前言
之前曾想做这样一个工具,用来遍历目录下的word.docx文档查询关键词,主要是有几个目的:
1.在项目开始阶段,通过关键词检索feature,我脑子实在是记不住文档都在哪;
2.收尾阶段,检查是否有TODO/TBD项遗留在文档中未补全;
3.检查是否有关键信息未修改,尤其对外交付文档中是有留存旧的项目信息等;
4.进一步拓展,支持通配符模糊索引和全局替换,类似linux里grep和sed的功能;
后来一忙起来就把这件事放下了,趁着现在有三天的假期,决定搞一波事~

效果展示
我策划的软件长这个样子:

但是我实在是懒得摆位置了,最后就长成了这个样子:

反正吧,外貌不重要,有趣的灵魂才重要!
使用时候呢,先选一下目录:
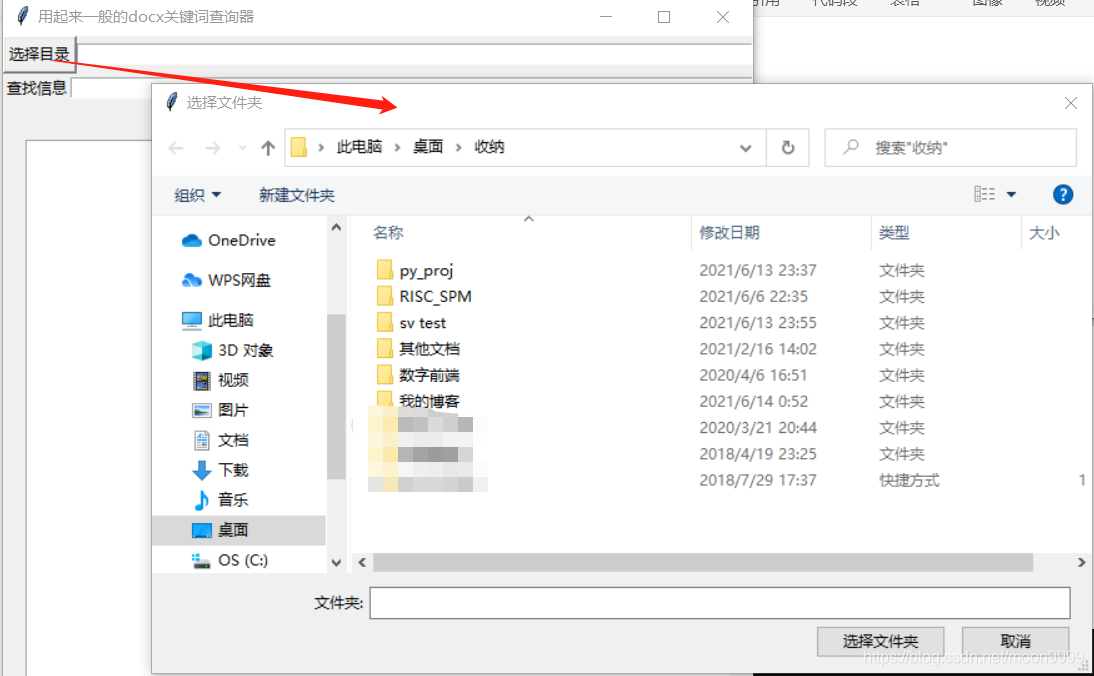
然后再输入下索引的关键词,点击开始检查:
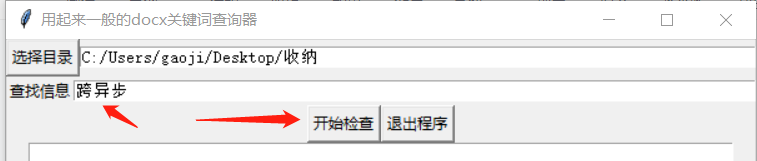
程序开始以选择目录为基准,向下递归检查多有的docx文档内容:

并在选择目录下生成一个.report文件:
![]()
点击查看结果就可以了:

目前我就实现到这一步,看起来还能用,以后有时间在继续优化,递归算法找文件的效率实在是太低,如果能看看everything是如何实现的就好了。
中场广告时间
对于这种小的程序,我自己非常喜欢Geany这款编译器,上手简单的可怕,调试执行功能也很舒服,界面对小白尤其很是善意,开源免费随便用,一键安装:

好了下面继续正文;
前期准备
这次用到的库有:
import tkinter
import os
import docx
import re
from zipfile import ZipFile
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from tkinter import *本来用的docx库,结果发现有些文件打不开,于是转头使用zipfile库了,毕竟(小科普时间)每一个docx文档的本质都是一个zip压缩文件,比如我这里有一个docx文档:

使用解压缩文件打开时,就可以看到里面的结构:

继续往里面点,就可以看到内容的源码啦:

因此用python解析docx文档时,用zipfile库就好了。
关键处理
根据根目录遍历之下所有docx文件,这个我直接从网上找的改了两行代码:
def get_process_files(root_dir):
"""process all files in directory"""
cur_dir=os.path.abspath(root_dir)
file_list=os.listdir(cur_dir)
process_list=[]
dir_extra_list = []
for file in file_list:
fullfile=cur_dir+"\\"+file
#print(fullfile)
if os.path.isfile(fullfile) and fullfile.endswith(".docx"):
process_list.append(fullfile)
#print("add " + fullfile)
elif os.path.isdir(fullfile):
dir_extra_list.extend(get_process_files(fullfile))
if len(dir_extra_list)!=0:
for x in dir_extra_list:
process_list.append(x)索引docx文件内是否包含关键词:
def search_keyword(filename, key_word):
try:
document = ZipFile(filename)
xml = document.read("word/document.xml")
wordObj = BeautifulSoup(xml.decode("utf-8"), features="lxml")
texts = wordObj.findAll("w:t")
except:
ignore_list.append(filename + "未能打开")
#print("请手动检查" + filename)
pass
for text in texts:
#print(text.text)
try:
if re.search(key_word, text.text):
#print(filename + "找到关键字")
return True
except:
pass
return False剩下的所有操作都在tk_mian里面了:
def tk_main():
root = Tk()
root.geometry("600x600")
root.title("用起来一般的docx关键词查询器")对应整个软件的外框;
f1 = Frame(root, height = 100, width = 400)
f1.pack()
button1 = Button(f1, text='选择目录', command=get_path)
button1.pack(side = LEFT)
text1 = Text(f1, height = 1, undo=True, autoseparators=False)
text1.pack(side = RIGHT)对应这里:
![]()
f2 = Frame(root, height = 100, width = 400)
f2.pack()
label1 = Label(f2, text="查找信息")
label1.pack(side=LEFT)
text2 = Text(f2, height = 1, undo=True, autoseparators=False)
text2.pack(side = RIGHT)
f3 = Frame(root, height = 100, width = 400)对应这里:
![]()
f3 = Frame(root, height = 100, width = 400)
f3.pack()
button2 = Button(f3, text='开始检查', command=start_check)
button2.pack(side=LEFT)
button3 = Button(f3, text='退出程序', command=root.quit)
button3.pack(side=RIGHT)
f4 = Frame(root, height = 100, width = 400)
f4.pack()
text3 = Text(f4, height = 100, undo=True, autoseparators=False)
text3.pack(side = RIGHT)对应这里和这里:
“选择目录”按钮关联的函数是:
def get_path():
from tkinter import filedialog
tk_file_path = filedialog.askdirectory() #获得选择好的文件夹
text1.insert(INSERT, tk_file_path)“开始检查”按钮关联的函数是下面,就是把“选择目录”后面文本框内的地址还有“查找信息”后面文本框的内容给提取出来,送给search_key_file函数:
def start_check():
#print(text1.get(1.0, "end"))
fullpath = text1.get(1.0, "end").strip()
keyword = text2.get(1.0, "end").strip()
full_docx = get_process_files(fullpath)
key_docx = search_key_file(full_docx, keyword)
def search_key_file(list, keyword):
global rpt_path
key_file = []
fullpath = text1.get(1.0, "end").strip()
keyword = text2.get(1.0, "end").strip()
rpt_path = os.path.join(fullpath, "关键词检查_" + keyword + ".report")
for file in list:
str = "正在检查文件: " + file
text3.mark_set('here',1.0)
text3.insert('here', str + "\n")
if search_keyword(file, keyword) is True:
key_file.append(file)
#print("找到一个")
with open(rpt_path, 'w') as file:
file.write("对以下文件中找到关键字:\n")
for line in key_file:
file.write(line + "\n")
with open(rpt_path, 'a') as file:
file.write("\n")
file.write("以下文件未能打开,请手动检索:\n")
for line in ignore_list:
file.write(line + "\n")
with open(rpt_path, 'a') as file:
file.write("\n")
file.write("共尝试对以下文件进行了检查:\n")
for line in list:
file.write(line + "\n")
text3.mark_set('here',1.0)
text3.insert('here', "检索完成,请打开REOPRT文件查看结果:" + rpt_path + "\n")
text3.insert('here', "检索完成,请打开REOPRT文件查看结果:" + rpt_path + "\n")
text3.insert('here', "检索完成,请打开REOPRT文件查看结果:" + rpt_path + "\n")
return key_fileOK,其实所有的代码就这样了;
打包python为exe
使用pyinstaller进行软件打包:
这么小的程序,不要控制台了:

打包完成,非常可爱,13M的小软件,方便携带与发送啊:

妥妥的,有点累我要去吃饭了,不仅饿还非常的困。。。。。





























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










