代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 生成非线性可分的数据集(月亮形状)
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=1000, noise=0.3, random_state=42)
# 可视化生成的数据集
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.scatter(X[y == 0][:, 0], X[y == 0][:, 1], color='red', label='Class 0')
plt.scatter(X[y == 1][:, 0], X[y == 1][:, 1], color='blue', label='Class 1')
plt.title('Generated Non-linearly Separable Dataset')
plt.xlabel('Feature 1')
plt.ylabel('Feature 2')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 将数据集分为训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
# 初始化基分类器
clf1 = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42)
clf2 = SVC(random_state=42, probability=True)
clf3 = LogisticRegression(random_state=42)
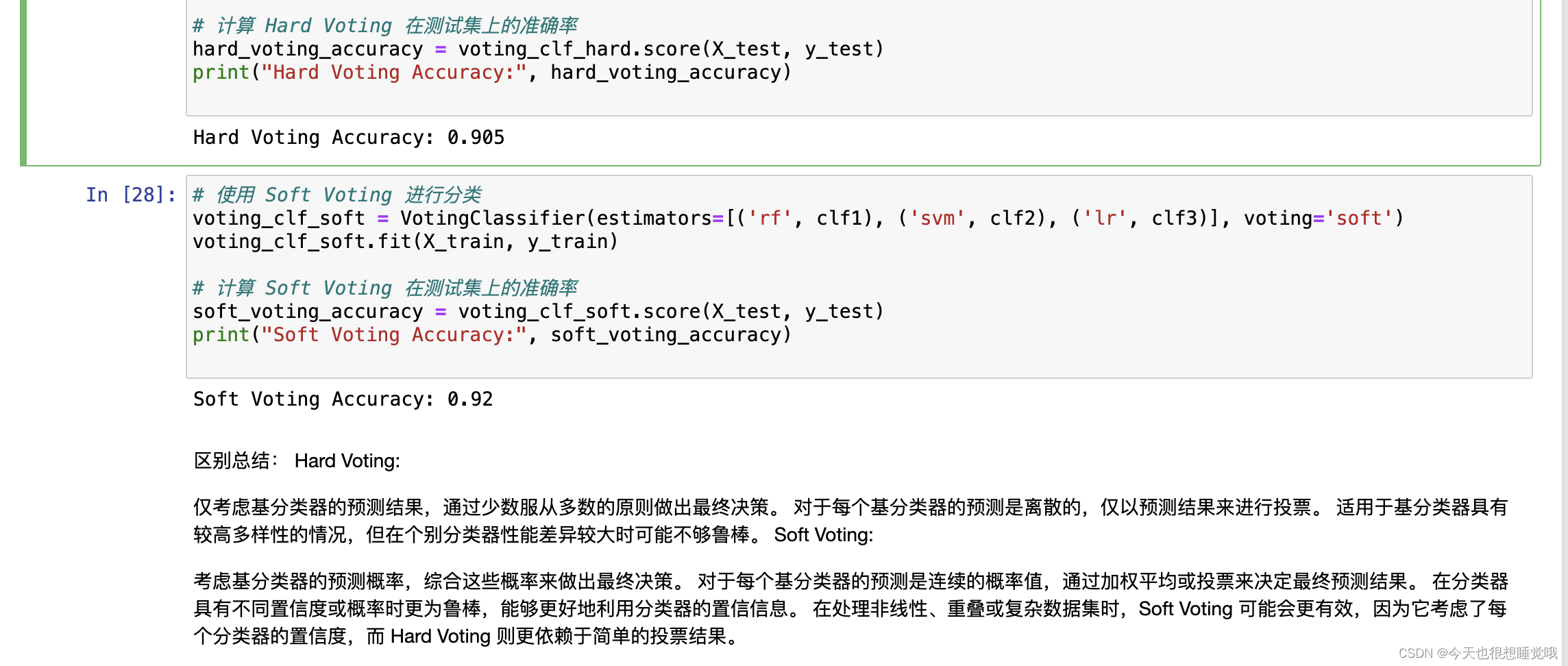
# 使用 Hard Voting 进行分类
voting_clf_hard = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('rf', clf1), ('svm', clf2), ('lr', clf3)], voting='hard')
voting_clf_hard.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 计算 Hard Voting 在测试集上的准确率
hard_voting_accuracy = voting_clf_hard.score(X_test, y_test)
print("Hard Voting Accuracy:", hard_voting_accuracy)
# 使用 Soft Voting 进行分类
voting_clf_soft = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('rf', clf1), ('svm', clf2), ('lr', clf3)], voting='soft')
voting_clf_soft.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 计算 Soft Voting 在测试集上的准确率
soft_voting_accuracy = voting_clf_soft.score(X_test, y_test)
print("Soft Voting Accuracy:", soft_voting_accuracy)
结果:























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








