多层感知器(MLP)被认为是最基本的神经网络构建模块之一。感知器将数据向量作为输入,计算出一个输出值。在MLP中,许多感知器被分组,以便单个层的输出是一个新的向量,而不是单个输出值。在PyTorch中这只需设置线性层中的输出特性的数量即可完成。MLP的另一个方面是,它将多个层与每个层之间的非线性结合在一起。
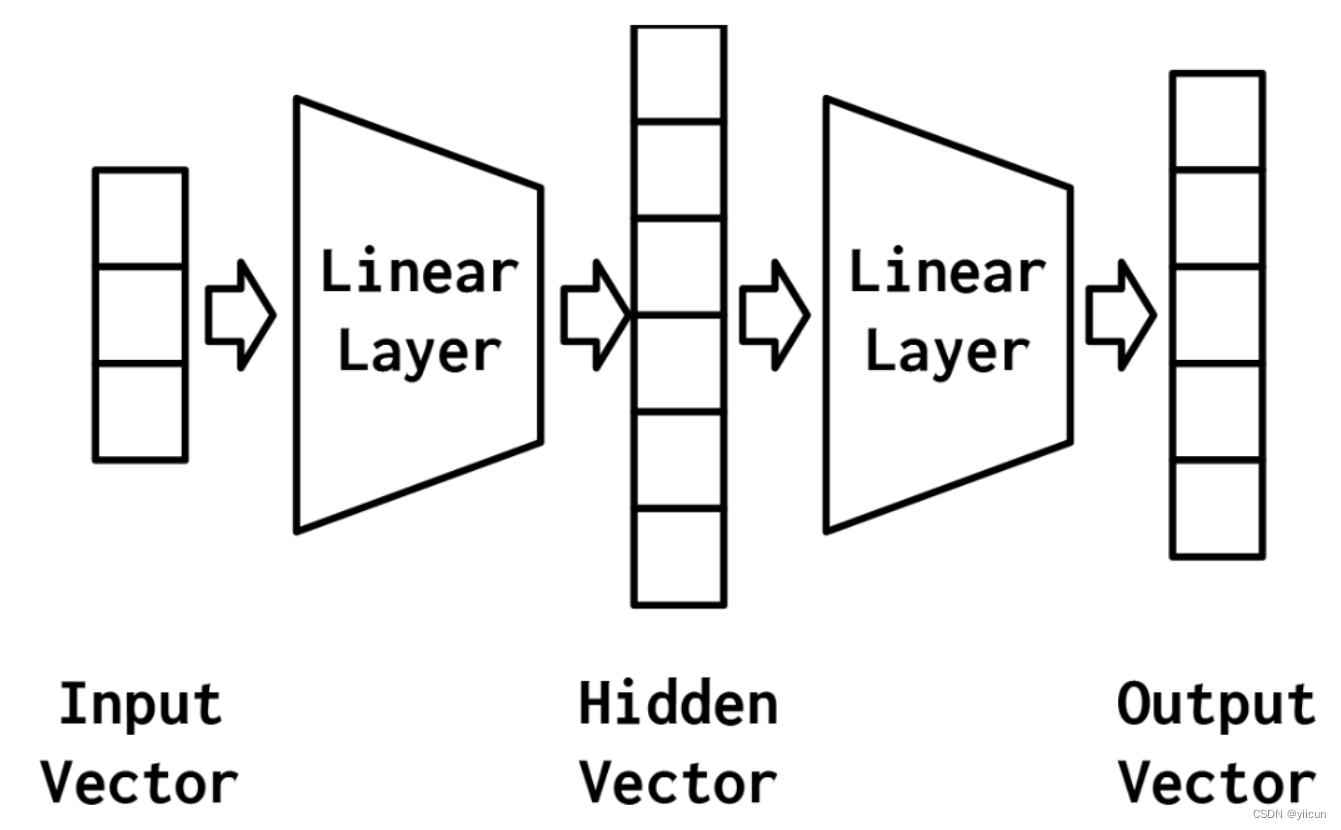
最简单的MLP,如上图所示,由三个表示阶段和两个线性层组成。第一阶段是输入向量。这是给定给模型的向量。给定输入向量,第一个线性层计算一个隐藏向量——表示的第二阶段。隐藏向量之所以这样被调用,是因为它是位于输入和输出之间的层的输出。我们所说的“层的输出”是什么意思?理解这个的一种方法是隐藏向量中的值是组成该层的不同感知器的输出。使用这个隐藏的向量,第二个线性层计算一个输出向量。在像Yelp评论分类这样的二进制任务中,输出向量仍然可以是1。在多类设置中,将在本实验后面的“示例:带有多层感知器的姓氏分类”一节中看到,输出向量是类数量的大小。虽然在这个例子中,我们只展示了一个隐藏的向量,但是有可能有多个中间阶段,每个阶段产生自己的隐藏向量。最终的隐藏向量总是通过线性层和非线性的组合映射到输出向量。
mlp的力量来自于添加第二个线性层和允许模型学习一个线性分割的的中间表示——该属性的能表示一个直线(或更一般的,一个超平面)可以用来区分数据点落在线(或超平面)的哪一边的。学习具有特定属性的中间表示,如分类任务是线性可分的,这是使用神经网络的最深刻后果之一,也是其建模能力的精髓。
演示
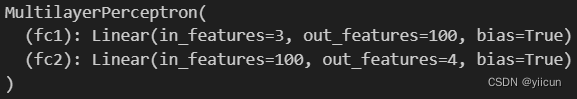
先实例化MLP。由于MLP实现的通用性,可以为任何大小的输入建模。为了演示,我们使用大小为3的输入维度、大小为4的输出维度和大小为100的隐藏维度。在print语句的输出中,每个层中的单元数很好地排列在一起,以便为维度3的输入生成维度4的输出。
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class MultilayerPerceptron(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim):
"""
Args:
input_dim (int): the size of the input vectors
hidden_dim (int): the output size of the first Linear layer
output_dim (int): the output size of the second Linear layer
"""
super(MultilayerPerceptron, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x_in, apply_softmax=False):
"""The forward pass of the MLP
Args:
x_in (torch.Tensor): an input data tensor.
x_in.shape should be (batch, input_dim)
apply_softmax (bool): a flag for the softmax activation
should be false if used with the Cross Entropy losses
Returns:
the resulting tensor. tensor.shape should be (batch, output_dim)
"""
intermediate = F.relu(self.fc1(x_in))
output = self.fc2(intermediate)
if apply_softmax:
output = F.softmax(output, dim=1)
return output
batch_size = 2 # number of samples input at once
input_dim = 3
hidden_dim = 100
output_dim = 4
# Initialize model
mlp = MultilayerPerceptron(input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim)
print(mlp)运行结果
传递一些随机输入来快速测试模型的“连接”
import torch
def describe(x):
print("Type: {}".format(x.type()))
print("Shape/size: {}".format(x.shape))
print("Values: \n{}".format(x))
x_input = torch.rand(batch_size, input_dim)
describe(x_input)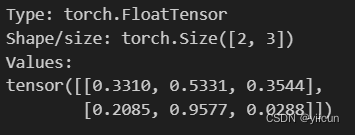
y_output = mlp(x_input, apply_softmax=False)
describe(y_output)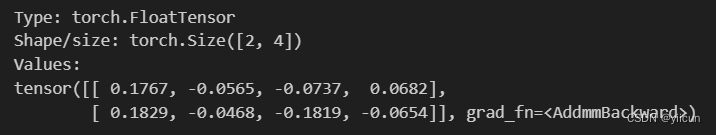
姓氏分类
基于数据集训练输入姓氏输出其国籍的模型
Imports
from argparse import Namespace
from collections import Counter
import json
import os
import string
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from tqdm import tqdm_notebook数据预处理
字典
class Vocabulary(object):
"""用于处理文本并提取词汇以进行映射的类"""
def __init__(self, token_to_idx=None, add_unk=True, unk_token="<UNK>"):
"""
参数:
token_to_idx (dict): 一个预先存在的将标记映射到索引的映射
add_unk (bool): 一个指示是否添加UNK标记的标志
unk_token (str): 要添加到词汇表中的UNK标记
"""
if token_to_idx is None:
token_to_idx = {}
self._token_to_idx = token_to_idx
self._idx_to_token = {idx: token
for token, idx in self._token_to_idx.items()}
self._add_unk = add_unk
self._unk_token = unk_token
self.unk_index = -1
if add_unk:
self.unk_index = self.add_token(unk_token)
def to_serializable(self):
"""返回一个可序列化的字典"""
return {'token_to_idx': self._token_to_idx,
'add_unk': self._add_unk,
'unk_token': self._unk_token}
@classmethod
def from_serializable(cls, contents):
"""从一个序列化的字典实例化词汇表"""
return cls(**contents)
def add_token(self, token):
"""基于标记更新映射字典。
参数:
token (str): 要添加到词汇表中的项目
返回:
index (int): 对应于标记的整数
"""
try:
index = self._token_to_idx[token]
except KeyError:
index = len(self._token_to_idx)
self._token_to_idx[token] = index
self._idx_to_token[index] = token
return index
def add_many(self, tokens):
"""将一组标记添加到词汇表中
参数:
tokens (list): 一组字符串标记
返回:
indices (list): 与标记对应的索引列表
"""
return [self.add_token(token) for token in tokens]
def lookup_token(self, token):
"""检索与标记相关联的索引,如果标记不存在,则返回UNK索引。
参数:
token (str): 要查找的标记
返回:
index (int): 对应于标记的索引
注意:
`unk_index` 需要 >=0 (已添加到词汇表中)
以执行UNK功能
"""
if self.unk_index >= 0:
return self._token_to_idx.get(token, self.unk_index)
else:
return self._token_to_idx[token]
def lookup_index(self, index):
"""返回与索引相关联的标记
参数:
index (int): 要查找的索引
返回:
token (str): 与索引相关的标记
抛出:
KeyError: 如果索引不在词汇表中
"""
if index not in self._idx_to_token:
raise KeyError("索引 (%d) 不在词汇表中" % index)
return self._idx_to_token[index]
def __str__(self):
return "<Vocabulary(size=%d)>" % len(self)
def __len__(self):
return len(self._token_to_idx)矢量化
class SurnameVectorizer(object):
"""协调Vocabularies并将它们投入使用的Vectorizer"""
def __init__(self, surname_vocab, nationality_vocab):
"""
参数:
surname_vocab (Vocabulary): 将字符映射到整数的词汇表
nationality_vocab (Vocabulary): 将国籍映射到整数的词汇表
"""
self.surname_vocab = surname_vocab
self.nationality_vocab = nationality_vocab
def vectorize(self, surname):
"""
参数:
surname (str): 姓氏
返回:
one_hot (np.ndarray): 一个压缩的one-hot编码
"""
vocab = self.surname_vocab
one_hot = np.zeros(len(vocab), dtype=np.float32)
for token in surname:
one_hot[vocab.lookup_token(token)] = 1
return one_hot
@classmethod
def from_dataframe(cls, surname_df):
"""从数据集DataFrame实例化Vectorizer
参数:
surname_df (pandas.DataFrame): 姓氏数据集
返回:
SurnameVectorizer的实例
"""
surname_vocab = Vocabulary(unk_token="@")
nationality_vocab = Vocabulary(add_unk=False)
for index, row in surname_df.iterrows():
for letter in row.surname:
surname_vocab.add_token(letter)
nationality_vocab.add_token(row.nationality)
return cls(surname_vocab, nationality_vocab)
@classmethod
def from_serializable(cls, contents):
surname_vocab = Vocabulary.from_serializable(contents['surname_vocab'])
nationality_vocab = Vocabulary.from_serializable(contents['nationality_vocab'])
return cls(surname_vocab=surname_vocab, nationality_vocab=nationality_vocab)
def to_serializable(self):
return {'surname_vocab': self.surname_vocab.to_serializable(),
'nationality_vocab': self.nationality_vocab.to_serializable()}数据集
class SurnameDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, surname_df, vectorizer):
"""
Args:
surname_df (pandas.DataFrame): the dataset
vectorizer (SurnameVectorizer): vectorizer instatiated from dataset
"""
self.surname_df = surname_df
self._vectorizer = vectorizer
class SurnameVectorizer(object):
"""协调Vocabularies并将它们投入使用的Vectorizer"""
def __init__(self, surname_vocab, nationality_vocab):
"""
参数:
surname_vocab (Vocabulary): 将字符映射到整数的词汇表
nationality_vocab (Vocabulary): 将国籍映射到整数的词汇表
"""
self.surname_vocab = surname_vocab
self.nationality_vocab = nationality_vocab
def vectorize(self, surname):
"""
参数:
surname (str): 姓氏
返回:
one_hot (np.ndarray): 一个压缩的one-hot编码
"""
vocab = self.surname_vocab
one_hot = np.zeros(len(vocab), dtype=np.float32)
for token in surname:
one_hot[vocab.lookup_token(token)] = 1
return one_hot
@classmethod
def from_dataframe(cls, surname_df):
"""从数据集DataFrame实例化Vectorizer
参数:
surname_df (pandas.DataFrame): 姓氏数据集
返回:
SurnameVectorizer的实例
"""
surname_vocab = Vocabulary(unk_token="@")
nationality_vocab = Vocabulary(add_unk=False)
for index, row in surname_df.iterrows():
for letter in row.surname:
surname_vocab.add_token(letter)
nationality_vocab.add_token(row.nationality)
return cls(surname_vocab, nationality_vocab)
@classmethod
def from_serializable(cls, contents):
surname_vocab = Vocabulary.from_serializable(contents['surname_vocab'])
nationality_vocab = Vocabulary.from_serializable(contents['nationality_vocab'])
return cls(surname_vocab=surname_vocab, nationality_vocab=nationality_vocab)
def to_serializable(self):
return {'surname_vocab': self.surname_vocab.to_serializable(),
'nationality_vocab': self.nationality_vocab.to_serializable()}
self.train_df = self.surname_df[self.surname_df.split=='train']
self.train_size = len(self.train_df)
self.val_df = self.surname_df[self.surname_df.split=='val']
self.validation_size = len(self.val_df)
self.test_df = self.surname_df[self.surname_df.split=='test']
self.test_size = len(self.test_df)
self._lookup_dict = {'train': (self.train_df, self.train_size),
'val': (self.val_df, self.validation_size),
'test': (self.test_df, self.test_size)}
self.set_split('train')
# Class weights
class_counts = surname_df.nationality.value_counts().to_dict()
def sort_key(item):
return self._vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_token(item[0])
sorted_counts = sorted(class_counts.items(), key=sort_key)
frequencies = [count for _, count in sorted_counts]
self.class_weights = 1.0 / torch.tensor(frequencies, dtype=torch.float32)
@classmethod
def load_dataset_and_make_vectorizer(cls, surname_csv):
"""Load dataset and make a new vectorizer from scratch
Args:
surname_csv (str): location of the dataset
Returns:
an instance of SurnameDataset
"""
surname_df = pd.read_csv(surname_csv)
train_surname_df = surname_df[surname_df.split=='train']
return cls(surname_df, SurnameVectorizer.from_dataframe(train_surname_df))
@classmethod
def load_dataset_and_load_vectorizer(cls, surname_csv, vectorizer_filepath):
"""Load dataset and the corresponding vectorizer.
Used in the case in the vectorizer has been cached for re-use
Args:
surname_csv (str): location of the dataset
vectorizer_filepath (str): location of the saved vectorizer
Returns:
an instance of SurnameDataset
"""
surname_df = pd.read_csv(surname_csv)
vectorizer = cls.load_vectorizer_only(vectorizer_filepath)
return cls(surname_df, vectorizer)
@staticmethod
def load_vectorizer_only(vectorizer_filepath):
"""a static method for loading the vectorizer from file
Args:
vectorizer_filepath (str): the location of the serialized vectorizer
Returns:
an instance of SurnameVectorizer
"""
with open(vectorizer_filepath) as fp:
return SurnameVectorizer.from_serializable(json.load(fp))
def save_vectorizer(self, vectorizer_filepath):
"""saves the vectorizer to disk using json
Args:
vectorizer_filepath (str): the location to save the vectorizer
"""
with open(vectorizer_filepath, "w") as fp:
json.dump(self._vectorizer.to_serializable(), fp)
def get_vectorizer(self):
""" returns the vectorizer """
return self._vectorizer
def set_split(self, split="train"):
""" selects the splits in the dataset using a column in the dataframe """
self._target_split = split
self._target_df, self._target_size = self._lookup_dict[split]
def __len__(self):
return self._target_size
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""the primary entry point method for PyTorch datasets
Args:
index (int): the index to the data point
Returns:
a dictionary holding the data point's:
features (x_surname)
label (y_nationality)
"""
row = self._target_df.iloc[index]
surname_vector = \
self._vectorizer.vectorize(row.surname)
nationality_index = \
self._vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_token(row.nationality)
return {'x_surname': surname_vector,
'y_nationality': nationality_index}
def get_num_batches(self, batch_size):
"""Given a batch size, return the number of batches in the dataset
Args:
batch_size (int)
Returns:
number of batches in the dataset
"""
return len(self) // batch_size
def generate_batches(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=True,
drop_last=True, device="cpu"):
"""
A generator function which wraps the PyTorch DataLoader. It will
ensure each tensor is on the write device location.
"""
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=dataset, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=shuffle, drop_last=drop_last)
for data_dict in dataloader:
out_data_dict = {}
for name, tensor in data_dict.items():
out_data_dict[name] = data_dict[name].to(device)
yield out_data_dict模型
class SurnameClassifier(nn.Module):
""" A 2-layer Multilayer Perceptron for classifying surnames """
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim):
"""
Args:
input_dim (int): the size of the input vectors
hidden_dim (int): the output size of the first Linear layer
output_dim (int): the output size of the second Linear layer
"""
super(SurnameClassifier, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x_in, apply_softmax=False):
"""The forward pass of the classifier
Args:
x_in (torch.Tensor): an input data tensor.
x_in.shape should be (batch, input_dim)
apply_softmax (bool): a flag for the softmax activation
should be false if used with the Cross Entropy losses
Returns:
the resulting tensor. tensor.shape should be (batch, output_dim)
"""
intermediate_vector = F.relu(self.fc1(x_in))
prediction_vector = self.fc2(intermediate_vector)
if apply_softmax:
prediction_vector = F.softmax(prediction_vector, dim=1)
return prediction_vector训练例程
def make_train_state(args):
return {'stop_early': False,
'early_stopping_step': 0,
'early_stopping_best_val': 1e8,
'learning_rate': args.learning_rate,
'epoch_index': 0,
'train_loss': [],
'train_acc': [],
'val_loss': [],
'val_acc': [],
'test_loss': -1,
'test_acc': -1,
'model_filename': args.model_state_file}
def update_train_state(args, model, train_state):
"""Handle the training state updates.
Components:
- Early Stopping: Prevent overfitting.
- Model Checkpoint: Model is saved if the model is better
:param args: main arguments
:param model: model to train
:param train_state: a dictionary representing the training state values
:returns:
a new train_state
"""
# Save one model at least
if train_state['epoch_index'] == 0:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), train_state['model_filename'])
train_state['stop_early'] = False
# Save model if performance improved
elif train_state['epoch_index'] >= 1:
loss_tm1, loss_t = train_state['val_loss'][-2:]
# If loss worsened
if loss_t >= train_state['early_stopping_best_val']:
# Update step
train_state['early_stopping_step'] += 1
# Loss decreased
else:
# Save the best model
if loss_t < train_state['early_stopping_best_val']:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), train_state['model_filename'])
# Reset early stopping step
train_state['early_stopping_step'] = 0
# Stop early ?
train_state['stop_early'] = \
train_state['early_stopping_step'] >= args.early_stopping_criteria
return train_state
def compute_accuracy(y_pred, y_target):
_, y_pred_indices = y_pred.max(dim=1)
n_correct = torch.eq(y_pred_indices, y_target).sum().item()
return n_correct / len(y_pred_indices) * 100
def set_seed_everywhere(seed, cuda):
np.random.seed(seed)
torch.manual_seed(seed)
if cuda:
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
def handle_dirs(dirpath):
if not os.path.exists(dirpath):
os.makedirs(dirpath)
args = Namespace(
# Data and path information
surname_csv="data/surnames/surnames_with_splits.csv",
vectorizer_file="vectorizer.json",
model_state_file="model.pth",
save_dir="model_storage/ch4/surname_mlp",
# Model hyper parameters
hidden_dim=300,
# Training hyper parameters
seed=1337,
num_epochs=100,
early_stopping_criteria=5,
learning_rate=0.001,
batch_size=64,
# Runtime options
cuda=False,
reload_from_files=False,
expand_filepaths_to_save_dir=True,
)
if args.expand_filepaths_to_save_dir:
args.vectorizer_file = os.path.join(args.save_dir,
args.vectorizer_file)
args.model_state_file = os.path.join(args.save_dir,
args.model_state_file)
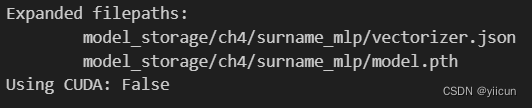
print("Expanded filepaths: ")
print("\t{}".format(args.vectorizer_file))
print("\t{}".format(args.model_state_file))
# Check CUDA
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
args.cuda = False
args.device = torch.device("cuda" if args.cuda else "cpu")
print("Using CUDA: {}".format(args.cuda))
# Set seed for reproducibility
set_seed_everywhere(args.seed, args.cuda)
# handle dirs
handle_dirs(args.save_dir)输出
训练
if args.reload_from_files:
# training from a checkpoint
print("Reloading!")
dataset = SurnameDataset.load_dataset_and_load_vectorizer(args.surname_csv,
args.vectorizer_file)
else:
# create dataset and vectorizer
print("Creating fresh!")
dataset = SurnameDataset.load_dataset_and_make_vectorizer(args.surname_csv)
dataset.save_vectorizer(args.vectorizer_file)
vectorizer = dataset.get_vectorizer()
classifier = SurnameClassifier(input_dim=len(vectorizer.surname_vocab),
hidden_dim=args.hidden_dim,
output_dim=len(vectorizer.nationality_vocab))
classifier = classifier.to(args.device)
dataset.class_weights = dataset.class_weights.to(args.device)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(dataset.class_weights)
optimizer = optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(), lr=args.learning_rate)
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer=optimizer,
mode='min', factor=0.5,
patience=1)
train_state = make_train_state(args)
epoch_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='training routine',
total=args.num_epochs,
position=0)
dataset.set_split('train')
train_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='split=train',
total=dataset.get_num_batches(args.batch_size),
position=1,
leave=True)
dataset.set_split('val')
val_bar = tqdm_notebook(desc='split=val',
total=dataset.get_num_batches(args.batch_size),
position=1,
leave=True)
try:
for epoch_index in range(args.num_epochs):
train_state['epoch_index'] = epoch_index
# Iterate over training dataset
# setup: batch generator, set loss and acc to 0, set train mode on
dataset.set_split('train')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.0
running_acc = 0.0
classifier.train()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# the training routine is these 5 steps:
# --------------------------------------
# step 1. zero the gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# step 2. compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# step 3. compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# step 4. use loss to produce gradients
loss.backward()
# step 5. use optimizer to take gradient step
optimizer.step()
# -----------------------------------------
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
# update bar
train_bar.set_postfix(loss=running_loss, acc=running_acc,
epoch=epoch_index)
train_bar.update()
train_state['train_loss'].append(running_loss)
train_state['train_acc'].append(running_acc)
# Iterate over val dataset
# setup: batch generator, set loss and acc to 0; set eval mode on
dataset.set_split('val')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.
running_acc = 0.
classifier.eval()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# step 3. compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.to("cpu").item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
val_bar.set_postfix(loss=running_loss, acc=running_acc,
epoch=epoch_index)
val_bar.update()
train_state['val_loss'].append(running_loss)
train_state['val_acc'].append(running_acc)
train_state = update_train_state(args=args, model=classifier,
train_state=train_state)
scheduler.step(train_state['val_loss'][-1])
if train_state['stop_early']:
break
train_bar.n = 0
val_bar.n = 0
epoch_bar.update()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Exiting loop")
模型评估
classifier.load_state_dict(torch.load(train_state['model_filename']))
classifier = classifier.to(args.device)
dataset.class_weights = dataset.class_weights.to(args.device)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(dataset.class_weights)
dataset.set_split('test')
batch_generator = generate_batches(dataset,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
device=args.device)
running_loss = 0.
running_acc = 0.
classifier.eval()
for batch_index, batch_dict in enumerate(batch_generator):
# compute the output
y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
# compute the loss
loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
loss_t = loss.item()
running_loss += (loss_t - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
# compute the accuracy
acc_t = compute_accuracy(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
running_acc += (acc_t - running_acc) / (batch_index + 1)
train_state['test_loss'] = running_loss
train_state['test_acc'] = running_acc
print("Test loss: {};".format(train_state['test_loss']))
print("Test Accuracy: {}".format(train_state['test_acc']))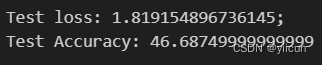
模型推理
def predict_nationality(surname, classifier, vectorizer):
# 使用向量化器将姓氏转换为向量化格式
vectorized_surname = vectorizer.vectorize(surname)
# 将向量化的姓氏转换为 Torch 张量并为分类器输入调整形状
vectorized_surname = torch.tensor(vectorized_surname).view(1, -1)
# 将向量化的姓氏传递给分类器,并应用 softmax 函数以获得概率
result = classifier(vectorized_surname, apply_softmax=True)
# 找到具有最高概率的国籍
probability_values, indices = result.max(dim=1)
index = indices.item()
# 使用索引查找预测的国籍
predicted_nationality = vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_index(index)
probability_value = probability_values.item()
# 以字典形式返回预测的国籍和概率值
return {'nationality': predicted_nationality, 'probability': probability_value}
new_surname = input("Enter a surname to classify: ")
classifier = classifier.to("cpu")
prediction = predict_nationality(new_surname, classifier, vectorizer)
print("{} -> {} (p={:0.2f})".format(new_surname,
prediction['nationality'],
prediction['probability']))运行结果
![]()
Top-K推理
vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_index(8)
def predict_topk_nationality(name, classifier, vectorizer, k=5):
vectorized_name = vectorizer.vectorize(name)
vectorized_name = torch.tensor(vectorized_name).view(1, -1)
prediction_vector = classifier(vectorized_name, apply_softmax=True)
probability_values, indices = torch.topk(prediction_vector, k=k)
# returned size is 1,k
probability_values = probability_values.detach().numpy()[0]
indices = indices.detach().numpy()[0]
results = []
for prob_value, index in zip(probability_values, indices):
nationality = vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_index(index)
results.append({'nationality': nationality,
'probability': prob_value})
return results
new_surname = input("Enter a surname to classify: ")
classifier = classifier.to("cpu")
k = int(input("How many of the top predictions to see? "))
if k > len(vectorizer.nationality_vocab):
print("Sorry! That's more than the # of nationalities we have.. defaulting you to max size :)")
k = len(vectorizer.nationality_vocab)
predictions = predict_topk_nationality(new_surname, classifier, vectorizer, k=k)
print("Top {} predictions:".format(k))
print("===================")
for prediction in predictions:
print("{} -> {} (p={:0.2f})".format(new_surname,
prediction['nationality'],
prediction['probability']))输入一个姓氏进行测试
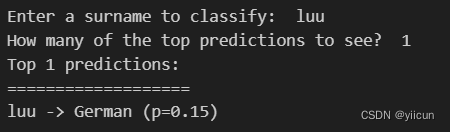
可见效果良好





















 1279
1279

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








