分类算法
1.sklearn转换器和估计器
转换器:特征工程父类, 实例化一个转换器(Transformer)
调用fit_transform()
估计器: 实例一个estimator 2. estimator.fit(x_train, y_train) 计算
调用完成,模型生成
3. 模型评估:
1)直接对比真实值和预测值
y_predict =estimator.predict(x_test)
y_test==y_predict
2)计算准确率
accuracy =estimator.score(x_text, y_text)
2.K--近邻算法

核心思想:
根据“邻居”判断类别
计算距离:曼哈顿距离 明可夫斯基距离
** k取的过小 容易受到异常点的影响 ** k值过大 样本不均衡的影响
案例1:鸢尾花种类预测
1)获取数据 2)数据集划分 3)特征工程 标准化 4)KNN预估器流程 5)
def knn_demo():
iris = load_iris()
x_train, x_text, y_train, y_text = train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target, random_state=6)
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_text = transfer.transform(x_text)
estimator = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_text)
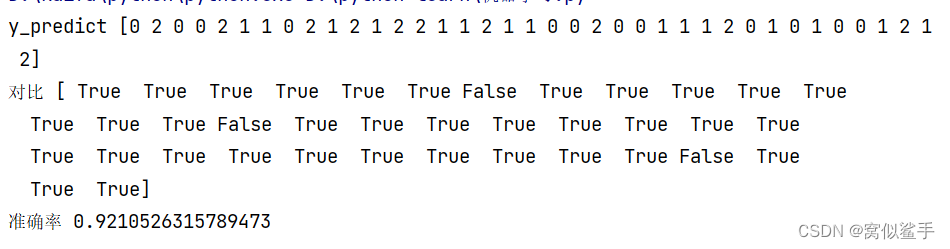
print("y_predict", y_predict)
print("对比", y_text == y_predict)
#计算准确率
score = estimator.score(x_text, y_text)
print("准确率", score)
x_train 用fit.transform x_text 用transform

3.模型选择与调优

3.1 交叉验证
目的:为了让被评估的模型更加准确可惜

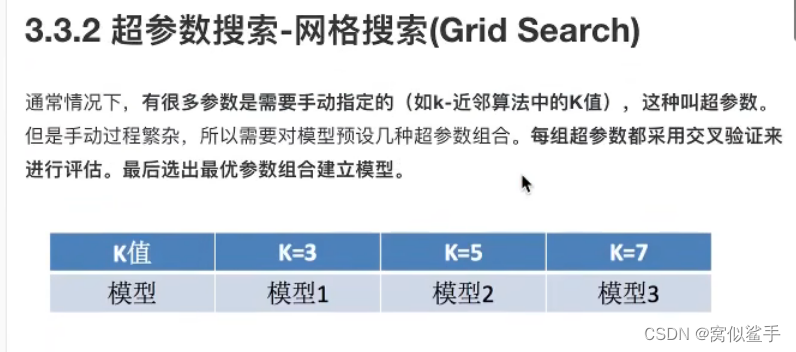
3.2 超参数搜索-网格搜索
K的取值
3.3鸢尾花案列增加K值调优
def knn_demo_gscv():
iris = load_iris()
x_train, x_text, y_train, y_text = train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target, random_state=6)
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_text = transfer.transform(x_text)
param_grid={"n_neighbors":[1,3,5,7,9,11]}
estimator = KNeighborsClassifier()
estimator=GridSearchCV(estimator,param_grid,cv=10) cv 几折交叉验证
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_text)
print("y_predict", y_predict)
print("对比", y_text == y_predict)
#计算准确率
score = estimator.score(x_text, y_text)
print("准确率", score)
print("最佳参数:\n",estimator.best_params_)
print("最佳结果:\n", estimator.best_score_)
print("最佳估计器:\n", estimator.best_estimator_)
print("交叉验证结果:\n", estimator.cv_results_)
return None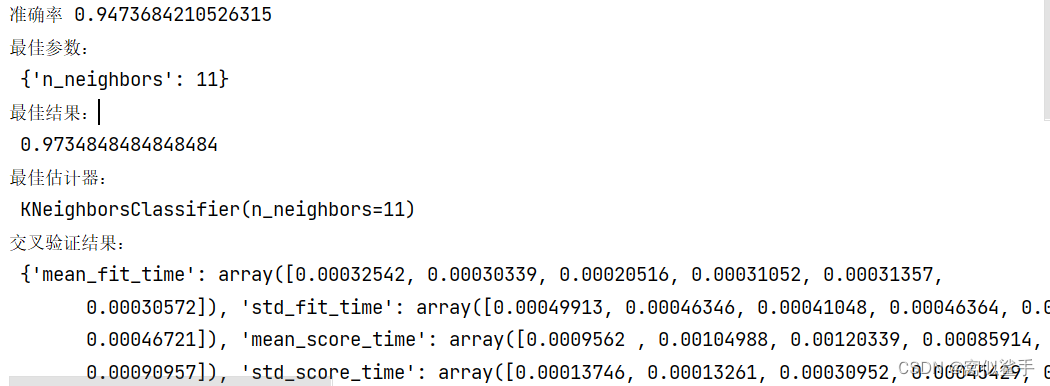
3.4 facebook签到预测
流程分析:1)获取数据 2)数据处理 目的:特征值x,目标值y a.缩小数据范围 b.time->年月日时分秒 c. 过滤签到次数少的地点 3)特征工程 4)KNN算法预估流程 模型选择调优 模型评估
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV
data=pd.read_csv("D:\\facebook\\FaceBook_train.csv\\FaceBook_train.csv")
#基本数据处理
data=data.query("x<2.5 & x>2 & y>1.0")
#处理时间特征
time_value=pd.to_datetime(data["time"],unit="s")
time=pd.DatetimeIndex(time_value)
data["day"]=time.day
data["weekday"]=time.weekday
data["hour"]=time.hour
place_count=data.groupby("place_id").count()["row_id"]
#print(place_count[place_count>3].head())
data_final=data[data["place_id"].isin(place_count[place_count>3].index.values)]
x=data_final[["x","y","accuracy","day","weekday","hour"]]
y=data_final["place_id"]
#数据集划分
x_train,x_text,y_train,y_text=train_test_split(x,y)
#特征工程:标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_text = transfer.transform(x_text)
#KNN算法预估器
estimator = KNeighborsClassifier()
#加入网格搜索和交叉验证
#参数准备
param_grid = {"n_neighbors": [1,3, 5,6, 7, 9]}
estimator = GridSearchCV(estimator, param_grid, cv=5)
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
#模型评估
#1)直接对比真实值和预测值
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_text)
print("y_predict", y_predict)
print("对比", y_text == y_predict)
# 计算准确率
score = estimator.score(x_text, y_text)
print("准确率", score)
print("最佳参数:\n", estimator.best_params_)
print("最佳结果:\n", estimator.best_score_)
print("最佳估计器:\n", estimator.best_estimator_)
print("交叉验证结果:\n", estimator.cv_results_)
4.朴素贝叶斯算法
联合概率:包含多个条件,且所有条件同时成立的概率
条件概率:就是事件A在另外一个事件B已经发生条件下的发生概率
朴素?
假设:特征与特征之间是相互独立朴素贝叶斯算法:朴素+贝叶斯应用场景: 文本分类 单词作为特征

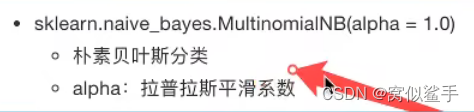
拉普拉斯平滑系数

20类新闻分类案例
def nb_news():
#获取数据集
news=fetch_20newsgroups(subset="all")
#划分数据集
x_train, x_text, y_train, y_text = train_test_split(news.data,news.target)
#特征工程
transfer=TfidfVectorizer
x_train=transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_text=transfer.transform(x_text)
#朴素贝叶斯算法预估器流程
estimator=MultinomialNB()
estimator.fit(x_train,y_train)
#模型评估
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_text)
print("y_predict", y_predict)
print("对比", y_text == y_predict)
# 计算准确率
score = estimator.score(x_text, y_text)
print("准确率", score)
朴素贝叶斯算法总结
优点:对缺失数据不太敏感,算法也比较简车,常用于文本分类。分类准确度高,速度快
缺点:由于使用了样本属性独立性的假设,所以如果特征属性有关联时其效果




















 6624
6624











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








