多层感知器(MLP)被认为是最基本的神经网络构建模块之一。最简单的MLP是对第3章感知器的扩展。感知器将数据向量作为输入,计算出一个输出值。在MLP中,许多感知器被分组,以便单个层的输出是一个新的向量,而不是单个输出值。在PyTorch中,正如您稍后将看到的,这只需设置线性层中的输出特性的数量即可完成。MLP的另一个方面是,它将多个层与每个层之间的非线性结合在一起。
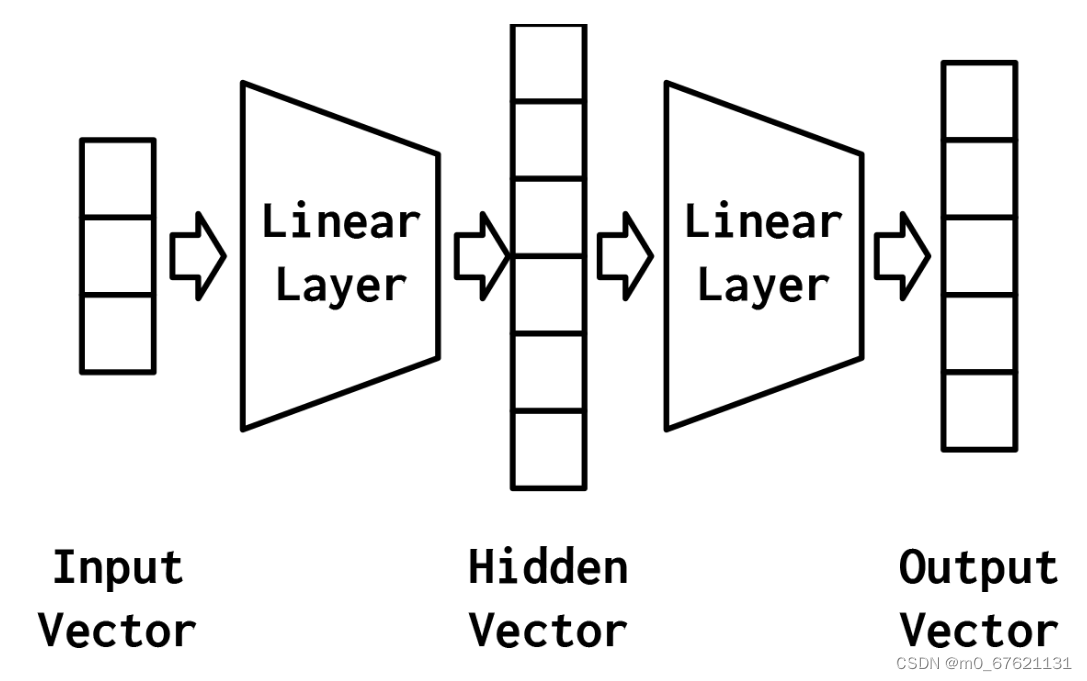
最简单的MLP,如图4-2所示,由三个表示阶段和两个线性层组成。第一阶段是输入向量。这是给定给模型的向量。在“示例:对餐馆评论的情绪进行分类”中,输入向量是Yelp评论的一个收缩的one-hot表示。给定输入向量,第一个线性层计算一个隐藏向量——表示的第二阶段。隐藏向量之所以这样被调用,是因为它是位于输入和输出之间的层的输出。我们所说的“层的输出”是什么意思?理解这个的一种方法是隐藏向量中的值是组成该层的不同感知器的输出。使用这个隐藏的向量,第二个线性层计算一个输出向量。在像Yelp评论分类这样的二进制任务中,输出向量仍然可以是1。在多类设置中,将在本实验后面的“示例:带有多层感知器的姓氏分类”一节中看到,输出向量是类数量的大小。虽然在这个例子中,我们只展示了一个隐藏的向量,但是有可能有多个中间阶段,每个阶段产生自己的隐藏向量。最终的隐藏向量总是通过线性层和非线性的组合映射到输出向量。
我们使用MLP来进行姓氏分类任务,将姓氏分类到其原籍国家。这种应用可以帮助理解如何处理和利用人口统计信息,如国籍,以确保在建模和产品应用中避免引入不公平的结果。
重要教训包括MLP的实现和训练源于感知器的基本原理,但通过引入多层和非线性激活函数,MLP能够更有效地处理复杂的分类任务。在这个过程中,我们将姓氏的字符进行拆分和向量化,类似于处理文本数据时的方法,通过词汇表、向量化器和DataLoader构建数据处理管道,以便将原始数据转换为模型可处理的格式。
MLP的模型结构与实验3中感知器的例子类似,但在这里我们引入了多类输出和适当的损失函数,如交叉熵损失,以优化模型的训练过程。训练过程类似于“餐馆评论的情绪分类”的例子,利用反向传播和优化器进行模型参数的调整,以提高分类准确性。
总结来说,这个例子展示了如何利用MLP处理具有受保护属性的数据,如人口统计信息,同时强调了在使用这些信息时需要谨慎的重要性,以确保结果的公平性和准确性。
载入数据集和实现姓氏矢量器
class SurnameDataset(Dataset):
# Implementation is nearly identical to Section 3.5
def __getitem__(self, index):
row = self._target_df.iloc[index]
surname_vector = \
self._vectorizer.vectorize(row.surname)
nationality_index = \
self._vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_token(row.nationality)
return {'x_surname': surname_vector,
'y_nationality': nationality_index}class SurnameVectorizer(object):
""" The Vectorizer which coordinates the Vocabularies and puts them to use"""
def __init__(self, surname_vocab, nationality_vocab):
self.surname_vocab = surname_vocab
self.nationality_vocab = nationality_vocab
def vectorize(self, surname):
"""Vectorize the provided surname
Args:
surname (str): the surname
Returns:
one_hot (np.ndarray): a collapsed one-hot encoding
"""
vocab = self.surname_vocab
one_hot = np.zeros(len(vocab), dtype=np.float32)
for token in surname:
one_hot[vocab.lookup_token(token)] = 1
return one_hot
@classmethod
def from_dataframe(cls, surname_df):
"""Instantiate the vectorizer from the dataset dataframe
Args:
surname_df (pandas.DataFrame): the surnames dataset
Returns:
an instance of the SurnameVectorizer
"""
surname_vocab = Vocabulary(unk_token="@")
nationality_vocab = Vocabulary(add_unk=False)
for index, row in surname_df.iterrows():
for letter in row.surname:
surname_vocab.add_token(letter)
nationality_vocab.add_token(row.nationality)
return cls(surname_vocab, nationality_vocab)数据矢量化类
class Vocabulary(object):
"""Class to process text and extract vocabulary for mapping"""
def __init__(self, token_to_idx=None, add_unk=True, unk_token="<UNK>"):
"""
Args:
token_to_idx (dict): a pre-existing map of tokens to indices
add_unk (bool): a flag that indicates whether to add the UNK token
unk_token (str): the UNK token to add into the Vocabulary
"""
if token_to_idx is None:
token_to_idx = {}
self._token_to_idx = token_to_idx
self._idx_to_token = {idx: token
for token, idx in self._token_to_idx.items()}
self._add_unk = add_unk
self._unk_token = unk_token
self.unk_index = -1
if add_unk:
self.unk_index = self.add_token(unk_token)
def to_serializable(self):
""" returns a dictionary that can be serialized """
return {'token_to_idx': self._token_to_idx,
'add_unk': self._add_unk,
'unk_token': self._unk_token}
@classmethod
def from_serializable(cls, contents):
""" instantiates the Vocabulary from a serialized dictionary """
return cls(**contents)
def add_token(self, token):
"""Update mapping dicts based on the token.
Args:
token (str): the item to add into the Vocabulary
Returns:
index (int): the integer corresponding to the token
"""
try:
index = self._token_to_idx[token]
except KeyError:
index = len(self._token_to_idx)
self._token_to_idx[token] = index
self._idx_to_token[index] = token
return index
def add_many(self, tokens):
"""Add a list of tokens into the Vocabulary
Args:
tokens (list): a list of string tokens
Returns:
indices (list): a list of indices corresponding to the tokens
"""
return [self.add_token(token) for token in tokens]
def lookup_token(self, token):
"""Retrieve the index associated with the token
or the UNK index if token isn't present.
Args:
token (str): the token to look up
Returns:
index (int): the index corresponding to the token
Notes:
`unk_index` needs to be >=0 (having been added into the Vocabulary)
for the UNK functionality
"""
if self.unk_index >= 0:
return self._token_to_idx.get(token, self.unk_index)
else:
return self._token_to_idx[token]
def lookup_index(self, index):
"""Return the token associated with the index
Args:
index (int): the index to look up
Returns:
token (str): the token corresponding to the index
Raises:
KeyError: if the index is not in the Vocabulary
"""
if index not in self._idx_to_token:
raise KeyError("the index (%d) is not in the Vocabulary" % index)
return self._idx_to_token[index]
def __str__(self):
return "<Vocabulary(size=%d)>" % len(self)
def __len__(self):
return len(self._token_to_idx)分类器模型
class SurnameClassifier(nn.Module):
""" A 2-layer Multilayer Perceptron for classifying surnames """
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim):
"""
Args:
input_dim (int): the size of the input vectors
hidden_dim (int): the output size of the first Linear layer
output_dim (int): the output size of the second Linear layer
"""
super(SurnameClassifier, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x_in, apply_softmax=False):
"""The forward pass of the classifier
Args:
x_in (torch.Tensor): an input data tensor.
x_in.shape should be (batch, input_dim)
apply_softmax (bool): a flag for the softmax activation
should be false if used with the Cross Entropy losses
Returns:
the resulting tensor. tensor.shape should be (batch, output_dim)
"""
intermediate_vector = F.relu(self.fc1(x_in))
prediction_vector = self.fc2(intermediate_vector)
if apply_softmax:
prediction_vector = F.softmax(prediction_vector, dim=1)
return prediction_vector训练
classifier = classifier.to(args.device)
dataset.class_weights = dataset.class_weights.to(args.device)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(dataset.class_weights)
optimizer = optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(), lr=args.learning_rate)
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer=optimizer,
mode='min', factor=0.5,
patience=1)
train_state = make_train_state(args)
epoch_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='training routine',
total=args.num_epochs,
position=0)
dataset.set_split('train')
train_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='split=train',
total=dataset.get_num_batches(args.batch_size),
position=1,
leave=True)
dataset.set_split('val')
val_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='split=val',
total=dataset.get_num_batches(args.batch_size),
position=1,
leave=True)
try:
for epoch_index in range(args.num_epochs):
train_state['epoch_index'] = epoch_index
# Iterate over training dataset
# setup: batch generator, set loss and acc to 0, set train mode on
dataset.set_split('train')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.0
running_acc = 0.0
classifier.train()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# the training routine is these 5 steps:
# --------------------------------------
# step 1. zero the gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# step 2. compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# step 3. compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# step 4. use loss to produce gradients
loss.backward()
# step 5. use optimizer to take gradient step
optimizer.step()
# -----------------------------------------
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
# update bar
train_bar.set_postfix(loss=running_loss, acc=running_acc,
epoch=epoch_index)
train_bar.update()
train_state['train_loss'].append(running_loss)
train_state['train_acc'].append(running_acc)
# Iterate over val dataset
# setup: batch generator, set loss and acc to 0; set eval mode on
dataset.set_split('val')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.
running_acc = 0.
classifier.eval()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# step 3. compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.to("cpu").item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
val_bar.set_postfix(loss=running_loss, acc=running_acc,
epoch=epoch_index)
val_bar.update()
train_state['val_loss'].append(running_loss)
train_state['val_acc'].append(running_acc)
train_state = update_train_state(args=args, model=classifier,
train_state=train_state)
scheduler.step(train_state['val_loss'][-1])
if train_state['stop_early']:
break
train_bar.n = 0
val_bar.n = 0
epoch_bar.update()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Exiting loop")
结果预测
def predict_nationality(surname, classifier, vectorizer):
"""Predict the nationality from a new surname
Args:
surname (str): the surname to classifier
classifier (SurnameClassifer): an instance of the classifier
vectorizer (SurnameVectorizer): the corresponding vectorizer
Returns:
a dictionary with the most likely nationality and its probability
"""
vectorized_surname = vectorizer.vectorize(surname)
vectorized_surname = torch.tensor(vectorized_surname).view(1, -1)
result = classifier(vectorized_surname, apply_softmax=True)
probability_values, indices = result.max(dim=1)
index = indices.item()
predicted_nationality = vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_index(index)
probability_value = probability_values.item()
return {'nationality': predicted_nationality, 'probability': probability_value}TOP-k预测结果
def predict_topk_nationality(surname, classifier, vectorizer, k=5):
"""Predict the top K nationalities from a new surname
Args:
surname (str): the surname to classifier
classifier (SurnameClassifer): an instance of the classifier
vectorizer (SurnameVectorizer): the corresponding vectorizer
k (int): the number of top nationalities to return
Returns:
list of dictionaries, each dictionary is a nationality and a probability
"""
vectorized_surname = vectorizer.vectorize(surname)
vectorized_surname = torch.tensor(vectorized_surname).unsqueeze(dim=0)
prediction_vector = classifier(vectorized_surname, apply_softmax=True)
probability_values, indices = torch.topk(prediction_vector, k=k)
# returned size is 1,k
probability_values = probability_values[0].detach().numpy()
indices = indices[0].detach().numpy()
results = []
for kth_index in range(k):
nationality = vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_index(indices[kth_index])
probability_value = probability_values[kth_index]
results.append({'nationality': nationality,
'probability': probability_value})
return results
new_surname = input("Enter a surname to classify: ")
k = int(input("How many of the top predictions to see? "))
if k > len(vectorizer.nationality_vocab):
print("Sorry! That's more than the # of nationalities we have.. defaulting you to max size :)")
k = len(vectorizer.nationality_vocab)
predictions = predict_topk_nationality(new_surname, classifier, vectorizer, k=k)
print("Top {} predictions:".format(k))
print("===================")
for prediction in predictions:
print("{} -> {} (p={:0.2f})".format(new_surname,
prediction['nationality'],
prediction['probability']))





















 815
815

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








