(Convolutional Layer),分别用blockX_convX表示
5个池化层(pool layer),分别用blockX_pool表示
3个全连接层(full connected layer),分别用fcX表示VGG-16

2.1 VGG-16模型搭建
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class vgg16(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(vgg16,self).__init__()
# conv1
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3),stride=(1,1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2,2))
)
# conv2
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
)
# conv3
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
)
# conv4
self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
)
# conv5
self.conv5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
)
# fc
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=512*7*7, out_features=4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
x = self.conv5(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
model = vgg16().to(device)
model
2.2 查看模型详情
import torchsummary as summary
summary.summary(model, (3, 224, 224))
三、训练模型
3.1 编写训练函数
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fun, opt):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
num_batches = len(dataloader)
train_acc, train_loss = 0, 0
for x,y in dataloader:
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
# 预测
pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fun(pred, y)
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 记录loss与acc
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc,train_loss
3.2 编写测试函数
def test(dataloader, model, loss_fun):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
num_batches = len(dataloader)
test_acc, test_loss = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x,y in dataloader:
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
# 计算loss
pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fun(pred, y)
test_loss += loss.item()
test_acc += (pred.argmax(1)==y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_acc /= size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss
3.3 正式训练
import copy
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
loss_fun = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
epochs = 40
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_acc = []
test_loss = []
best_acc = 0 #设置一个最佳准确率,作为最佳模型的判别指标
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fun, optimizer)
model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fun)
# 保存最佳模型 best_model
if epoch_test_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = epoch_test_acc
best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
# 获取当前的学习率
lr = optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.2f}, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.2f}, Test_loss:{:.3f}, lr:{:.2E}')
print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss, epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss, lr))
# 保存最佳模型到文件中
Path = './best_mode.pth'
torch.save(model.state_dict(), Path)
print('Done')

三、结果可视化
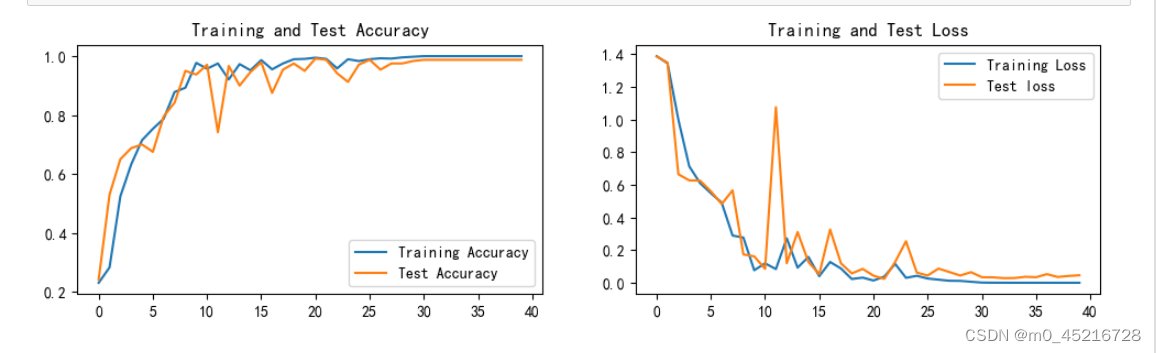
4.1 loss与Accuracy可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] =False
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100
plt.figure(figsize = (12,3))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.plot(range(epochs), train_acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(range(epochs), test_acc, label='Test Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Test Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.plot(range(epochs), train_loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(range(epochs), test_loss, label='Test loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Test Loss')
plt.show()
4.2 指定图片进行评估
from PIL import Image
classes = list(total_data.class_to_idx)
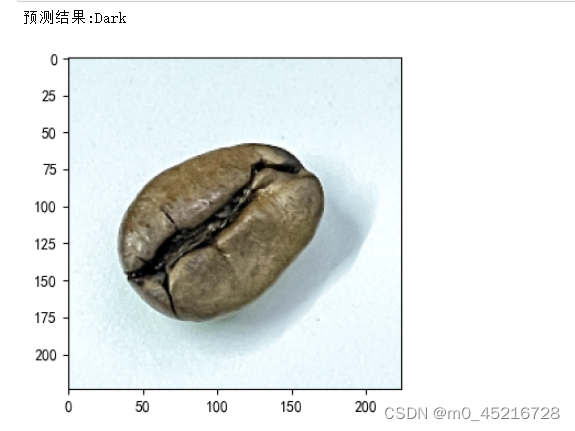
def pred_one_image(image_path, model, transform, classes):
test_image = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
plt.imshow(test_image)
test_image = transform(test_image)
image = test_image.to(device).unsqueeze(0)
model.eval()
output = model(image)
_,pred = torch.max(output, dim=1)
pred_class = classes[pred]
print('预测结果:'{pred_class})
pred_one_image(image_path='./7-data/Dark/dark(4).png',model=model, transform=train_transform, classes=classes)
4.3 模型评估
best_model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, best_model, loss_fun)
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss
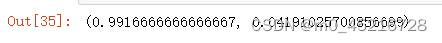
# 查看是否与记录的最高准确率一样
epoch_test_acc
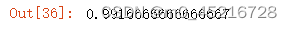
将优化器改为SGD后发现惊人的现象,训练集的
import copy
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
loss_fun = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
epochs = 40
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_acc = []
test_loss = []
best_acc = 0 #设置一个最佳准确率,作为最佳模型的判别指标
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fun, optimizer)
model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fun)
# 保存最佳模型 best_model
if epoch_test_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = epoch_test_acc
best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
# 获取当前的学习率
lr = optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.2f}, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.2f}, Test_loss:{:.3f}, lr:{:.2E}')
print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss, epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss, lr))
# 保存最佳模型到文件中
Path = './best_mode.pth'
torch.save(model.state_dict(), Path)
print('Done')

总结:
1.自己用PPT搭建网络模型,并学会如何搭建简单的卷积、池化和全连接
2.训练的速度很慢,参数量多
3.训练集和测试集在第30个epoch是能达到准确率最佳的状态
4.将优化器从Adam改为SGD后发现惊人的现象,训练集的准确率在初期就达到100%,测试集也在初期准确率就达到98.5%,并且一直维持,Adam优化器需要早30个epoch后才能达到这个效果。为什么会出现这样的情况呢?





















 1098
1098











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








