练习部分解释:跟网上大多数博客都不一样,因为之前我已经在notebook上做完了,再总结一遍放在博客上。
Class 1:神经网络和深度学习
Week 2:神经网络基础编程练习
目录
1、关于sigmoid的用法
- sigmoid、sigmoid积分、reshape、normalize归一化数据、softmax
import numpy as np
# 1、sigmoid函数
def sigmoid(x):
s = 1.0/(1 + 1/np.exp(x))
return s
# 2、梯度(积分)
def sigmoid_derivative(x):
s = 1.0/(1 + 1/np.exp(x))
ds = s*(1-s)
return ds
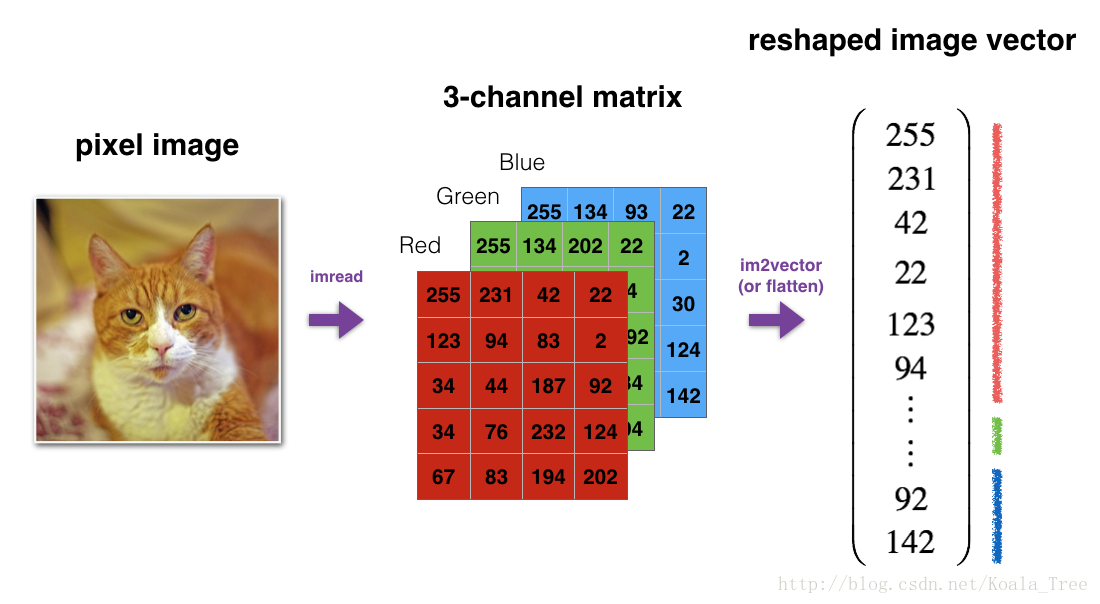
# 3、reshape (length,height,3) to (length*height*3,1)
def image2vector(image):
v = image.reshape(image.shape[0]*image.shape[1]*image.shape[2],1)
return v
# 4、normalize rows 归一化数据
# 归一化后,梯度下降收敛的更快
def normalizeRows(x):
x_norm = np.linalg.norm(x,axis=1,keepdims = True) # 计算每一行的长度,得到一个列向
x = x/x_norm
return x
# 5、softmax
def softmax(x):
x_exp = np.exp(x) #(n,m)
x_sum = np.sum(x_exp,axis=1,keepdims=True) #(n,1)
s = x_exp/x_sum #(n,m)
return s
if __name__=="__main__":
x = np.array([1,2,3])
print(sigmoid(x))
print(sigmoid_derivative(x))
image = np.array([[[0.6,0.3],[0.9,0.5],[0.4,0.3]],
[[0.9,0.2],[0.6,0.8],[0.7,0.1]],
[[0.3,0.4],[0.6,0.7],[0.9,0.9]]])
print(image2vector(image))
x = np.array([[0,3,4],[1,6,4]])
print(normalizeRows(x))
x = np.array([[9,2,5,0,0],[7,5,0,0,0]])
print(softmax(x))[ 0.73105858 0.88079708 0.95257413]
[ 0.19661193 0.10499359 0.04517666]
[[ 0.6]
[ 0.3]
[ 0.9]
[ 0.5]
[ 0.4]
[ 0.3]
[ 0.9]
[ 0.2]
[ 0.6]
[ 0.8]
[ 0.7]
[ 0.1]
[ 0.3]
[ 0.4]
[ 0.6]
[ 0.7]
[ 0.9]
[ 0.9]]
[[ 0. 0.6 0.8 ]
[ 0.13736056 0.82416338 0.54944226]]
[[ 9.80897665e-01 8.94462891e-04 1.79657674e-02 1.21052389e-04
1.21052389e-04]
[ 8.78679856e-01 1.18916387e-01 8.01252314e-04 8.01252314e-04
8.01252314e-04]]2、内积、L1/L2损失函数
import time
import numpy as np
x1 = [9, 2, 5, 0, 0, 7, 5, 0, 0, 0, 9, 2, 5, 0, 0]
x2 = [9, 2, 2, 9, 0, 9, 2, 5, 0, 0, 9, 2, 5, 0, 0]
# 1 dot product、outer product、elementwise、general dot product
dot = 0
for i in range(len(x1)):
dot += x1[i]*x2[i]
outer = np.zeros((len(x1),len(x2)))
for i in range(len(x1)):
for j in range(len(x2)):
outer[i,j] = x1[i]*x2[j]
mul = np.zeros(len(x1))
for i in range(len(x1)):
mul[i] = x1[i]*x2[i]
W = np.random.rand(3,len(x1))
gdot = np.zeros(W.shape[0])
for i in range(W.shape[0]):
for j in range(len(x1)):
gdot[i] += W[i,j]*x1[j]
#print(dot)
#print(outer)
#print(mul)
# 2、向量化实现
dot = np.dot(x1,x2)
outer = np.outer(x1,x2)
mul = np.multiply(x1,x2)
#print(dot)
#print(outer)
#print(mul)
def L1(yhat,y):
loss = np.sum(np.abs(y-yhat))
return loss
def L2(yhat,y):
loss = np.sum(np.power((y-yhat),2))
return loss
if __name__=="__main__":
yhat = np.array([0.9,0.2,0.1,0.4,0.9])
y = np.array([1,0,0,1,1])
print(L1(yhat,y))
print(L2(yhat,y))
1.1
0.433、数据集
import numpy as np
import h5py
def load_dataset():
train_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/train_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels
test_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/test_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes
if __name__=="__main__":
train_set_x_orig, train_set_y, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y, classes = load_dataset()
print(train_set_x_orig.shape,test_set_x_orig.shape,train_set_y.shape,test_set_y.shape,classes.shape)
x = train_set_x_orig[25]
print(x.shape)
4、神经网络模型
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
import scipy
import pylab
from PIL import Image
from lr_utils import load_dataset
from scipy import ndimage
# 1、下载数据集
train_set_x_orig, train_set_y, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y, classes = load_dataset()
# 2、显示图像
index = 90
#plt.imshow(train_set_x_orig[index])
#pylab.show() # 加上才能显示图片
# squeeze()函数:除去size=1的维度,(4,1,3)变成(4,3),(4,2,3)则不变
print ("y = " + str(train_set_y[:, index]) + ", it's a '" \
+ classes[np.squeeze(train_set_y[:, index])].decode("utf-8") + "' picture.")
# 3、显示图像大小
m_train = train_set_x_orig.shape[0]
m_test = test_set_x_orig.shape[0]
num_px = train_set_x_orig.shape[1]
print("TrainSet: " + str(train_set_x_orig.shape))
print("TestSet: " + str(test_set_x_orig.shape))
print("TrainLabel: " + str(train_set_y.shape))
print("TestLabel: " + str(test_set_y.shape))
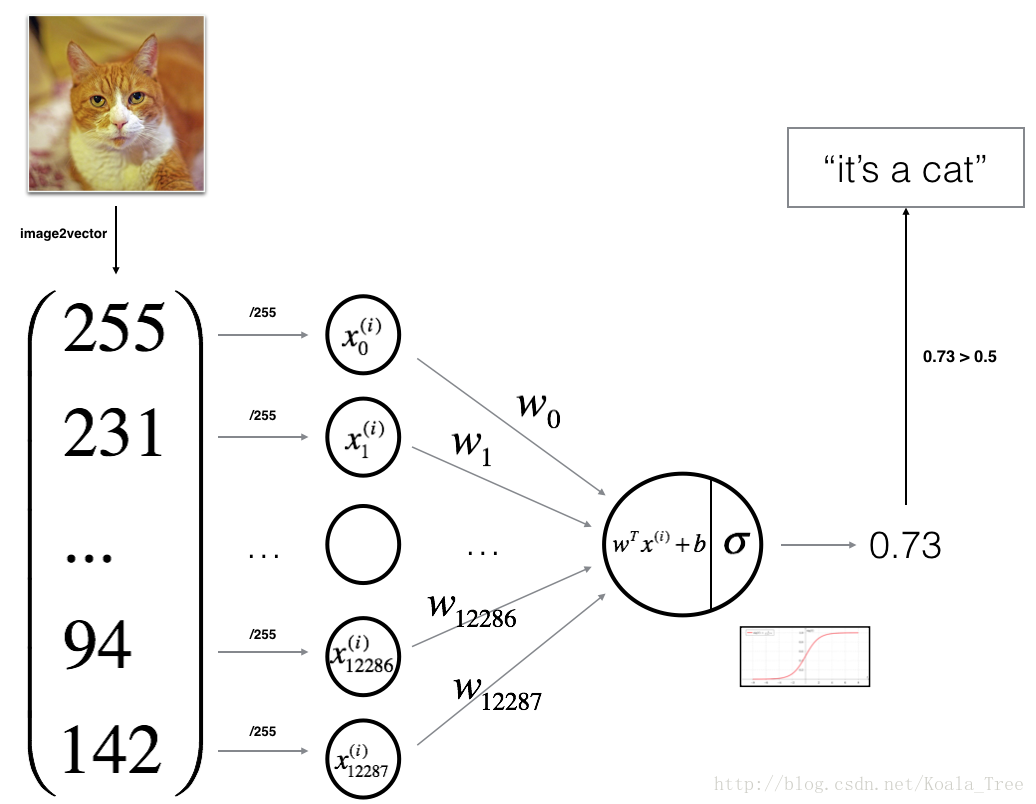
# 4、reshape图片,且转换成列向量
train_set_x_flatten = train_set_x_orig.reshape(train_set_x_orig.shape[0],-1).T
test_set_x_flatten = test_set_x_orig.reshape(test_set_x_orig.shape[0],-1).T
print(train_set_x_flatten.shape,test_set_x_flatten.shape)
# 5、标准化数据集
train_set_x = train_set_x_flatten/255
test_set_x = test_set_x_flatten/255
# 6、
def sigmoid(z):
s = 1.0/(1 + np.exp(-z))
return s
# 7、初始化参数
def initialize_zeros(dim):
w = np.zeros([dim,1])
b = 0
assert(w.shape == (dim,1))
assert(isinstance(b,float) or isinstance(b,int))
return w,b
# 8、forward and backward propagation
# 计算损失函数、梯度
def propagate(w,b,x,y):
'''
function:
implement the cost function and gradient
Arguments:
w --- 权重 (num_px*num_px*3, 1)
b --- 偏置
X --- 输入 (num_px*num_px*3, 样本数)
Y --- 标签
return:
cost --- 逻辑回归的 log 损失函数
dw ---
db ---
'''
m = x.shape[1]
# 前向传播
y_ = sigmoid(np.dot(w.T,x) + b)
cost = -(1.0/m)*np.sum(y*np.log(y_) + (1-y)*np.log(1-y_))
# 后向传播
dw = (1.0/m)*np.dot(x,(y_-y).T)
db = (1.0/m)*np.sum(y_-y)
assert(dw.shape == w.shape)
assert(db.dtype == float)
cost = np.squeeze(cost)
assert(cost.shape == ())
grads = {"dw":dw, "db":db}
return grads,cost
w,b,x,y = np.array([[1.],[2.]]), 2, np.array([[1,2,-1],[3,4,-3]]), np.array([[1,0,1]])
grads, cost = propagate(w,b,x,y)
print(grads,cost)
# 9、optimization 优化算法(梯度下降)
def optimize(w, b, x, y, num_iterations, learning_rate, print_cost = False):
'''
rerutn: params, grads, cost
'''
costs = []
for i in range(num_iterations):
grads,cost = propagate(w,b,x,y)
dw = grads["dw"]
db = grads["db"]
w = w - dw*learning_rate
b = b - db*learning_rate
if i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
if print_cost and i%100==0:
print("cost after iteration %i : %f" %(i,cost))
params = {"w":w, "b":b}
grads = {"dw":dw, "db":db}
return params,grads,costs
params, grads, costs = optimize(w, b, x, y, num_iterations= 100, learning_rate = 0.009, print_cost = False)
print(params,grads)
# 10、预测
def predict(w,b,x):
m = x.shape[1]
y_p = np.zeros([1,m])
w = w.reshape(x.shape[0],1)
y_ = sigmoid(np.dot(w.T,x)+b)
for i in range(y_.shape[1]):
if y_[0,i] > 0.5:
y_p[0,i]=1
else:
y_p[0,i]=0
assert(y_p.shape == (1,m))
return y_p
w = np.array([[0.1124579],[0.23106775]])
b = -0.3
x = np.array([[1.,-1.1,-3.2],[1.2,2.,0.1]])
print ("predictions = " + str(predict(w, b, x)))
# 11、将所有的功能合并到模型中
def model(x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test, num_iterations=2000, learning_rate=0.5, print_cost=False):
w,b = initialize_zeros(x_train.shape[0])
parameters,grads,costs = optimize(w,b,x_train,y_train,num_iterations,learning_rate,print_cost)
w = parameters["w"]
b = parameters["b"]
y_p_train = predict(w,b,x_train)
y_p_test = predict(w,b,x_test)
print("train accuracy:{} %".format(100-np.mean(np.abs(y_p_train-y_train))*100))
print("test accuracy:{} % ".format(100-np.mean(np.abs(y_p_test-y_test))*100))
d = {"costs":costs,
"y_p_train":y_p_train,
"y_p_test":y_p_test,
"w":w,
"b":b,
"learning_rate":learning_rate,
"num_iterations":num_iterations}
return d
# 训练集正确率99%,测试集正确率70%,过拟合了
d = model(train_set_x,train_set_y,test_set_x,test_set_y,num_iterations=2000,learning_rate=0.005,print_cost=True)
# 12、画出代价函数和梯度
'''
costs = np.squeeze(d["costs"])
plt.plot(costs)
plt.ylabel("cost")
plt.xlabel("iterations(per hundreds)")
plt.title("learning rate = "+str(d["learning_rate"]))
plt.show()
'''
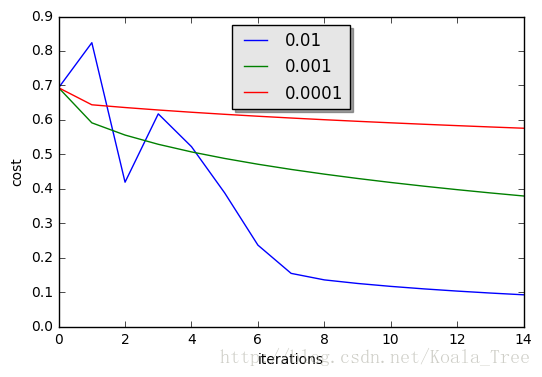
# 13、学习率的选择
learning_rate = [0.01,0.001,0.0001]
models = {}
for i in learning_rate:
print("learning rate is: " + str(i))
models[str(i)] = model(train_set_x,train_set_y,test_set_x,test_set_y,
num_iterations=1500,learning_rate=i,print_cost=False)
for i in learning_rate:
plt.plot(np.squeeze(models[str(i)]["costs"]), label=str(models[str(i)]["learning_rate"]))
plt.ylabel("cost")
plt.xlabel("iteration")
legend = plt.legend(loc='upper center', shadow=True)
frame = legend.get_frame()
frame.set_facecolor('0.90')
plt.show()
'''
# 14、用自己的图像来测试
fname = 'images/other_test.jpg'
image = np.array(ndimage.imread(fname,flatten=False))
my_image = scipy.misc.imresize(image,size=(num_px,num_px)).reshape((1,num_px*num_px*3)).T
my_predicted_image = predict(d["w"],d["b"],my_image)
plt.imshow(image)
pylab.show()
print("y = " + str(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)) + ", your algorithm predicts a \"" \
+ classes[int(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)),].decode("utf-8") + "\" picture.")
'''y = [0], it's a 'non-cat' picture.
TrainSet: (209, 64, 64, 3)
TestSet: (50, 64, 64, 3)
TrainLabel: (1, 209)
TestLabel: (1, 50)
(12288, 209) (12288, 50)
{'dw': array([[ 0.99772382],
[ 2.3265089 ]]), 'db': 0.002187770724565441} 5.66894829829
{'b': 1.9241133755874054, 'w': array([[ 0.18954212],
[ 0.16465723]])} {'dw': array([[ 0.69128662],
[ 1.43797759]]), 'db': 0.2187345002480347}
predictions = [[ 1. 1. 0.]]
cost after iteration 0 : 0.693147
cost after iteration 100 : 0.584508
cost after iteration 200 : 0.466949
cost after iteration 300 : 0.376007
cost after iteration 400 : 0.331463
cost after iteration 500 : 0.303273
cost after iteration 600 : 0.279880
cost after iteration 700 : 0.260042
cost after iteration 800 : 0.242941
cost after iteration 900 : 0.228004
cost after iteration 1000 : 0.214820
cost after iteration 1100 : 0.203078
cost after iteration 1200 : 0.192544
cost after iteration 1300 : 0.183033
cost after iteration 1400 : 0.174399
cost after iteration 1500 : 0.166521
cost after iteration 1600 : 0.159305
cost after iteration 1700 : 0.152667
cost after iteration 1800 : 0.146542
cost after iteration 1900 : 0.140872
train accuracy:99.04306220095694 %
test accuracy:70.0 %
learning rate is: 0.01
train accuracy:99.52153110047847 %
test accuracy:68.0 %
learning rate is: 0.001
train accuracy:88.99521531100478 %
test accuracy:64.0 %
learning rate is: 0.0001
train accuracy:68.42105263157895 %
test accuracy:36.0 %
总结:
1、归一化后的数据,梯度下降收敛速度更快
2、构建学习算法结构、初始化参数、计算损失函数和梯度、梯度下降优化算法
3、学习算法的一般结构
初始化模型参数
通过最小化损失函数,学习模型参数
使用学习后的参数去预测新数据
分析结果
4、出现了过拟合,增加迭代步数,训练集正确率上升,测试集正确率下降
5、学习率的选择
学习率决定更新参数的速度
学习率太高,可能会超过最优值,
学习率太小,收敛速度慢























 1100
1100

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








