一、Xmind整理: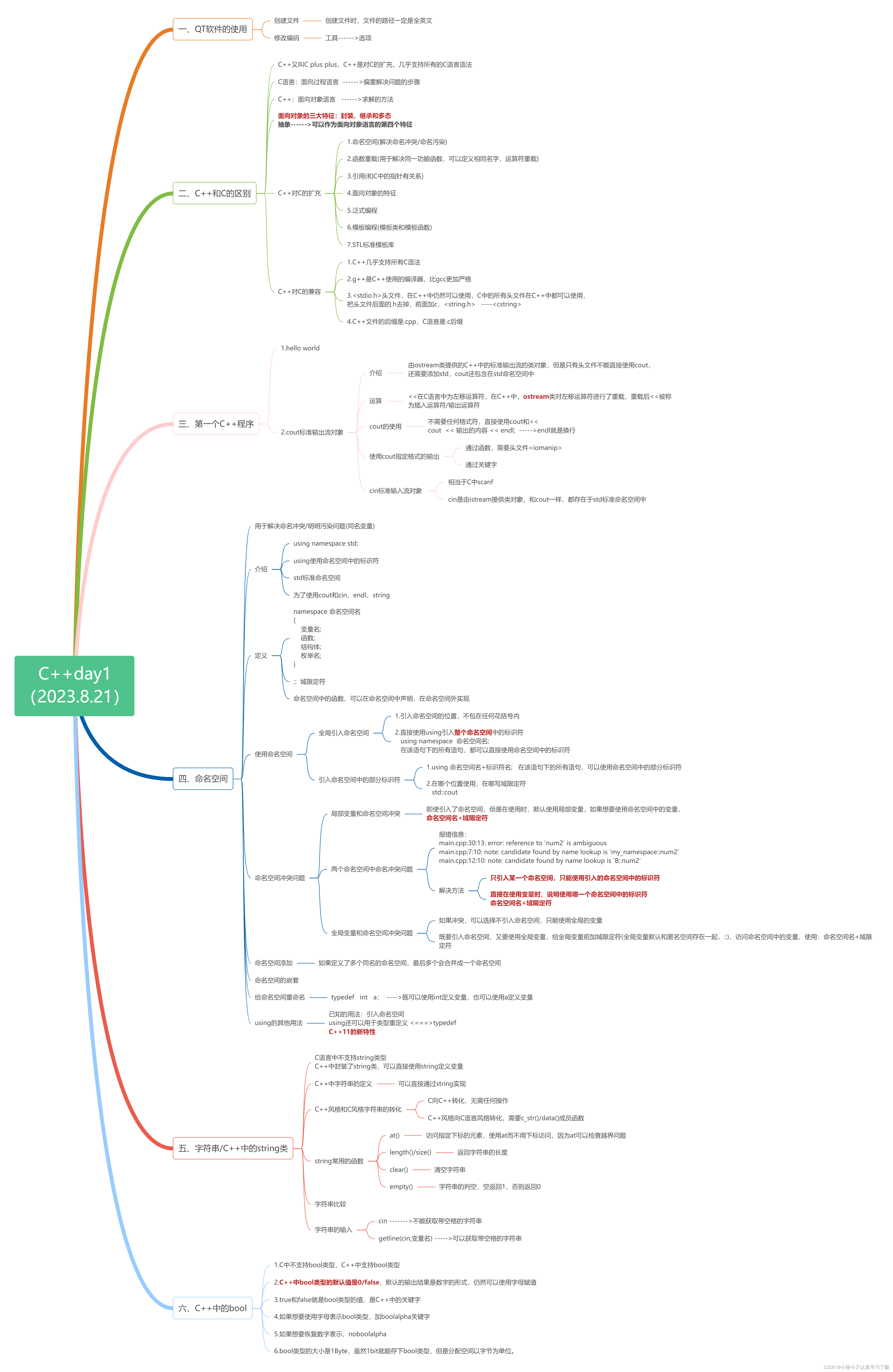
二、上课笔记整理:
1.第一个c++程序:hello world
#include <iostream>
//#:预处理标识符
//<iostream>:输入输出流类所在的头文件
//istream:输入流类
//ostream:输出流类
using namespace std; //std:标准命名空间
//using使用命名空间
//namespace就是命名空间的关键字
//std是标准命名空间名
int main()
{
cout << "第一个C++程序" << endl;
//cout:ostream类的一个类对象,输出,但是不需要格式符
// <<:左移运算符的重载,重载为插入运算符(输出运算符)
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
2.cout的使用
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 16;
cout << a << endl; //16
//----------通过关键字控制格式-----------
cout << hex << a << endl; //10 hex十六进制输出
cout << a << endl; //10 ---->因为上一行的cout已经指定了格式,如果想结束掉上述的格式,重新指定格式
cout << dec << a << endl; //dec表示十进制的输出
cout << oct << a << endl; //oct表示八进制输出
cout << "-----------------------------" << endl;
// ---------通过函数控制格式-------------
cout << setbase(16) << a << endl;
cout << setbase(8) << a << endl;
cout << a << endl; //20,使用函数仍然改变了cout的输出格式
cout << setbase(10) << a << endl;
cout << "指定宽度的输出<==>%nd" << endl;
cout << setw(4) << left << a ; //功能和%-4d一样,左对齐使用left,如果不加left默认是右对齐
cout << "小数的指定宽度输出 " << endl;
cout << setprecision(4) << 3.1456 << endl;
//指定的是包含小数点的位置,3.146
return 0;
}
3.输出斐波那契的前10项。 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 ····
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int Fbi(int n)
{
if(n==1||n==2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return Fbi(n-1)+Fbi(n-2);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cout << "请输入一个数" << endl;
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
Fbi(i);
cout << Fbi(i) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
4. cin标准输入流对象
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
//scanf("%d",&a); //需要控制格式
cin >> a; //cin加上右移运算符重载,再加上变量名,使用cin输入不需要加变量的地址
cout << a << endl;
char c;
cin >> c; //cin可以实现任意类型的输入
cout << "从终端获取的字符c=" << c << endl;
return 0;
}
5.终端输入一个字符,判断该字符的类型,字母(大写/小写)、数字字符,其他字符。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a;
//scanf("%d",&a); //需要控制格式
cin >> a; //cin加上右移运算符重载,再加上变量名,使用cin输入不需要加变量的地址
if(a>='0'&&a<='9')
{
cout << "a是一个数字" << endl;
}
else if(a>='A'&&a<='Z')
{
cout << "a是一个大写字母" << endl;
}
else if(a>='a'&&a<='z')
{
cout << "a是一个小写字母" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
6.局部变量和命名空间冲突
#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
namespace my_namespace { //定义了一个命名空间
int a=2000;
int num2;
void fun(); //命名空间中写函数的声明
}
void my_namespace::fun() //定义了一个命名空间中的函数
{
std::cout << "test" << std::endl;
}
using namespace my_namespace; //引入命名空间中的所有标识符
using my_namespace::num2; //引入命名空间中的部分标识符
int main()
{
using std::cout; //引入std中的cout标识符
using std::endl; //引入std中的endl标识符
int a = 90;
cout << "局部变量a=" << a << endl;
cout << my_namespace::a << endl;
fun();
return 0;
}
7.全局变量和命名空间冲突问题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int a = 3000;
namespace my_namespace { //定义了一个命名空间
int a=2000;
int num2;
void fun(); //命名空间中写函数的声明
}
namespace B {
int num2;
}
void my_namespace::fun() //定义了一个命名空间中的函数
{
std::cout << "test" << std::endl;
}
using namespace my_namespace; //引入命名空间中的所有标识符
using namespace B;
int main()
{
my_namespace::num2=900; //在使用变量时,使用域限定符
cout << B::num2 << endl;
cout << my_namespace::a << endl; //通过域限定符和命名空间名访问指定变量a
cout << ::a << endl; //访问全局变量a
return 0;
}
【5】命名空间添加
如果定义了多个同名的命名空间,最后多个会合并成一个命名空间
namespace B {
int num2;
int a = 10;
}
namespace B { //并没有定义新的命名空间B,改行的B会和前面B合并成一个命名空间
int b;
}
8.命名空间的嵌套
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace A { //定义了一个命名空间A
int a=0;
namespace B { //嵌套一个命名空间B
int a=100;
char c='a';
}
}
using namespace A;
using namespace A::B; //全局引入A中的命名空间B
int main()
{
//cout << A::a << endl; //0
//cout << A::B::a << endl; //100,嵌套的命名空间,访问里面空间标识符时,需要逐级访问
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
9.给命名空间重命名
namespace 新名字 = 旧名字;
namespace NEW = A; //把命名空间A重命名为NEW
新名字和旧名字都可以继续使用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace A { //定义了一个命名空间A
int a=0;
namespace B { //嵌套一个命名空间B
int a=100;
char c='a';
}
}
namespace NEW = A; //给命名空间A重命名为NEW
using namespace NEW;
//using namespace A::B; //全局引入A中的命名空间B
int main()
{
//cout << A::a << endl; //0
//cout << A::B::a << endl; //100,嵌套的命名空间,访问里面空间标识符时,需要逐级访问
cout << NEW::B::c << endl;
return 0;
}
10.using的其他用法
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
typedef int a;
a num1 =100;
cout << num1 << endl;
using INT = int; //把基本数据类型int重定义为INT,后面可以直接使用INT定义变量
INT num2 = 90;
cout << sizeof(INT) << endl;
return 0;
}
11.C++中字符串的定义
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[]="hello"; //C语言风格的字符串,C++中仍然支持,结尾有'\0'
cout << sizeof(str) << endl;
cout << strlen(str) << endl; //可以手动导入<cstring>头文件,使用strlen函数
//通过string类实现变量的定义
string str1 = "hello"; //定义了一个string类型的饿字符串str1并初始化hello
string str2 = str;
cout << str2 << endl; //C语言风格的字符串会自动转换成C++风格的字符串并且可以直接使用
str2 = "hi"; //给str2字符串赋值
//----------使用单个的字符给字符串赋值-----------
string str3(5,'a'); //定义了一个str3字符串,使用5个a初始化
cout << str3 << endl;
string str4("world"); //定义了一个字符串str4,使用world初始化
cout << str4 << endl;
//----------多个字符串之间的赋值------------
str3 = str4;
cout << "s3=" << str3 << endl;
cout << "s4=" << str4 << endl;
}
12.C++风格和C风格字符串的转化
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[]="hello";
string str1 = str; //C风格可以直接转化为C++风格
//cout << strlen(str1) << endl; //C++风格的字符串向C风格转化,需要特定的操作
cout << strlen(str1.data()) << endl; //使用过data函数后,str1可以被strlen计算
//cout << strcat(str1.c_str(),"world") << endl;
//因为str1.c_str()返回的时hello的字符数组形式,是一个const char*
char str3[100]="world";
strcat(str3,str1.c_str());
cout << str3 << endl;
return 0;
}
13.string常用的函数 empty()
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[]="hello";
string str1 = str; //C风格可以直接转化为C++风格
// cout << str1.at(7) << endl;
cout << str1.length() << endl;
cout << str1.size() << endl;
str1.clear();
cout << str1 << endl;
cout << str1.size() << endl;
cout << str1.empty() << endl;
return 0;
}
14.字符串比较
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[]="hello";
string str1 = str; //C风格可以直接转化为C++风格
string str2 = "hi";
if(str1<str2) //字符串在C++中可以直接参与比较,结果0/1
{
cout << "str1<str2" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
15.字符串的输入
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[]="hello";
string str1 = str; //C风格可以直接转化为C++风格
string str2;
//cin >> str2; //不能实现字符串带空格的输入
getline(cin,str2);
cout << str2 << endl;
return 0;
}
16.终端输入一个字符串,以'\n'作为标志停止,判断字母和数字的个数,空格的个数。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
getline(cin,str);
int len = str.size(); //作为循环条件
int num1=0,num2=0,num3=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(str.at(i)>='a'&&str.at(i)<='z'||str.at(i)>='A'&&str.at(i)<='Z')
{
num1++;
}
else if(str.at(i)>='0'&&str.at(i)<='9')
{
num2++;
}
else if(str.at(i)==' ')
{
num3++;
}
}
cout << num1 << endl;
cout << num2 << endl;
cout << num3 << endl;
return 0;
}
17.C++中的bool
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
bool a=true;
cout << a << endl; //默认是数字表示
cout << boolalpha << a << endl; //加上boolalpha显示字母表示
bool b=0;
cout << noboolalpha << b << endl; //加上noboolalpha回到数字表示
cout << sizeof(b) << endl;
return 0;
}























 306
306

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








