概述
目前已经学习了特征点和地图点,接下来我们进行帧和关键帧的学习,这是连接特征点和地图点的桥梁。其中帧只用于当前Track过程的图像构造和位姿估计,而关键帧会对后续的建图和回环检测产生影响。
一个帧应该包括:
相机相关信息,特征点提取,对双目和RGBD相机的特征点的预处理(双目视差公式,双目特征点处理和双目图像特征点匹配),RGBD图像特征点的处理(根据深度信息构造右目图像),畸变矫正,特征点分配,构造函数。
程序解析
frame类的介绍
这里介绍了主要就是三种构造函数,后面三种分别是双目,RGB-D,和单目相机的构造函数。
Frame();
// Copy constructor.
Frame(const Frame &frame);
// Constructor for stereo cameras.
Frame(const cv::Mat &imLeft, const cv::Mat &imRight, const double &timeStamp, ORBextractor* extractorLeft, ORBextractor* extractorRight, ORBVocabulary* voc, cv::Mat &K, cv::Mat &distCoef, const float &bf, const float &thDepth);
// Constructor for RGB-D cameras.
Frame(const cv::Mat &imGray, const cv::Mat &imDepth, const double &timeStamp, ORBextractor* extractor,ORBVocabulary* voc, cv::Mat &K, cv::Mat &distCoef, const float &bf, const float &thDepth);
// Constructor for Monocular cameras.
Frame(const cv::Mat &imGray, const double &timeStamp, ORBextractor* extractor,ORBVocabulary* voc, cv::Mat &K, cv::Mat &distCoef, const float &bf, const float &thDepth);
剩下的参数以及相关含义的中文我在代码里注释了。然后这里有一个畸变与矫正,在现实世界中相机镜头存在一个类似“鱼眼看世界”的问题,就是通过相机成的像,可能会产生径向畸变或者切向畸变,而我们的slam系统需要的是一个精确的计算,如果用这些畸变的帧来进行位姿估计等操作,会不准确,所以这里我们需要对相机拍的帧进行矫正。其中单目相机必须矫正,RGB-D相机可能矫正,双目相机不需要矫正。矫正相关的函数和公式后续我会介绍。另外关于相机的相关参数,作者都设置为static类型,表示所有的帧都共享一组相机参数。
// Extract ORB on the image. 0 for left image and 1 for right image.
//ORB特征提取
void ExtractORB(int flag, const cv::Mat &im);
// Compute Bag of Words representation.
//词袋表示计算
void ComputeBoW();
// Set the camera pose.
//设置相机位姿
void SetPose(cv::Mat Tcw);
// Computes rotation, translation and camera center matrices from the camera pose.
//更新位姿矩阵
void UpdatePoseMatrices();
// Returns the camera center.
//获取相机中心
inline cv::Mat GetCameraCenter(){
return mOw.clone();
}
// Returns inverse of rotation
//获取旋转逆矩阵
inline cv::Mat GetRotationInverse(){
return mRwc.clone();
}
// Check if a MapPoint is in the frustum of the camera
// and fill variables of the MapPoint to be used by the tracking
//视锥体检查
bool isInFrustum(MapPoint* pMP, float viewingCosLimit);
// Compute the cell of a keypoint (return false if outside the grid)
//计算关键点所属的网格坐标
bool PosInGrid(const cv::KeyPoint &kp, int &posX, int &posY);
//区域特征查询
vector<size_t> GetFeaturesInArea(const float &x, const float &y, const float &r, const int minLevel=-1, const int maxLevel=-1) const;
// Search a match for each keypoint in the left image to a keypoint in the right image.
// If there is a match, depth is computed and the right coordinate associated to the left keypoint is stored.
//双目深度计算
void ComputeStereoMatches();
// Associate a "right" coordinate to a keypoint if there is valid depth in the depthmap.
//RGB深度计算
void ComputeStereoFromRGBD(const cv::Mat &imDepth);
// Backprojects a keypoint (if stereo/depth info available) into 3D world coordinates.
//反投影到3d
cv::Mat UnprojectStereo(const int &i);
public:
// Vocabulary used for relocalization.
//ORB词典(回环检测用)
ORBVocabulary* mpORBvocabulary;
// Feature extractor. The right is used only in the stereo case.
//特征提取器
ORBextractor* mpORBextractorLeft, *mpORBextractorRight;
// Frame timestamp.
//时间戳
double mTimeStamp;
// Calibration matrix and OpenCV distortion parameters.
//相机内参矩阵
cv::Mat mK;
static float fx;
static float fy;
static float cx;
static float cy;
static float invfx;
static float invfy;
//畸变系数
cv::Mat mDistCoef;
// Stereo baseline multiplied by fx.
//基线×焦距(双目)
float mbf;
// Stereo baseline in meters.
//基线长度
float mb;
// Threshold close/far points. Close points are inserted from 1 view.
// Far points are inserted as in the monocular case from 2 views.
//远近点阈值
float mThDepth;
// Number of KeyPoints.
//特征点数量
int N;
// Vector of keypoints (original for visualization) and undistorted (actually used by the system).
// In the stereo case, mvKeysUn is redundant as images must be rectified.
// In the RGB-D case, RGB images can be distorted.
//原始关键点
std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> mvKeys, mvKeysRight;
//去畸变关键点
std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> mvKeysUn;
// Corresponding stereo coordinate and depth for each keypoint.
// "Monocular" keypoints have a negative value.
//右目深度坐标(右目只需要记录纵坐标即可,因为这里认为横坐标跟左目的一样)
std::vector<float> mvuRight;
//深度值
std::vector<float> mvDepth;
// Bag of Words Vector structures.
//词袋向量,特征向量
DBoW2::BowVector mBowVec;
DBoW2::FeatureVector mFeatVec;
// ORB descriptor, each row associated to a keypoint.
//ORB描述子(一行256个比特位,表示一个关键点)
cv::Mat mDescriptors, mDescriptorsRight;
// MapPoints associated to keypoints, NULL pointer if no association.
//与关键点相关的地图点。
std::vector<MapPoint*> mvpMapPoints;
// Flag to identify outlier associations.
//外点标记
std::vector<bool> mvbOutlier;
// Keypoints are assigned to cells in a grid to reduce matching complexity when projecting MapPoints.
static float mfGridElementWidthInv;//网格宽度的倒数
static float mfGridElementHeightInv;//网格高度的倒数
//特征点网格
std::vector<std::size_t> mGrid[FRAME_GRID_COLS][FRAME_GRID_ROWS];
// Camera pose.
//相机位姿(世界到相机)
cv::Mat mTcw;
// Current and Next Frame id.
//当前和下一个帧的id
static long unsigned int nNextId;
long unsigned int mnId;
// Reference Keyframe.
//参考关键帧
KeyFrame* mpReferenceKF;
// Scale pyramid info.
//比例金字塔信息,就我们之前在关键点提取中得到的图像金字塔的信息
int mnScaleLevels;
float mfScaleFactor;
float mfLogScaleFactor;
vector<float> mvScaleFactors;
vector<float> mvInvScaleFactors;
vector<float> mvLevelSigma2;
vector<float> mvInvLevelSigma2;
// Undistorted Image Bounds (computed once).
//图像边界
static float mnMinX;
static float mnMaxX;
static float mnMinY;
static float mnMaxY;
//初始化标志
static bool mbInitialComputations;
private:
// Undistort keypoints given OpenCV distortion parameters.
// Only for the RGB-D case. Stereo must be already rectified!
// (called in the constructor).
//关键点去畸变
void UndistortKeyPoints();
// Computes image bounds for the undistorted image (called in the constructor).
//计算图像边界
void ComputeImageBounds(const cv::Mat &imLeft);
// Assign keypoints to the grid for speed up feature matching (called in the constructor).
//特征点分配到网路
void AssignFeaturesToGrid();
// Rotation, translation and camera center
cv::Mat mRcw;//旋转矩阵
cv::Mat mtcw;//平移矩阵
cv::Mat mRwc;//旋转逆矩阵
cv::Mat mOw; //==mtwc,相机中心位置
};
构造函数介绍
先看这个拷贝构造函数,这个构造函数主要用于,保留当前帧由于后续处理,关键帧创建时的数据复制,重定位中保存参考帧的状态。
参数复制部分:
Frame::Frame(const Frame &frame)
:mpORBvocabulary(frame.mpORBvocabulary),//共享词汇表帧指针
mpORBextractorLeft(frame.mpORBextractorLeft), //共享特征提取器指针
mpORBextractorRight(frame.mpORBextractorRight),
mTimeStamp(frame.mTimeStamp),
mK(frame.mK.clone()), //相机内参矩阵 .clone时深拷贝的意思
mDistCoef(frame.mDistCoef.clone()),//畸变系数拷贝
mbf(frame.mbf),
mb(frame.mb),
mThDepth(frame.mThDepth),
N(frame.N),
mvKeys(frame.mvKeys),//关键点向量拷贝
mvKeysRight(frame.mvKeysRight),
mvKeysUn(frame.mvKeysUn),
mvuRight(frame.mvuRight),//右目坐标向量
mvDepth(frame.mvDepth), //深度向量
mBowVec(frame.mBowVec), //词袋向量拷贝
mFeatVec(frame.mFeatVec),//特征向量拷贝
描述子和地图点参数拷贝
mDescriptors(frame.mDescriptors.clone()), //左目描述子
mDescriptorsRight(frame.mDescriptorsRight.clone()),//右目描述子
mvpMapPoints(frame.mvpMapPoints), //地图点指针向量,跟之前地图点提到的是一个双向关联关系
mvbOutlier(frame.mvbOutlier), //外点标记向量
mnId(frame.mnId),//帧的id拷贝
mpReferenceKF(frame.mpReferenceKF), //参考关键帧
mnScaleLevels(frame.mnScaleLevels),//金字塔层数
mfScaleFactor(frame.mfScaleFactor),//金字塔尺度因子
mfLogScaleFactor(frame.mfLogScaleFactor),//尺度因子对数,下面基本都是金字塔相关参数
mvScaleFactors(frame.mvScaleFactors),
mvInvScaleFactors(frame.mvInvScaleFactors),
mvLevelSigma2(frame.mvLevelSigma2),
mvInvLevelSigma2(frame.mvInvLevelSigma2)
构造函数体,网格和位姿处理,第一部分for是网格结构复制,第二个if是位姿复制,先判断是否位空矩阵,在调用SetPose复制位姿并更新相关的位姿分量(mRcw, mtcw, mRwc, mOw)。
for(int i=0;i<FRAME_GRID_COLS;i++)
for(int j=0; j<FRAME_GRID_ROWS; j++)
mGrid[i][j]=frame.mGrid[i][j];
if(!frame.mTcw.empty())
SetPose(frame.mTcw);
再看双目相机的构造函数
看函数定义部分:
imLeft,imRight左右目相机图像
timeStamp时间戳
extractorLeft,extractorRight 左右目特征提取器
voc ORB词典用于回环检测
K,distCoef 相机内参矩阵,畸变系数
bf 基线×焦距后面会介绍
thDepth远近点深度阈值,这个就是用来判断你用双目得到的点的深度是否符合要求,要是超过这个阈值我们就认为你生成这个点不太准确。
Frame::Frame(const cv::Mat &imLeft, const cv::Mat &imRight, const double &timeStamp,
ORBextractor* extractorLeft, ORBextractor* extractorRight, ORBVocabulary* voc,
cv::Mat &K, cv::Mat &distCoef, const float &bf, const float &thDepth)
帧id和尺度信息,包括当前帧id和金字塔的相关层级信息。
// Frame ID
mnId = nNextId++;
// Scale Level Info
mnScaleLevels = mpORBextractorLeft->GetLevels();
mfScaleFactor = mpORBextractorLeft->GetScaleFactor();
mfLogScaleFactor = log(mfScaleFactor);
mvScaleFactors = mpORBextractorLeft->GetScaleFactors();
mvInvScaleFactors = mpORBextractorLeft->GetInverseScaleFactors();
mvLevelSigma2 = mpORBextractorLeft->GetScaleSigmaSquares();
mvInvLevelSigma2 = mpORBextractorLeft->GetInverseScaleSigmaSquares();
并行ORB关键点提取,这里创建左右目相机的关键点提取线程,并行提取。
// ORB extraction
thread threadLeft(&Frame::ExtractORB, this, 0, imLeft);
thread threadRight(&Frame::ExtractORB, this, 1, imRight);
threadLeft.join();
threadRight.join();
特征点处理和立体匹配,UndistortKeyPoints()这个适用于关键点去畸变,ComputeStereoMatches()这个是双目立体匹配函数后续会着重介绍。
N = mvKeys.size();
if(mvKeys.empty())
return;
UndistortKeyPoints();
ComputeStereoMatches();
地图点和外点的初始化
mvpMapPoints = vector<MapPoint*>(N,static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL));
mvbOutlier = vector<bool>(N,false);
系统的初始化计算,仅仅会在第一帧双目帧是计算一次,包括,图像边界,相机参数(fx焦距x,fy焦距y,cx主点x,cy主点y)
// This is done only for the first Frame (or after a change in the calibration)
if(mbInitialComputations)
{
ComputeImageBounds(imLeft);
mfGridElementWidthInv=static_cast<float>(FRAME_GRID_COLS)/(mnMaxX-mnMinX);
mfGridElementHeightInv=static_cast<float>(FRAME_GRID_ROWS)/(mnMaxY-mnMinY);
fx = K.at<float>(0,0);
fy = K.at<float>(1,1);
cx = K.at<float>(0,2);
cy = K.at<float>(1,2);
invfx = 1.0f/fx;
invfy = 1.0f/fy;
mbInitialComputations=false;
}
计算实际基线距离后续有用会介绍,和将特征点分配到网格,分配到网格主要是为了加速计算。
mb = mbf/fx;
AssignFeaturesToGrid();
这个是RGB-D相机的构造函数,参数啥的都差不多,我们只说一下与双目的区别
Frame::Frame(const cv::Mat &imGray, const cv::Mat &imDepth, const double &timeStamp, ORBextractor* extractor,ORBVocabulary* voc, cv::Mat &K, cv::Mat &distCoef, const float &bf, const float &thDepth)
:mpORBvocabulary(voc),mpORBextractorLeft(extractor),mpORBextractorRight(static_cast<ORBextractor*>(NULL)),
mTimeStamp(timeStamp), mK(K.clone()),mDistCoef(distCoef.clone()), mbf(bf), mThDepth(thDepth)
区别就一个深度信息的获取,rgb-d只需要从深度图中获取即可,但是双目需要计算。
// RGB-D:
ComputeStereoFromRGBD(imDepth); // 从深度图获取3D信息
// 双目:
ComputeStereoMatches(); // 通过左右目匹配计算深度
单目与双目的构造函数区别主要还是在于深度图的获取,单目较为麻烦需要需要通过多帧三角化或运动恢复结构来获取深度。
接下来看一些基础函数,这两个函数是管理相机位姿的函数,SetPose是初始化相机位姿的,UpdatePoseMatrices这个是从相机位姿矩阵中提取相关参数,这里我介绍一下相关参数的作用
首先明确mTcw是一个4*4的矩阵结构如下

其中Rcw(参数mRcw)为旋转矩阵,即从世界坐标系变化到相机坐标系的旋转部分,而tcw(参数mtcw)为其平移部分,所以从世界坐标系变化为相机坐标系:Rcw*世界坐标点+tcw
mRwc为先转矩阵的逆矩阵,从相机坐标系下变化为世界坐标系的旋转部分,mOw为相机在世界坐标系的坐标点,所以从相机坐标系下变化为世界坐标系:mRwc*相机坐标点+mOw
void Frame::SetPose(cv::Mat Tcw)
{
mTcw = Tcw.clone();
UpdatePoseMatrices();
}
void Frame::UpdatePoseMatrices()
{
mRcw = mTcw.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3);
mRwc = mRcw.t();
mtcw = mTcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3);
mOw = -mRcw.t()*mtcw;
}
特征提取和处理
ORB特征提取,这里主要是一个封装函数,调用的是关键点提取的入口函数,还记得我们之前关键点提取部分的重载()这运算符吗,调用的就是这个,传入图像,图像掩码,输出关键点,以及关键点描述子。
void Frame::ExtractORB(int flag, const cv::Mat &im)
{
if(flag==0)
(*mpORBextractorLeft)(im,cv::Mat(),mvKeys,mDescriptors);
else
(*mpORBextractorRight)(im,cv::Mat(),mvKeysRight,mDescriptorsRight);
}
关键点去畸变
这里是对相机关键点去畸变,将实际的相机模型转化为理想的小孔成像模型。,第一个if是判断是否需要进行矫正,双目时不需要矫正的,你们可以去看一下双目的配置文件其中的畸变系数都是0.然后是创建一个N×2的矩阵来装你的关键点和校正后的关键点,先把关键点复制到mat中,下面就是进行矫正,最后把校正后的关键点复制回mvKeys中即可,OpenCV使用Brown-Conrady畸变模型具体数学原理我也不太懂感兴趣你们可以去了解一下。
void Frame::UndistortKeyPoints()
{
if(mDistCoef.at<float>(0)==0.0)
{
mvKeysUn=mvKeys;
return;
}
// Fill matrix with points
cv::Mat mat(N,2,CV_32F);
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
mat.at<float>(i,0)=mvKeys[i].pt.x;
mat.at<float>(i,1)=mvKeys[i].pt.y;
}
// Undistort points
mat=mat.reshape(2);
cv::undistortPoints(mat,mat,mK,mDistCoef,cv::Mat(),mK);
mat=mat.reshape(1);
// Fill undistorted keypoint vector
mvKeysUn.resize(N);
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
cv::KeyPoint kp = mvKeys[i];
kp.pt.x=mat.at<float>(i,0);
kp.pt.y=mat.at<float>(i,1);
mvKeysUn[i]=kp;
}
}
图像边界计算
分为有畸变和没有畸变,主要说畸变部分,主要思路就是取四个原始图像的角点右上右下左上左下,然后创建4×2的矩阵对这四个角点进行与上述相同的矫正,最后选取右上和右下的x坐标的最小值为,左边界,以此类推。
void Frame::ComputeImageBounds(const cv::Mat &imLeft)
{
if(mDistCoef.at<float>(0)!=0.0)
{
cv::Mat mat(4,2,CV_32F);
mat.at<float>(0,0)=0.0; mat.at<float>(0,1)=0.0;
mat.at<float>(1,0)=imLeft.cols; mat.at<float>(1,1)=0.0;
mat.at<float>(2,0)=0.0; mat.at<float>(2,1)=imLeft.rows;
mat.at<float>(3,0)=imLeft.cols; mat.at<float>(3,1)=imLeft.rows;
// Undistort corners
mat=mat.reshape(2);
cv::undistortPoints(mat,mat,mK,mDistCoef,cv::Mat(),mK);
mat=mat.reshape(1);
mnMinX = min(mat.at<float>(0,0),mat.at<float>(2,0));
mnMaxX = max(mat.at<float>(1,0),mat.at<float>(3,0));
mnMinY = min(mat.at<float>(0,1),mat.at<float>(1,1));
mnMaxY = max(mat.at<float>(2,1),mat.at<float>(3,1));
}
else
{
mnMinX = 0.0f;
mnMaxX = imLeft.cols;
mnMinY = 0.0f;
mnMaxY = imLeft.rows;
}
}
特征组织与加速结构
这两个函数完成了将关键点分配到相应网格中,先看AssignFeaturesToGrid(),先计算每个网格中应该分配多少个关键点,总关键点格式/(网格数量)*二分之一,然后为每个网格分配空间,PosInGrid函数用于计算当前关键点所属的网格坐标,计算方式关键点坐标x,y分别减去去图像左和上边界之后得到有效坐标,再分别除以网格的宽度和高度即可得到,最后判断一下合法性即可。
void Frame::AssignFeaturesToGrid()
{
int nReserve = 0.5f*N/(FRAME_GRID_COLS*FRAME_GRID_ROWS);
for(unsigned int i=0; i<FRAME_GRID_COLS;i++)
for (unsigned int j=0; j<FRAME_GRID_ROWS;j++)
mGrid[i][j].reserve(nReserve);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
const cv::KeyPoint &kp = mvKeysUn[i];
int nGridPosX, nGridPosY;
if(PosInGrid(kp,nGridPosX,nGridPosY))
mGrid[nGridPosX][nGridPosY].push_back(i);
}
}
bool Frame::PosInGrid(const cv::KeyPoint &kp, int &posX, int &posY)
{
posX = round((kp.pt.x-mnMinX)*mfGridElementWidthInv);
posY = round((kp.pt.y-mnMinY)*mfGridElementHeightInv);
//Keypoint's coordinates are undistorted, which could cause to go out of the image
if(posX<0 || posX>=FRAME_GRID_COLS || posY<0 || posY>=FRAME_GRID_ROWS)
return false;
return true;
}
再看区域特征查询函数,这个函数主要作用是指定圆形区域和金字塔层级范围内,快速找到所有符合条件的特征点索引,先依旧给结果容器分配空间,之后要分别计算X和Y方向上的网格范围,计算逻辑,(当前位置x或y +或- 给定范围r-左边界或上边界)除以网格宽度或者长度(向上或者向下取整),最后判断边界保证计算的网格范围合法,随后金字塔层级检查,最后加是在泥鳅的网格范围里找关键点,逻辑是找到一个非空的网格,取出所有的校正后的关键点,判断金字塔层级,判断是否在-r到+r的范围内,符合就加到vIndices中。
vector<size_t> Frame::GetFeaturesInArea(const float &x, const float &y, const float &r, const int minLevel, const int maxLevel) const
{
vector<size_t> vIndices;
vIndices.reserve(N);
const int nMinCellX = max(0,(int)floor((x-mnMinX-r)*mfGridElementWidthInv));
if(nMinCellX>=FRAME_GRID_COLS)
return vIndices;
const int nMaxCellX = min((int)FRAME_GRID_COLS-1,(int)ceil((x-mnMinX+r)*mfGridElementWidthInv));
if(nMaxCellX<0)
return vIndices;
const int nMinCellY = max(0,(int)floor((y-mnMinY-r)*mfGridElementHeightInv));
if(nMinCellY>=FRAME_GRID_ROWS)
return vIndices;
const int nMaxCellY = min((int)FRAME_GRID_ROWS-1,(int)ceil((y-mnMinY+r)*mfGridElementHeightInv));
if(nMaxCellY<0)
return vIndices;
const bool bCheckLevels = (minLevel>0) || (maxLevel>=0);
for(int ix = nMinCellX; ix<=nMaxCellX; ix++)
{
for(int iy = nMinCellY; iy<=nMaxCellY; iy++)
{
const vector<size_t> vCell = mGrid[ix][iy];
if(vCell.empty())
continue;
for(size_t j=0, jend=vCell.size(); j<jend; j++)
{
const cv::KeyPoint &kpUn = mvKeysUn[vCell[j]];
if(bCheckLevels)
{
if(kpUn.octave<minLevel)
continue;
if(maxLevel>=0)
if(kpUn.octave>maxLevel)
continue;
}
const float distx = kpUn.pt.x-x;
const float disty = kpUn.pt.y-y;
if(fabs(distx)<r && fabs(disty)<r)
vIndices.push_back(vCell[j]);
}
}
}
return vIndices;
}
传感器的深度计算
先看双目立体匹配函数,整个函数较为复杂主要作用是为左目特征点在右目中找到相应对应的特征点之后再计算特征点的深度。
我先介绍一下双目视差公式相关的内容,这个图片是从哔站上一个up主截的。首先明确这里假设相机标定之后左目和右目对应特征点的纵坐标是一样的,横坐标的差值就是视差,基线b(代码中用mb表示)就是两个光心之间的距离,这样的话我们找左目对应的右目特征点的范围就缩小了其实,而找到右目对应的特征点之后就可以用双目视差公式(其实就是个三角形相似)求观测距离也就是深度,这个图里的推导公式是有点问题的。我重新推一下,首先左目光心坐标=(0,f),右目光心=(b,f),所以两个特征点之间的横坐标距离=b+xr-xl=b-视差(d),所以上下两个三角形,底边比底边,高比高=(b-d)/b=(z-f)/z,最后推导得到深度z=b*f/d,=基线*焦距/视差。后续作者在找右目特征点的时候又加了一些约束,遇到再看。
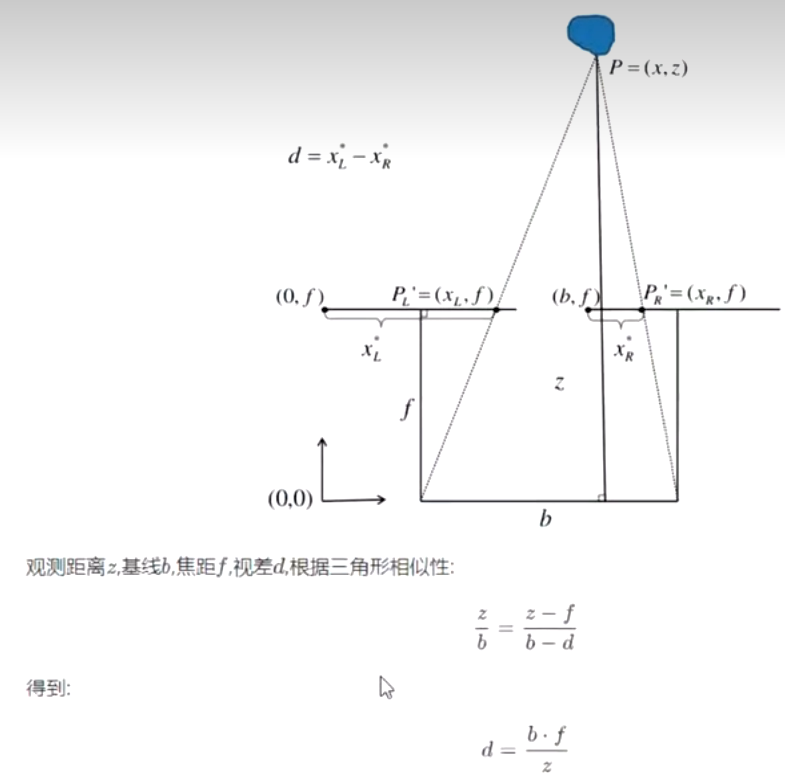
ok来看第一步初始化参数设置
mvuRight = vector<float>(N,-1.0f); // 右目对应点横坐标(-1表示无匹配)
mvDepth = vector<float>(N,-1.0f); // 深度(-1表示无匹配)
const int thOrbDist = (ORBmatcher::TH_HIGH+ORBmatcher::TH_LOW)/2; // ORB描述子匹配阈值(中等)
const int nRows = mpORBextractorLeft->mvImagePyramid[0].rows; // 左目图像行数(垂直方向范围)
第二步将右目特征点按照行进行分组,这里的分组逻辑是,首先根据平行基线原理与左目对应的右目特征点纵坐标相等,但是又不能局限于一行,这里作者根据金字塔层级尺度设置上下搜索范围,将这个点加到所有的垂直覆盖的所有行。比如,当前这个右目点的垂直范围是1-5,那么把这个点反别加到vRowIndices的1-5行中,因为左目1-5行的所有特征点都要搜索这个点。
vector<vector<size_t> > vRowIndices(nRows,vector<size_t>()); // 每行对应的右目特征点索引
for(int iR=0; iR<Nr; iR++) {
const cv::KeyPoint &kp = mvKeysRight[iR];
const float &kpY = kp.pt.y;
const float r = 2.0f*mvScaleFactors[mvKeysRight[iR].octave]; // 垂直搜索半径(随尺度变化)
const int maxr = ceil(kpY+r);
const int minr = floor(kpY-r);
for(int yi=minr;yi<=maxr;yi++)
vRowIndices[yi].push_back(iR); // 右目点加入其垂直覆盖的所有行
}
接下来来看特征描述子匹配先看第一部分,先是进行了一些参数定义,minD和maxD是进行行的限制,就是匹配这个左目点的左右一个范围内的右目点。这里设置minD和maxD的原理是根据视差原理来进行的,因为其实这两就是左右目视差,物体越近视差越小,物体越远视差越大,最小视差=0,最大视差,也就是深度最小(物体最近)时这里规定相机最近能测的距离是基线也就是(mb)实际上最近能测得距离应该为基线的1-5倍,这样最大视差就=mbf/minZ其实就等于焦距。接下来的for循环就是遍历每一个左目点,然后获取相应参数,在遍历这个左目对应可能匹配的右目点,有两个限制一个是金字塔层级要在这个左目点的加减1层范围内,第二个就是视差范围要在上面求的那个范围内,最后计算汉明距离(256个描述子相同的越多汉明距离越近),找到最小的汉明距离。
// Set limits for search
const float minZ = mb;
const float minD = 0;
const float maxD = mbf/minZ;
// For each left keypoint search a match in the right image
vector<pair<int, int> > vDistIdx;
vDistIdx.reserve(N);
for(int iL=0; iL<N; iL++)
{
const cv::KeyPoint &kpL = mvKeys[iL];
const int &levelL = kpL.octave;
const float &vL = kpL.pt.y;
const float &uL = kpL.pt.x;
const vector<size_t> &vCandidates = vRowIndices[vL];
if(vCandidates.empty())
continue;
const float minU = uL-maxD;
const float maxU = uL-minD;
if(maxU<0)
continue;
int bestDist = ORBmatcher::TH_HIGH;
size_t bestIdxR = 0;
const cv::Mat &dL = mDescriptors.row(iL);
// Compare descriptor to right keypoints
for(size_t iC=0; iC<vCandidates.size(); iC++)
{
const size_t iR = vCandidates[iC];
const cv::KeyPoint &kpR = mvKeysRight[iR];
if(kpR.octave<levelL-1 || kpR.octave>levelL+1)
continue;
const float &uR = kpR.pt.x;
if(uR>=minU && uR<=maxU)
{
const cv::Mat &dR = mDescriptorsRight.row(iR);
const int dist = ORBmatcher::DescriptorDistance(dL,dR);
if(dist<bestDist)
{
bestDist = dist;
bestIdxR = iR;
}
}
}
下面是亚像素级优化提高匹配精度,主要分为两步,第一步继续在上面得到的初始匹配点,用滑动窗口的方法,在一定范围内继续寻找更好的像素点(更注重局部灰度值匹配),原理就是在左目图像上点截出一个9*9的窗口然后再初始右目匹配点,周围加减5个像素的范围内的每个像素也画出一个9*9的窗口然后计算L1范数(像素插值的绝对值之和),找到哪儿跟L1范数最小的右目像素点。这里涉及到,需要将当前金字塔层级的关键点的x和y坐标还原成原图像尺度,具体方法就是获取当前层金字塔的逆尺度,scaleFactor = mvInvScaleFactors[kpL.octave]然后再把相应的x和y坐标*这个逆尺度,在提取图像块的过程中还要消除光照影响,方法是在当前图像的基础上-图像中心点的灰度值。后续for循环就是计算L1范数,并记录下来(后续亚像素纠正使用)。
if(bestDist<thOrbDist)
{
// coordinates in image pyramid at keypoint scale
const float uR0 = mvKeysRight[bestIdxR].pt.x;
const float scaleFactor = mvInvScaleFactors[kpL.octave];
const float scaleduL = round(kpL.pt.x*scaleFactor);
const float scaledvL = round(kpL.pt.y*scaleFactor);
const float scaleduR0 = round(uR0*scaleFactor);
// sliding window search
const int w = 5;
cv::Mat IL = mpORBextractorLeft->mvImagePyramid[kpL.octave].rowRange(scaledvL-w,scaledvL+w+1).colRange(scaleduL-w,scaleduL+w+1);
IL.convertTo(IL,CV_32F);
IL = IL - IL.at<float>(w,w) *cv::Mat::ones(IL.rows,IL.cols,CV_32F);
int bestDist = INT_MAX;
int bestincR = 0;
const int L = 5;
vector<float> vDists;
vDists.resize(2*L+1);
const float iniu = scaleduR0+L-w;
const float endu = scaleduR0+L+w+1;
if(iniu<0 || endu >= mpORBextractorRight->mvImagePyramid[kpL.octave].cols)
continue;
for(int incR=-L; incR<=+L; incR++)
{
cv::Mat IR = mpORBextractorRight->mvImagePyramid[kpL.octave].rowRange(scaledvL-w,scaledvL+w+1).colRange(scaleduR0+incR-w,scaleduR0+incR+w+1);
IR.convertTo(IR,CV_32F);
IR = IR - IR.at<float>(w,w) *cv::Mat::ones(IR.rows,IR.cols,CV_32F);
float dist = cv::norm(IL,IR,cv::NORM_L1);
if(dist<bestDist)
{
bestDist = dist;
bestincR = incR;
}
vDists[L+incR] = dist;
}
第二步即为亚像素纠正,主要是一个抛物线拟合,之前求得右目对应的关键点的坐标都是整数这里的目的是根据之前求得L1范数,根据最优点前后,这三个点拟合一条抛物线曲线,最后抛物线曲线的最低点即为我们要找的点。其中计算部分,scaleduR0为初始最优点的证书坐标,bestincR这个是在滑动窗口里找的最优点整数偏移量,deltaR是上面拟合的小数偏移量,把他们三者相加*当前金字塔层级系数即为最找要中的右目点的坐标。
// Sub-pixel match (Parabola fitting)
const float dist1 = vDists[L+bestincR-1];
const float dist2 = vDists[L+bestincR];
const float dist3 = vDists[L+bestincR+1];
const float deltaR = (dist1-dist3)/(2.0f*(dist1+dist3-2.0f*dist2));
if(deltaR<-1 || deltaR>1)
continue;
// Re-scaled coordinate
float bestuR = mvScaleFactors[kpL.octave]*((float)scaleduR0+(float)bestincR+deltaR);
最后就是深度计算,这里就是用的之前说的视差公式求得这里不再多说
float bestuR = mvScaleFactors[kpL.octave]*((float)scaleduR0+(float)bestincR+deltaR);
float disparity = (uL-bestuR);
if(disparity>=minD && disparity<maxD)
{
if(disparity<=0)
{
disparity=0.01;
bestuR = uL-0.01;
}
mvDepth[iL]=mbf/disparity;
mvuRight[iL] = bestuR;
vDistIdx.push_back(pair<int,int>(bestDist,iL));
}
下面这块是剔除深度过度偏移阈值的不合理的深度点。1阈值设定是1.5*1.4*中位数,1.5是经验系数,1.4是.4 是 L1 范数与 L2 范数的近似转换系数。
sort(vDistIdx.begin(),vDistIdx.end());
const float median = vDistIdx[vDistIdx.size()/2].first;
const float thDist = 1.5f*1.4f*median;
for(int i=vDistIdx.size()-1;i>=0;i--)
{
if(vDistIdx[i].first<thDist)
break;
else
{
mvuRight[vDistIdx[i].second]=-1;
mvDepth[vDistIdx[i].second]=-1;
}
}
RGB-D深度计算。这里作者为了和双目统一,对RGB-D相机设置了虚拟右目,首先深度很好求,就直接从原始深度图读取即可,这里读取的x和y坐标是畸变矫正之前的坐标,计算虚拟右目x坐标用的是校正后的关键点坐标。计算方式就是上面提的双目视差公式。
void Frame::ComputeStereoFromRGBD(const cv::Mat &imDepth)
{
mvuRight = vector<float>(N,-1);
mvDepth = vector<float>(N,-1);
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
const cv::KeyPoint &kp = mvKeys[i];
const cv::KeyPoint &kpU = mvKeysUn[i];
const float &v = kp.pt.y;
const float &u = kp.pt.x;
const float d = imDepth.at<float>(v,u);
if(d>0)
{
mvDepth[i] = d;
mvuRight[i] = kpU.pt.x-mbf/d;
}
}
}
二维坐标反投影到三维空间
这个函数的作用是根据之前求得深度值并结合校正后的,关键点的坐标计算相应的真实世界坐标,首先,由相机坐标系下的三维坐标点P(x,y,z)投影到二维空间的公式是:cx,cy分别是相机的中心坐标。
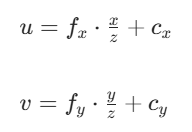
反推由二维投影到三维:
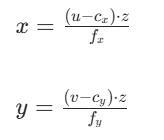
代码力就是这部分,invfx为fx的倒数。
const float u = mvKeysUn[i].pt.x;
const float v = mvKeysUn[i].pt.y;
const float x = (u-cx)*z*invfx;
const float y = (v-cy)*z*invfy;
最后还要将相机坐标系转化为世界坐标系,方法之前提过了。
return mRwc*x3Dc+mOw;
词袋表示计算
这里是将每个描述子进行编码,用于后续的帧间快速匹配、闭环检测、重定位等关键流程,因为后续要是直接对描述子计算汉明距离,开销太大这里将其转化为bow向量和特征词的映射关系,其中设计的函数后续会介绍,这里先只需要知道他的作用即可。
void Frame::ComputeBoW()
{
if(mBowVec.empty())
{
vector<cv::Mat> vCurrentDesc = Converter::toDescriptorVector(mDescriptors);
mpORBvocabulary->transform(vCurrentDesc,mBowVec,mFeatVec,4);
}
}
视锥体检查
这部分就是检查相应地图点是否可能在当前相机的视野内的,避免后续的无效计算。这里主要的判断方法是一些相关约束,正深度检查(最基础约束),成像范围检查(投影到图像并判断是否在画面内),尺度一致性检查(距离在地图点的尺度不变范围内),观测角度检查(观测方向与地图点法向量夹角适中),
这部分代码是,当前地图点先标记为不可观测,然后通过当前地图点的世界坐标得到相应的相机坐标系下的坐标,接下来就是一系列检查。
pMP->mbTrackInView = false;
// 3D in absolute coordinates
cv::Mat P = pMP->GetWorldPos();
// 3D in camera coordinates
const cv::Mat Pc = mRcw*P+mtcw;
const float &PcX = Pc.at<float>(0);
const float &PcY= Pc.at<float>(1);
const float &PcZ = Pc.at<float>(2);
正深度检查
// Check positive depth
if(PcZ<0.0f)
return false;
成像范围检查
// 1. 计算深度的倒数(用于投影公式,预计算提升效率)
const float invz = 1.0f / PcZ;
// 2. 相机坐标系 → 图像像素坐标(理想相机投影公式)
const float u = fx * PcX * invz + cx;
const float v = fy * PcY * invz + cy;
// 3. 检查像素坐标是否在图像有效范围内
if(u < mnMinX || u > mnMaxX)
return false;
if(v < mnMinY || v > mnMaxY)
return false;
尺度一致性检查,这里就是之前地图点提到的先获取最大和最小能观测到这个地图点的距离,在计算地图点到相机光心的距离,然后判断。
// 1. 获取地图点的尺度不变距离范围(基于ORB金字塔层级)
const float maxDistance = pMP->GetMaxDistanceInvariance();
const float minDistance = pMP->GetMinDistanceInvariance();
// 2. 计算地图点到相机光心的欧式距离(世界坐标系下)
const cv::Mat PO = P - mOw; // P:地图点世界坐标;mOw:相机光心世界坐标
const float dist = cv::norm(PO);
// 3. 检查距离是否在有效范围内
if(dist < minDistance || dist > maxDistance)
return false;
观测角度检查,这里主要检查的是一个余弦值,PO.dot(Pn)是对向量PO和Pn进行点积,就是PO的模*Pn的模*cos夹角,而Pn是单位向量,dist=PO的模,所以viewCos=PO与Pn的夹角。最后判断如果cos值太小代表夹角过大。
// 1. 获取地图点的法向量(指向“最佳观测方向”,比如首次观测方向)
cv::Mat Pn = pMP->GetNormal();
// 2. 计算观测方向与法向量的余弦值(夹角越小,余弦值越大)
const float viewCos = PO.dot(Pn) / dist;
// 3. 检查余弦值是否大于阈值(夹角是否过小)
if(viewCos < viewingCosLimit)
return false;
最后通过了所有的检测之后标记为可观测,并计算相应的参数用于后续跟踪线程
// 1. 预测地图点在当前帧中的ORB金字塔尺度层级
const int nPredictedLevel = pMP->PredictScale(dist, this);
// 2. 更新地图点的跟踪临时变量(供后续跟踪匹配使用)
pMP->mbTrackInView = true; // 标记为在视锥内
pMP->mTrackProjX = u; // 图像上的x坐标(像素)
pMP->mTrackProjXR = u - mbf * invz; // 右目虚拟x坐标(双目/RGBD模式,用于立体匹配)
pMP->mTrackProjY = v; // 图像上的y坐标(像素)
pMP->mnTrackScaleLevel = nPredictedLevel; // 预测的ORB尺度层级
pMP->mTrackViewCos = viewCos; // 观测角度的余弦值
return true;
总结
以上是我对于帧的相关参数和函数的解释,花了挺长时间的,希望能帮到大家。




















 345
345

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








